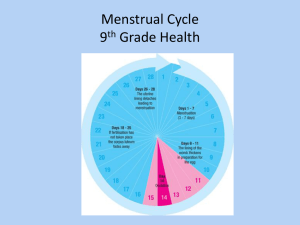
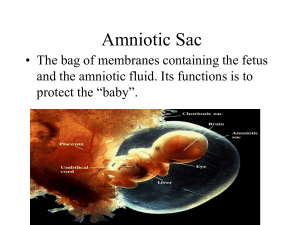
Q1.(a) (i) Mitosis and meiosis are types of cell division. For each
advertisement

Q1.(a) (i) Mitosis and meiosis are types of cell division. For each feature in the table, tick ( • only in mitosis • only in meiosis. ) one box to show if the feature occurs: Only in mitosis ( ) Feature Only in mitosis ( ) Produces new cells during growth and repair Produces gametes (sex cells) Produces genetically identical cells (2) (ii) Name the organ that produces gametes (sex cells) in: a man ........................................ a woman. ........................................ (2) (b) X and Y chromosomes are the sex chromosomes. They determine a person’s sex. What sex chromosomes will be found in the body cells of: (i) a man ........................................ (1) (ii) a woman? ........................................ (1) (c) A man and a woman decide to have a child. What is the chance that the child will be a boy? ............................................... (1) (Total 7 marks) Page 1 Q2.The diagram shows the position of two glands, A and B, in a woman. (a) (i) Name glands A and B. A ...................................................................... B ...................................................................... (2) (ii) Gland A produces the hormone Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH). FSH controls changes in gland B. How does FSH move from gland A to gland B? ............................................................................................................... (1) (b) (i) A woman is not able to become pregnant. The woman does not produce mature eggs. The woman decides to have In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF) treatment. Which two hormones will help the woman produce and release mature eggs? Tick ( ) one box. Page 2 FSH and Luteinising Hormone (LH) FSH and oestrogen Luteinising Hormone (LH) and oestrogen (1) (ii) Giving these hormones to the woman helps her to produce several mature eggs. Doctors collect the mature eggs from the woman in an operation. Describe how the mature eggs are used in IVF treatment so that the woman may become pregnant. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (3) (iii) IVF clinics have been set a target to reduce multiple births. At least 76% of IVF treatments should result in single babies and a maximum of 24% of treatments should result in multiple births. Suggest one reason why the clinics have been set this target to reduce multiple births. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (1) (c) Two clinics, R and S, used IVF treatment on women in 2007. Doctors at each clinic Page 3 used the results of the treatments to predict the success rate of treatments in 2008. The table shows the information. Total number of IVF treatments in 2007 Number of IVF Predicted percentage treatments resulting success rate in 2008 in pregnancy in 2007 Clinic R 1004 200 18–23 Clinic S 98 20 3–56 (i) Compare the success rates of the two clinics in 2007. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (1) (ii) The range of the predicted success rate in 2008 for clinic R is much smaller than the range of the predicted success rate for clinic S. Suggest why. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (2) (Total 11 marks) Q3.The diagram shows some of the cell divisions that occur during human reproduction. Page 4 (a) (i) Name the type of cell division that produces cell D from cell B. ............................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Which organ in the male body produces cell C from cell A? ............................................................................................................... (1) (b) (i) Cells A and B each contain 46 chromosomes. How many chromosomes would there be in the nucleus of cell C? (1) (ii) Why is it important that cell C has this number of chromosomes? ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... Page 5 (2) (Total 5 marks) Q4. (a) The diagram shows changes in the uterus lining during 28 days of a menstrual cycle. Describe how changes in the lining shown in the diagram adapt it for its function if an egg is fertilised. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (b) The concentration of a certain hormone in the blood of a woman was measured during her menstrual cycle. The woman's temperature was also measured each day during this cycle. Graph 1 shows the results obtained for the measurement of the concentration of the hormone. Graph 2 shows the results obtained for the measurement of her body temperature. Page 6 (i) What evidence is there that changes in the concentration of the hormone may be connected with changes in body temperature? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) What is the difference between the minimum and maximum temperatures shown by Graph 2? Show your working. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) Page 7 Q5. (a) Describe, as fully as you can, how a human foetus gets rid of the carbon dioxide produced during respiration. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (b) The female menstrual cycle is controlled by a number of hormones. The graph below shows the concentrations of four of these hormones at different times during the menstrual cycle. The functions of the four hormones include: FSH – stimulates the development of immature cells into eggs in the ovary. LH – stimulates the release of the mature egg cell. Oestrogen – stimulates production of LH, but inhibits FSH production. Progesterone – inhibis production of both LH and FSH. Page 8 Use this information to explain as fully as you can: (i) how the concentration of oestrogen can affect and control the development and release of an egg during the monthly cycle; ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (ii) why progesterone continues to be produced throughout pregnancy. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (c) Explain, as fully as you can, how one or more of these hormones could be used to treat infertility. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) Page 9 (d) A hormone called mifepristone is used in low doses as a female contraceptive. Higher doses can be used to induce an abortion. As a consequence mifepristone is often referred to as ‘the morning-after pill’. The use of mifepristone is currently tightly controlled by the medical profession. Evaluate the benefits and problems which might arise from making this hormone more freely available. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 16 marks) Q6. The photograph shows some cells in the root of an onion plant. Page 10 By UAF Center for Distance Education [CC BY 2.0], via Flickr (a) Cells X and Y have just been produced by cell division. (i) Name the type of cell division that produced cells X and Y. ............................................................................................................... (1) (ii) What happens to the genetic material before the cell divides? ............................................................................................................... (1) (b) A gardener wanted to produce a new variety of onion. Explain why sexual reproduction could produce a new variety of onion. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ (3) (Total 5 marks) Page 11 Q7. The diagram shows a strawberry plant. The parent plant grows side shoots. New plants grow on the side shoots. © D.G. Mackean The new plants will all have the same inherited characteristics as the original parent plant. Complete the sentences to explain why. Use words from the box. asexual differentiation embryos fertilisation gametes genes mitosis sexual (a) The new plant is produced by ..................................................................... reproduction. (1) (b) In this type of reproduction, body cells divide by ............................................................. (1) (c) The new plant has the same ............................................................. as the parent plant. (1) (Total 3 marks) Page 12 Q8. We breed animals with the characteristics that we prefer. (a) The photograph shows a rabbit with some of its babies. Photograph supplied by iStockphoto/Thinkstock Use words from the box to complete the sentences about inheritance in rabbits. characteristic (i) chromosome gene gamete The colour of a rabbit’s fur is known as a ............................................... (1) (ii) This colour is controlled by a ................................................................. (1) (iii) Each sex cell of a rabbit is known as a ................................................. (1) (b) The diagram shows one way of producing calves. Page 13 Use words from the box to complete the sentences. asexual clones cuttings gametes genetic sexual A bull was mated with a cow. This is ............................................. reproduction. The embryo produced was split into four parts. The calves in the diagram have identical genetic information. This is because the calves were produced by ............................................. reproduction. The identical calves are known as .............................................. (3) (Total 6 marks) Page 14 Q9. The drawing shows a flower. Six parts are labelled P, Q, R, S, T and U. (a) The names of three of these parts are given in the table. Write the letter of each part next to its name in the table. 3 marks (b) Which two letters on the drawing show parts of the stamen? ................................ and .................................. Page 15 1 mark Maximum 4 marks The diagram shows a baby developing inside its mother’s body. Q10. (Adapted from Introduction to Biology, D.G.Makean; published by John Murray 1971) (a) Eggs are produced in organ X. What is the name of organ X? .................................................................................................................... 1 mark (b) The baby grows in a bag of amniotic fluid which is inside organ Y. What is the name of organ Y? .................................................................................................................... 1 mark (c) (i) Through which part, labelled in the diagram, is food passed from the mother to the baby? ............................................................................................................. 1 mark Page 16 (ii) Name one useful substance, other than food, which passes from the mother to the unborn baby. ............................................................................................................. 1 mark (d) The diagram shows an organ system of the mother’s body. What is the name of this organ system? .................................................................................................................... 1 mark Maximum 5 marks Q11. (a) This question is about the menstrual cycle. Choose words from the list to complete the sentences. a daily the uterus the beginning the middle a monthly an ovary the end a weekly the vagina Menstruation is part of ......................................................... cycle. The cycle begins when the lining of ...................................... breaks away. An ovum (egg) is released from .......................................... at about .............................................. of each cycle. 4 marks (b) During adolescence, boys’ bodies change. Describe two of the changes. ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... 2 marks Maximum 6 marks Page 17 Q12. The diagrams below show the male and female human reproductive systems. not to scale (a) The table below contains descriptions of parts of the human reproductive system. Complete the table to give the name of each part. name of part description the tube that carries an egg to the uterus the organ that produces sperm he organ that produces the egg 3 marks (b) The diagram below shows an unborn baby. Page 18 Complete the sentences below by filling in the gaps. In humans, normal pregnancy lasts for .................. months. When the foetus is ready to be born, muscles in the uterus wall start to ............................................. . 2 marks After the baby is born, the .......................................................... connecting the foetus to the mother is cut. 1 marks maximum 6 marks Q13. During pregnancy a woman's body increases in mass. The table shows the average increase in mass in some parts of the body during pregnancy. part increase in mass during pregnancy (kg) foetus 3.6 uterus 0.9 placenta 0.7 red blood cells 0.2 amniotic fluid 0.9 Page 19 breast tissue 0.4 fat 3.9 (a) Explain why the mass of the placenta increases as the foetus develops. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ 2 marks (b) Pregnant women need to make sure they have plenty of iron in their diet. Use information in the table to explain why they need extra iron. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ 1 mark (c) The foetus is not part of a woman’s body before she becomes pregnant. Which two other parts from the table are not present in her body before she becomes pregnant? ........................................................ and ........................................................ 1 mark (d) (i) The diagram shows the blood supply in the placenta and umbilical cord. not to scale Page 20 When the mother breathes, oxygen and other gases pass to the foetus. Complete the flow diagram below to show how oxygen passes from the mother to the foetus. Use all the words from the list below. lungs umbilical cord blood of foetus windpipe placenta 2 marks (ii) When a pregnant woman breathes in cigarette smoke, carbon monoxide gas combines with some of her red blood cells. How could this harm the foetus? ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... 1 mark maximum 7 marks Q14. Diagram 1 shows a baby in its mother’s uterus. Page 21 diagram 1 (a) What is the normal length of pregnancy in humans? .................. months 1 mark (b) (i) What is the function of the amniotic fluid around the baby? ................................................................................................................ 1 mark (ii) As a baby is born, it is pushed out of the mother’s body. Look at the diagram above. What happens in the wall of the uterus to push the baby out? ................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................ 1 mark Page 22 (c) How does a baby get oxygen from its mother while it is inside its mother’s uterus? ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... 1 mark (d) Diagram 2 shows a section through the mother’s lungs. diagram 2 Look at diagram 2. From which labelled part is oxygen absorbed into the blood? .............................................. 1 mark maximum 5 marks Q15. Diagram 1 shows the female reproductive system. Page 23 diagram 1 (a) Diagram 2 is a graph showing how the thickness of the uterus changed over a 28-day cycle. diagram 2 (i) Why did the thickness of the lining of the uterus decrease between day 1 and day 5 of this cycle? ................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................ 1 mark (ii) Suggest which day in this cycle an ovum (egg) is most likely to be fertilised. Page 24 day .............. What evidence is there for this in the graph? ................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................ 1 mark (iii) The graph shows that the lining of the uterus builds up again between day 5 and day 14. Why is this necessary? ................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................ 1 mark (b) (i) Continue the line on the graph to show what would happen to the thickness of the lining of the uterus after 28 days if an ovum was fertilised. 1 mark (ii) Explain your answer. ................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................ 1 mark maximum 5 marks Q16. The diagrams below show a human ovum (egg) and a human sperm. Page 25 (a) What are eggs and sperm? Tick the correct box. animals cells organs 1 mark (b) Which part does a sperm use to swim towards an egg? ...................................................... 1 mark (c) Give the name of the male reproductive organ where sperm are made. ....................................................... 1 mark (d) The diagram below shows a sperm joining with an egg. What is this process called? Tick the correct box. Page 26 fertilisation growth nutrition respiration 1 mark Maximum 4 marks Page 27 M1.(a) (i) Feature Mitosis Meiosis only only Produces new cells during growth and repair Produces gametes (sex cells) Produces genetically identical cells All 3 correct = 2 marks 2 correct = 1 mark 0 or 1 correct = 0 marks 2 (ii) (a man) testis / testes accept testicle(s) 1 (a woman) ovary / ovaries do not accept ‘ova’ / ovule 1 (b) (i) XY / YX orX and Y 1 (ii) XXorX and X or 2 X’s accept X 1 (c) ½ / 0.5 / 50% / 1:1 / 1 in 2 do not accept 1:2 / 50/50 allow 50:50 allow 2 in 4 1 [7] Page 28 M2.(a) (i) A – pituitary allow hypothalamus 1 B – ovary / ovaries 1 (ii) in blood (stream) accept in plasma ignore dissolved 1 (b) (i) FSH and Luteinising Hormone (LH) 1 (ii) fertilised OR reference to sperm 1 form embryos / ball of cells or cell division 1 (embryo) inserted into mother’s womb / uterus allow (fertilised egg) is inserted into mother’s womb / uterus 1 (iii) any one from: • multiple births lead to low birth weight • multiple births cause possible harm to mother / fetus / embryo / baby / miscarriages allow premature ignore reference to cost / ethics / population 1 Page 29 (c) (i) any one from: • almost identical allow S (slightly) more successful • both approximately 20% 1 (ii) larger numbers (in clinic R) (in 2007) allow only 98 (in S) (compared to 1004 (in R)) 1 results likely to be more repeatable (in 2008) allow more reliable do not accept more reproducible / accurate / precise 1 [11] M3.(a) (i) meiosis allow mieosis 1 (ii) testis / testes allow testicle 1 (b) (i) 23 1 (ii) fuses / joins with cell D / with egg cell or used in fertilisation allow fuse with another cell 1 prevents doubling of chromosome number / restores original no. / 46 / diploid no. / normal no. / full no. Page 30 accept 23 from each parent / from each gamete 1 [5] M4. (a) any three from increased thickness or build up for attachment of zygote or so zygote can implant; allow gives more room for blood vessels 3 increased blood vessels to provide nutrients for zygote; allow embryo or fetus or baby or egg for zygote becomes thicker to form placenta; increased surface area for attachment of zygote; increased glands for secretion; (b) (i) rise in hormone corresponds with rise in temperature; allow peak of hormone at same time as increased temperature or when hormone high, temperature is high allow change in hormone concentration followed by change in temperature or when hormone rises followed shortly by rise in temperature or graphs follow same pattern or graphs are nearly the same 1 (ii) maximum 36.90 °C 1 minimum 36.55 °C; 0.35 °C; allow both marks for correct answer or one mark for 0.35 if Page 31 clearly round up or round down allow one mark for working if correct 1 [6] M5. (a) moves from foetal blood to mothers blood via placenta for 1 mark each 3 (b) (i) 3 of e.g. rising levels of oestrogen result in an increased LH level when LH level peaks egg release stimulated any 3 for 1 mark each 3 (ii) 3 of e.g. continues to inhibit FSH production and to inhibit LH production so that no eggs are matured or released Because of danger to later conceived fetus if 2 develop in uterus any 3 for 1 mark each 3 (c) 3 of e.g. FSH could stimulate eggs to mature in woman whose own level of FSH too low LH could stimulate egg release where woman’s own LH production depressed by oestrogen any 3 for 1 mark each 3 (d) maximum two benefits e.g. prevents unwanted pregnancy when mother’s physical health at risk or when mental health at risk or following e.g. rape maximum two problems e.g. involves killing ‘foetus’ rather than preventing gametes meeting may lead to irresponsible attitude to sexual behaviour reference to ethical/religious attitudes Page 32 for 1 mark each 4 [16] M6. (a) (i) mitosis correct spelling only 1 (ii) replicates / doubles / is copied / duplicates accept cloned ignore multiplied / reproduced 1 (b) fertilisation occurs / fusion (of gametes) accept converse for asexual, eg none in asexual / just division in asexual 1 so leading to mixing of genetic information / genes / DNA / chromosomes genes / DNA / chromosomes / genetic information comes from 1 parent in asexual ignore characteristics 1 one copy (of each allele / gene / chromosome) from each parent or gametes produced by meiosis or meiosis causes variation meiosis must be spelt correctly 1 [5] Page 33 M7. (a) asexual 1 (b) mitosis 1 (c) genes 1 [3] M8. (a) (i) characteristic 1 (ii) gene 1 (iii) gamete 1 (b) sexual 1 asexual 1 clones 1 [6] Page 34 M9. (a) name of part letter of part anther (*)T style (*)P stigma (*)U 3 (L4) (b) T and S letters may be in either order both letters are required for the mark 1 (L4) [4] M10. (a) ovary accept ‘ovaries’ do not accept ‘ovum’ 1 (L6) (b) uterus accept ‘womb’ 1 (L6) (c) (i) placenta do not accept ‘umbilical cord’ 1 (L6) (ii) any one from • oxygen • antibodies • water do not accept ‘air’ or ‘blood’ or ‘liquid or ‘food’ or any type of nutrient 1 (L6) Page 35 (d) reproductive system accept ‘reproductive’ or ‘reproduction’ do not accept ‘sex organs’ 1 (L6) [5] M11. (a) • a monthly 1 (L6) • the uterus accept ‘uterus’ 1 (L6) • an ovary accept ‘ovary’ 1 (L6) • the middle 1 (L6) (b) any two from • voice becomes deeper • increase in facial hair • increase in body hair accept ‘voice breaks or changes’ accept ‘grows a beard’ accept ‘growth of pubic hair or hairy chest or hair in armpits’ • growth of penis • growth of testes or testicles • start to produce sperm • growth spurt Page 36 accept ‘rapid growth’ do not accept ‘growth’ or ‘gets taller’ accept ‘development of more adult body shape’ or a description of a more adult body shape, such as ‘wider shoulders’ accept ‘sweats more’ 2 (L5) [6] M12. (a) part • oviduct • testes • ovary description accept ‘fallopian (tube)’ for oviduct ‘egg tube’ is insufficient accept ‘testis’ or ‘testicle(s)’ for testes do not accept ‘ovules’ for ovary accept only the technical terms given 3 (L5) (b) • 9 accept ‘9 ½’ accept a number in the range of 37– 42 only if the unit is changed to ‘weeks’ 1 (L5) • contract accept ‘contractions’ ‘tense’ is insufficient accept ‘contract and relax’ ‘squeeze’ is insufficient accept ‘(muscles) get shorter’ ‘get smaller’ is insufficient as the volume of the muscles does not change 1 (L5) • umbilical cord accept ‘cord’ or ‘umbilical’ Page 37 ‘tube’ is insufficient 1 (L5) [6] M13. (a) any one from • the placenta provides or passes oxygen or food or gets rid of waste accept responses that refer to a baby rather than a foetus • the foetus needs oxygen or food or to remove waste ‘the foetus needs blood from the placenta’ is insufficient 1 (L7) • as the foetus develops it needs more (food or oxygen from the placenta) ‘it needs or provides more oxygen’ is insufficient as the meaning is ambiguous accept, for two marks, ‘the placenta provides more oxygen or food or waste removal’ accept, for two marks, ‘the foetus needs more oxygen or food or waste removed as it grows’ a two mark answer must include one of the first two marking points and a reference to the foetus needing more food or oxygen from the placenta 1 (L7) (b) any one from • the number or mass of red blood cells increases accept ‘they need (to make) more red blood cells’ ‘the mass of blood increases’ is insufficient • iron is needed for the formation of red blood cells accept ‘for haemoglobin’ ‘the number of blood cells increases’ is insufficient ‘for red blood cells’ is insufficient 1 (L7) (c) placenta amniotic fluid both answers are required for the mark ‘umbilical cord’ is insufficient answers may be in either order 1 (L7) Page 38 (d) (i) • • windpipe lungs mother’s red blood cells award a mark for ‘windpipe’ and ‘lungs’ in the first places in the correct order placenta umbilical cord accept ‘umbilical’ or ‘cord’ blood of foetus accept ‘umbilical cord’ and ‘blood of foetus’ in either order award a mark for ‘placenta’, ‘umbilical cord’ and ‘blood of foetus’ in the last three places in an appropriate order all five answers are required for two marks 2 (L7) (ii) any one from • less oxygen passes through the placenta • less oxygen in the foetus’ blood accept ‘the foetus’ heart beat rises’ or ‘the foetus’ blood pressure goes up’ • smaller or brain damaged foetus accept ‘less oxygen in the mother’s blood’ accept ‘less oxygen for the foetus’ do not accept ‘no oxygen’ • baby may be premature accept responses that refer to a baby rather than a foetus accept ‘the red blood cells of the foetus will contain carbon monoxide’ do not accept ‘only carbon monoxide passes through the placenta’ ‘it passes to the foetus’ blood’ is insufficient ‘it poisons the foetus’ is insufficient 1 (L7) [7] Page 39 M14. (a) • 9 1 (L5) (b) (i) any one from • it protects the baby • it helps to maintain a constant temperature • it allows the baby to move accept ‘it keeps it safe’ accept ‘it keeps the baby warm’ accept ‘it absorbs shocks’ accept ‘it protects against infection or disease’ 1 (L6) (ii) • muscles contract accept ‘contractions’ ‘the uterus or it contracts’ is insufficient 1 (L6) (c) any one from • (through the) placenta • (through the) umbilical cord • (from the) mother’s blood ignore references to food ‘through the blood’ is insufficient ‘it gets everything from the mother’ is insufficient do not accept ‘the mother breathes for the child’ 1 (L5) (d) • alveolus ‘air sac’ is insufficient 1 (L6) [5] Page 40 M15. (a) (i) any one from • menstruation • the lining of the uterus is shed accept ‘the period’ accept ‘the lining of the uterus breaks up’ accept ‘the wall of the uterus breaks down’ do not accept ‘the uterus is shed’ ‘the wall of the uterus breaks’ is insufficient both the answer and the correct explanation are required for the mark 1 (L7) (ii) a day from day 14 to day 18 accept ‘in the middle’ do not accept ‘around day 14’ any one from • • it is just after ovulation or day of ovulation that is when an egg is likely to be in the oviduct or fallopian tube • that is just after an egg is released • an egg is released on day 14 accept ‘that is when an egg is released’ ‘it is in the middle of the cycle’ is insufficient 1 (L7) (iii) any one from • so that a fertilised egg can be implanted • to receive an egg 1 (L7) (b) (i) • a line which continues to rise or remains horizontal after day 28 accept a line rising or remaining horizontal after day 1 1 (L7) (ii) any one from • menstruation stops Page 41 accept ‘the embryo or foetus or baby needs a blood supply’ ‘provides support’ is insufficient • so the ovum or embryo will implant accept ‘the lining is not shed’ 1 (L7) [5] M16. (a) cells if more than one box is ticked, award no mark 1 (L3) (b) tail 1 (L3) (c) testis or testicle accept plurals 1 (L4) (d) fertilisation if more than one box is ticked, award no mark 1 (L3) [4] Page 42