Tropical rain forest, Tropical deciduous forest, Thorny - e-CTLT
advertisement

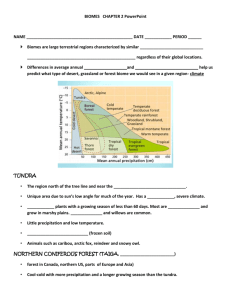
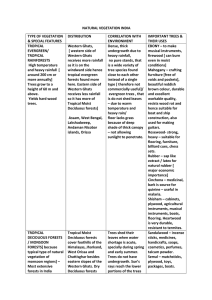
CONCEPT Natural Vegetation: Due to the varied climatic conditions, the vegetation of India can be divided into five types: Tropical rain forest, Tropical deciduous forest, Thorny bushes, Mountain vegetation and Mangrove forest. Tropical rain forest: Tropical rain forests occur in the areas which receive heavy rainfall. They do not shed their leaves at a time. Therefore, they always appear green and called evergreen forest. Andaman and Nicobar Islands, parts of North-Eastern states and a narrow strip of the western slope of the Western Ghats are home of these forests. Mahogany, ebony and rosewood are the important trees of these forests. Tropical deciduous forest: Forests where trees shed their leaves at a particular time of the year. They are found in Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Orissa and parts of Maharashtra. Sal, teak peepal, shisam and neem are the important trees of these forests. Thorny bushes: This type of vegetation is found in dry areas of the country, mainly in the states of Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana, eastern slopes of the Western Ghats and Gujarat. Cactus, khair, babool and keekar are the important trees of these forests. Mountain vegetation: A wide range of species is found in the mountains according to the variation in height. With increase in height, the temperature falls. At a height between 1500 metres and 2500metres most of the trees are conical in shape. These are called coniferous trees. Chir, deodar and pine are important trees of these forests. Mangrove forest: These forests can survive in saline water. They are found mainly in Sunderbans in west Bengal and in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Sundari is a well- known species of trees in mangrove forests. Wild life Wild life: Forests are home to a variety of wild life. There are thousands of species of animals and a large variety of reptiles, amphibians, mammals, birds, insects and worms which dwell in the forest. Tiger is our national animal and peacock is our national bird. The tiger is found in various parts of the country. Asiatic lion of gir and one- horned rhinoceroses in the forests of Assam are critically endangered. Elephants are found in Kerala and Karnataka. Camels and wild asses are found in kuchchh Activity h different pictures and visuals the students will try to find out the difference n weather and climate, major seasons, natural vegetation and wildlife of India Formative Assigments me the important trees of evergreen forest. Why does monsoon forest give a barren look? What is biosphere reserve? hat do you mean by Vegetation? many types of Wild Animals are found in india ? se Assignment Level-A at are the important trees of tropical deciduous forest? How are forests useful to us? What is the difference between Evergreen and Deciduous Forests? at is the benefit of Wild Animal ? are the Benefit of Vegetation ? Levelwise Assignment Level-B at are sunderbans? Where are these found in India? What do you mean by migratory birds? Give some examples. Distinguish between advancing monsoon and retreating monsoon. ou think Vegetation countriubutes to development of any Country ? Levelwise Assignment Level-C lain the different types of vegetation found in India. What are the steps taken by the government to protect wildlife? Why is the tropical rainforest also called evergreen forest? Wild Animals are Useless Explain ? PROJECT Make a list of national parks located in India. How many types of wild animals found in India?