natural vegetation india
advertisement
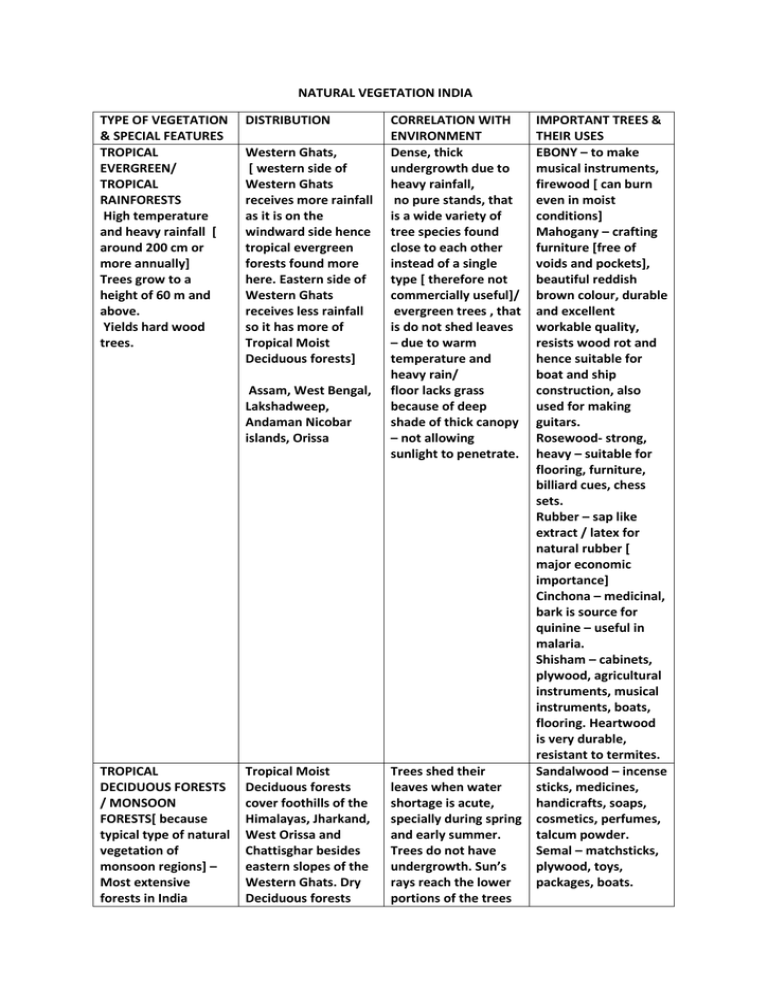
NATURAL VEGETATION INDIA TYPE OF VEGETATION & SPECIAL FEATURES TROPICAL EVERGREEN/ TROPICAL RAINFORESTS High temperature and heavy rainfall [ around 200 cm or more annually] Trees grow to a height of 60 m and above. Yields hard wood trees. DISTRIBUTION Western Ghats, [ western side of Western Ghats receives more rainfall as it is on the windward side hence tropical evergreen forests found more here. Eastern side of Western Ghats receives less rainfall so it has more of Tropical Moist Deciduous forests] Assam, West Bengal, Lakshadweep, Andaman Nicobar islands, Orissa TROPICAL DECIDUOUS FORESTS / MONSOON FORESTS[ because typical type of natural vegetation of monsoon regions] – Most extensive forests in India Tropical Moist Deciduous forests cover foothills of the Himalayas, Jharkand, West Orissa and Chattisghar besides eastern slopes of the Western Ghats. Dry Deciduous forests CORRELATION WITH ENVIRONMENT Dense, thick undergrowth due to heavy rainfall, no pure stands, that is a wide variety of tree species found close to each other instead of a single type [ therefore not commercially useful]/ evergreen trees , that is do not shed leaves – due to warm temperature and heavy rain/ floor lacks grass because of deep shade of thick canopy – not allowing sunlight to penetrate. Trees shed their leaves when water shortage is acute, specially during spring and early summer. Trees do not have undergrowth. Sun’s rays reach the lower portions of the trees IMPORTANT TREES & THEIR USES EBONY – to make musical instruments, firewood [ can burn even in moist conditions] Mahogany – crafting furniture [free of voids and pockets], beautiful reddish brown colour, durable and excellent workable quality, resists wood rot and hence suitable for boat and ship construction, also used for making guitars. Rosewood- strong, heavy – suitable for flooring, furniture, billiard cues, chess sets. Rubber – sap like extract / latex for natural rubber [ major economic importance] Cinchona – medicinal, bark is source for quinine – useful in malaria. Shisham – cabinets, plywood, agricultural instruments, musical instruments, boats, flooring. Heartwood is very durable, resistant to termites. Sandalwood – incense sticks, medicines, handicrafts, soaps, cosmetics, perfumes, talcum powder. Semal – matchsticks, plywood, toys, packages, boats. – MOIST DECIDUOUS & DRY DECIDUOUS [ on basis of water availability] Moist Deciduous= 100 to 200 cm annual rainfall Dry Deciduous = 70 to 100 cm annual rainfall. found in Bihar, Uttar Pradesh. Most of these forests have been cleared for cultivation and grazing. and as such grass grows. Trees not closely spaced as in tropical rainforests. Height of trees = 30 to 50 metres. TROPICAL DESERTRainfall less than 70 cm Rajasthan, Gujarat, Punjab, Haryana, dry parts of Madhya Pradesh, rain shadow areas of the Western Ghats. Xerophytes – have special ways of conserving water. Trees have very small leaves and thorns due to lack of moisture. Small, thick leaves minimise loss of water. Long roots penetrate deep into soil and spread in radial pattern in search of water. Areas of more scanty rainfall have scrubs and thorny bushes. LITTORAL/ SWAMPY / DELTA/ TIDAL FORESTS/ MANGROVES Deltas of Gangs, Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri. Trees survive both in fresh as well as brackish water. MOUNTAIN FORESTS/ VEGETATION – The northern slopes of Himalayas receive sun’s rays only for a few hours during the day at a low angle. The southern slopes receive comparatively vertical rays during the middle of the day. As a result the southern slopes being warmer have greater Himalayas Altitude is the most important factor controlling the type of vegetation in this mountainous region. Tropical deciduous forests are found in foothill zone. Above this zone are found sub-tropical hill vegetation including evergreen oaks, chestnuts and pine trees. Further higher Teak – weather resistant and hence used for out door furniture, boat decks, flooring. Sal – most suitable for railway sleepers, bridges, cart wheels. Bamboo – decoration, fuel, construction, furniture, paper. Babool- medicinal, leaves and bark help in arresting bleeding. Date Palm – edible vegetable oil, toddy or alcoholic beverage, coir from the outer shells of coconuts used as doormats, mattresses, ropes, being a water – resistant fibre. Kikar – bark and seeds source of tannin, seeds used to cure diarrhoea, leaves used to arrest bleeding. Sundari trees in Sunderbans delta – provide hard and durable timber for building and construction as well as for making boats. Oak – hard and tough wood – used for construction, making wagons. Pines – commercially important trees valued for timber, wood pulp and as ornamentals. Silver Fir – soft wood – used in making paper, packing crates. evapotranspiration and the vegetation is up to higher altitude on the southern slopes than the northern slopes. we find coniferous trees like deodar and cedar. Higher than this at 3,500 metres vegetation consists of shrubs, scrubs and grass. Deodar – durable – rot- resistant used in building.







