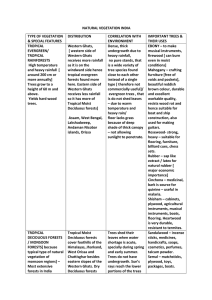
India's Vegetation & Biodiversity: Exam Q&A
advertisement

1)To which one of the following types of vegetation does rubber belong? a) b) c) d) TUNDRA TIDAL HIMALAYAN TROPICAL EVERGREEN Answer: D) Tropical Evergreen 2) Cinchona trees are found in the areas of rainfall of more than: a) 100 cm b) 50 cm c) 70 cm d) Less than 50 cm Answer: A) 100 cm 3) In which of the following states is the Simlipal bio-reserve located? a) Punjab b) Delhi c) Orissa d) West Bengal Answer: c) Orissa 4) Which one of the following bioreserves of India is not included in the world network of bio-reserves? a) Manas b) Nilgiri c) Gulf of Mannar d) Nanda Devi Answer: a) Manas 2i) Define an ecosystem: Answer: An ecosystem is an area that has a group of flora and fauna that are interdependent and interrelated to each other and their environment. The entirety of this interconnected web of plants, animals, and their environment is an ecosystem. 2ii) What factors are responsible for the distribution of plants and animals in India? Answer: 1) Relief- the topography and type of land formations. 2) Soil- the type of soil in an area and the nutrients it contains. 3) Photoperiod- length of daylight. 4) Precipitation- amount of rainfall or snowfall. 5) Temperature- amount of energy present in the air. 2iii) What is a bio-reserve? Give two examples. Answer: A bio-reserve is an area set aside by the government for the purpose of protecting the flora and fauna within its boundaries. Ex. Sunderbans, Gulf of Mannar, The Nilgiris, Nanda Devi, Nokrek, Great Nicobar, Manas, Simlipal, Dihang-Dibang, Dibru Saikhowa, Agasthyamalai, Kanchenjunga, Pachmari, Achanakmar-Amarkantak 2iv) Name two animals having their habitat in tropical and montane type of vegetation. Answer: Tropical: elephants, monkeys, lemurs, deer, one-horned rhinoceri, lions, tigers, pigs. Montane: Kashmir stag, spotted deer, wild sheep, jack rabbits, Tibetan antelope, yaks, snow leopards, squirrels, Shaggy horn wild ibex, bears, red pandas. 3i) Distinguish between flora and fauna. Answer: Fauna are the animals living in an area, ecosystem, biome, etc. Whereas the flora are the plants of that region. 3ii) Distinguish between tropical evergreen forests and tropical deciduous forests. Answer: Evergreen forests do not shed their leaves all at once due to the lack of specific dry season. Deciduous forests shed their leaves for a general 6-8 week period during the dry season. The evergreen forests generally receive more than 200 cm of rainfall annually where deciduous get between 70-200cm per annum. Because of this difference in rainfall, there is a stark difference in the height of the forests with the evergreens being much taller. 4) Name different types of vegetation found in India and describe the vegetation of high altitudes. Answer: The vegetation of India contains the following types: Tropical evergreen, tropical deciduous, thorn forests and scrubs, montane forests, mangrove forests. The vegetation of higher altitudes (montane region) starts with a wet temperate forests between 1000-2000m. The prominent trees are broad-leaf trees such as oaks and chestnuts. Next are temperate coniferous forests from 1500-3000m with trees such as Pine, Spruce, and Deodar. In between these and the alpine vegetation there are some temperate grasslands. The alpine vegetation usually starts from 3600m with trees such as Silver fir and Junipers. Alpine grasslands and scrubs and shrubs occur near the snow line and further up there tend to only be mosses and lichens in the tundra region. 5) Quite a few species of plants and animals are endangered in India. Why? Answer: Many organisms in India are endangered in India due to issues relating to the destruction of the ecosystems by human activities. These activities include poaching animals, pollution from air, land, and water forms, invasive or alien species being introduced to the habitats, and the destruction of habitats by deforestation and Global Warming. 6) Why does India have a rich heritage of flora and fauna? Answer: India has a diverse set of climates throughout the country from the cold deserts of Ladakh to the tropical islands of Lakshadweep and Andaman and Nicobar. These differences in climate cause different plants and animals to take up residence due to the fact that the climate of a region has a very big impact on the types of animals and plants a place will have. The relief differences as well play a major part in the rise of differentiated species in India. These soil and topographical differences cause many species of similar climates to differ as well.