BTCE 30 Fourth Semester B. Tech in Civil Engineering Examination
advertisement

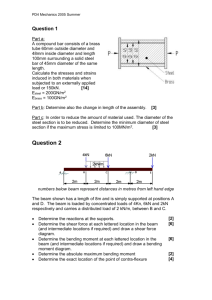
BTCE 30 Fourth Semester B. Tech in Civil Engineering Examination July/August 2012 Solid mechanics Time:-3Hours Max. Marks: - 75 SECTION-A Attempt any five questions: (5*5) 1. A steel plate is subjected to tensile stresses of 200Mpa and 150Mpa at right angles to each other. Determine the normal and tangential stresses on a plane inclined at 60 the 200Mpa stress. Also find the plane on which the resultant stress has maximum obliquity? 2. At a point in a strained material, the principal stresses are 120Mpa tensile and 60 Mpa compressive. Find the resultant stress and its direction on a plane inclined at 450 to axis of 120Mpa stress by Mohr’s circle diagram. Also determine the maximum intensity of shear stress in the material? 3. A plant in a material is subjected to a stress as shown in calculate Principal stresses. Maximum shear stress, and also the plane along which if acts σx =50Mpa. 4. A rectangular block of material is subjected to a tensile stress of 100Mpa on a plane and a tensile stress of 40Mpa on the plane at right angles to the former, to getter with a shear stress of 60Mpa on the same planes. Find (a) The direction of principal planes. (b) Magnitude of principal stresses. (c) Magnitude of the greatest shear? 5. In two dimensional problem the stresses at point are σx=100Mpa, σy=60Mpa.If the principal stress is limited to 150Mpa. Find out the value of shear stress Zxy 6. The state of stress at a point is specified by the following stress components σπ=70,σy=10,σz=-20, Zxy=-40. Zyz =Zxy =0 MN/m2.Determine the principal stresses and the direction cosines of the maximum principal stress. I1=σx+σy+σz=70+10-20=60. 7. A body is subjected to two normal strains of magnitude Ex=0.001 and Ey=0.002. Determine the normal and shearing strains on a plane inclined at 300 with the Ex strain? SECTION-B Attempt any two questions: (10*2) 8. The normal strains at a point in a material are Ex=15*10-3 ,Ey=10*10-3determine the normal and shearing strains on a plane inclined at 200 with Ex strain by drawing Mohr’s 9. A piece of material 15cm long by 2.5cm square is in compression under a load 100KN. If the modulus of elasticity of the material is 105 GPA and poisons’ ratio is 0.25. Find the alteration in length if all lateral strains prevented by the application of uniform lateral external pressure of suitable intercity? 10. A bar 15cm long and 5cm square in cross-section is subject to an axial compressive load of 15KN. Taking E=200Gp a and u=0.25, Calculate the change in volume of the bar. If the lateral strains of the bar are prevented by a uniform pressure on its four lateral faces, calculate this pressure value and the change in volume. Also calculate the value of K and G for the bar? SECTION-C Attempt any two questions: (15*2) 11. A cylindrical bar is 2cm in diameter and 100cm long. During a tensile test it is found that the longitudinal strain is 4 time the lateral strain. Calculate the modulus in volume, when the bar is subjected to a hydrostatic pressure o 100Mpa? 12. Determine the percentage change in volume of a steel bar 10cm square in section and 2cm long when subjected to an axial compressive load of 20KN. What change in volume would a 10cm cue of steel suffer at depth of 5Km is sea water? For steel E=200 GPA, G=80GPA, Weight of a cubic meter of sea water is 9806.5556? 13. A material has a young’s Modulus of 1.25*105 N/mm2 and a Poisson’s ratio of 0.25. Calculate the Modulus of rigidity and the bulk modulus?