Environmental Science Study Guide Answer Key
advertisement

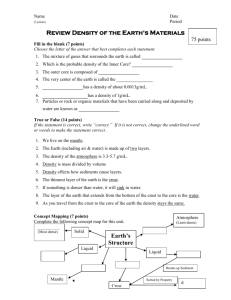
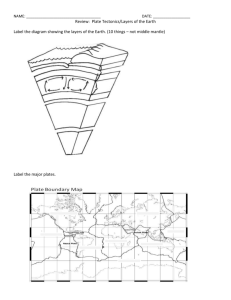
Name ________________________________ Environmental Science Study Guide (Answer Key) Chapter 3 1. How do mountains form? By colliding tectonic plates 2. Which region on Earth is the most geologically active? Boundaries between tectonic plates 3. Which layer of the atmosphere contains the ozone layer? Stratosphere 4. What is the Richter scale? Measures the magnitude of an earthquake 5. What is the molten rock in the upper mantle called? Magma 6. List the major tectonic plates. Pacific, North American, South American, African, Eurasian, Indian, Australian, Antarctic. 7. List the three mechanisms of energy transfer in the atmosphere. Radiation, convection, conduction 8. What causes air to be denser near Earth’s surface? Gravity 9. If we did not have the greenhouse effect, Earth’s atmosphere would be too _cold_ to support life. 10. Which sphere includes all water on or near Earth’s surface? hydrosphere 11. What sphere contains all areas where organisms can obtain the energy they need? biosphere 12. What drives currents at the surface of the ocean? wind 13. How would you define the water cycle? Unending circulation of Earth’s water supply 14. What is the most important erosional agent on Earth? Running water 15. What is the most important greenhouse gas? Carbon dioxide 16. Define a fault. A fracture in the earth where movement has occurred 17. Define an earthquake’s epicenter. The place on the surface directly above the focus 18. The San Francisco earthquake of 1906 occurred along what fault? San Andreas fault 19. Where does the greatest damage occur during an earth quake? In areas with older brick structures 20. What layers of Earth make up the lithosphere? Crust and upper mantle 21. What is Earth’s thin, rocky outer layer called? crust 22. How do we obtain most of the information about Earth’s interior? By studying seismic waves 23. What is Earth’s core made of? Iron and nickel 24. Why is Earth’s inner core solid? Because of the great pressure there 25. What does the Theory of Plate Tectonics state? The lithosphere is divided into plates that move on top of the asthenosphere 26. Which ocean layer has rapid temperature change as it gets deeper? thermocline 27. What is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere? nitrogen 28. What do we call three oxygen atoms together as a molecule? ozone 29. What is the order of the layers of the atmosphere (starting at the Earth’s surface)? Troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere 30. In what layer of the atmosphere does weather occur? troposphere 31. Define conduction. Transfer of heat through matter by molecular activity 32. Define greenhouse effect. The heating of the lower layer of the atmosphere from radiation absorbed by gases 33. Define radiation. Energy that is transferred as electromagnetic waves (How Earth receives energy from the sun). 34. What produces oxygen? Plants 35. Where do 75% of active volcanoes occur? Ring of Fire 36. Why does photosynthesis not occur in deep ocean waters? There is no sunlight 37. What happens as the amount of ozone in the stratosphere decreases? More ultraviolet light is able to reach Earth’s surface. 38. Which of Earth’s layers allows tectonic plates to move on top of it? Asthenosphere 39. What is the energy source for the water cycle? The sun Label A, B, C and D on the following diagram: A-precipitation B-evaporation/condensation C-runoff D-infiltration Label A, B, C, D, E, F and G on the following diagram: A-continental crust B-oceanic crust** C-lithosphere** D-lower mantle E-mantle** F-outer core G-inner core H-crust