Power, Structural, and Technical Systems AG3 & AG4
advertisement
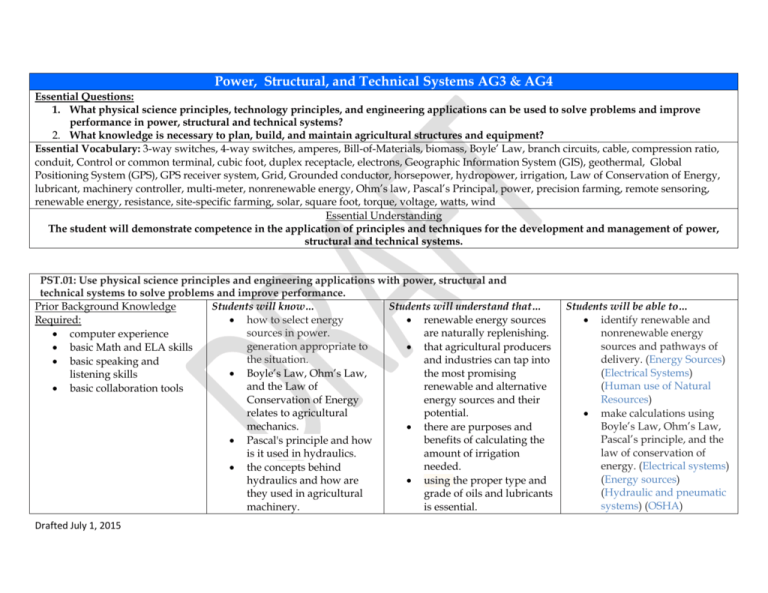
Power, Structural, and Technical Systems AG3 & AG4 Essential Questions: 1. What physical science principles, technology principles, and engineering applications can be used to solve problems and improve performance in power, structural and technical systems? 2. What knowledge is necessary to plan, build, and maintain agricultural structures and equipment? Essential Vocabulary: 3-way switches, 4-way switches, amperes, Bill-of-Materials, biomass, Boyle’ Law, branch circuits, cable, compression ratio, conduit, Control or common terminal, cubic foot, duplex receptacle, electrons, Geographic Information System (GIS), geothermal, Global Positioning System (GPS), GPS receiver system, Grid, Grounded conductor, horsepower, hydropower, irrigation, Law of Conservation of Energy, lubricant, machinery controller, multi-meter, nonrenewable energy, Ohm’s law, Pascal’s Principal, power, precision farming, remote sensoring, renewable energy, resistance, site-specific farming, solar, square foot, torque, voltage, watts, wind Essential Understanding The student will demonstrate competence in the application of principles and techniques for the development and management of power, structural and technical systems. PST.01: Use physical science principles and engineering applications with power, structural and technical systems to solve problems and improve performance. Students will know… Students will understand that… Prior Background Knowledge Required: how to select energy renewable energy sources sources in power. are naturally replenishing. computer experience generation appropriate to that agricultural producers basic Math and ELA skills the situation. and industries can tap into basic speaking and the most promising Boyle’s Law, Ohm’s Law, listening skills and the Law of renewable and alternative basic collaboration tools Conservation of Energy energy sources and their relates to agricultural potential. mechanics. there are purposes and benefits of calculating the Pascal's principle and how is it used in hydraulics. amount of irrigation needed. the concepts behind hydraulics and how are using the proper type and they used in agricultural grade of oils and lubricants machinery. is essential. Drafted July 1, 2015 Students will be able to… identify renewable and nonrenewable energy sources and pathways of delivery. (Energy Sources) (Electrical Systems) (Human use of Natural Resources) make calculations using Boyle’s Law, Ohm’s Law, Pascal’s principle, and the law of conservation of energy. (Electrical systems) (Energy sources) (Hydraulic and pneumatic systems) (OSHA) that the amount of irrigation water needed for a particular crop be calculated. there are the various types and grades of oils and lubricants. Vocabulary: biomass Boyle’s Law hydropower irrigation Law of conservation of Energy lubricant nonrenewable energy Ohm’s Law Pascal’s principle renewable energy solar wind geothermal (Lubricants) (structural plans and building codes) (irrigation) examine environmental impacts and efficiencies of energy sources. (Energy Sources) (Electrical Systems) (Human use of Natural Resources) identify basic theories applying to fluid dynamics. (Hydraulics and pneumatics) (Irrigation) calculate the seasonal demand and peak-use rates for crop irrigation using the figures in the charts. (irrigation) describe functions of engine oil and lubricants and explain the types and grades. (Lubricants) prepare and deliver a multi-part project and presentation using science and engineering applications with power, structural and technical systems to solve problems and improve performance. PST.02: Design, operate and maintain mechanical equipment, structures, biological systems, land treatment, power and technology. (NA) Students will know… Students will understand that… Students will be able to… Prior Background Knowledge Required: devices are properly schematic symbols and interpret electrical system Drafted July 1, 2015 computer experience basic Math and ELA skills basic speaking and listening skills basic collaboration tools installed in electrical circuits. operating principles of agricultural harvesting and handling equipment. Vocabulary: 3-way switches 4-way switches Bill-of-Materials branch circuits cable conduit control or common terminal duplex receptacle amps volts watts diagrams are used to communicate electrical plans. the power equation is a formula that defines the relationship between watts, amps, and volts. it is important to be able to read and draw sketches and scale drawings. symbols and diagrams. (Electrical Systems) (Structural Plans and Building Codes) discuss various types and sources of electricity. (Electrical Systems) (Structural Plans and Building Codes) development of a cutting list and/or a bill of materials. (structural plans and building codes) (equipment service) describe the operation and preparation of agricultural preparation, planting, and harvesting equipment. (equipment safety and use) (Equipment service) prepare and deliver a multi-part design, operation, and/or maintenance project and presentation of mechanical systems. PST.03: Service and repair mechanical equipment and power systems. Students will know… Students will understand that … Students will be able to… Prior Background Knowledge Required: how to troubleshoot and The Law of Conservation of identify the kinds and service mechanical systems. Energy states that energy applications of electricity, computer experience cannot be created nor including direct and how to service and repair basic Math and ELA skills destroyed. alternating current. (Energy steering, suspension, basic speaking and Sources) (Electrical traction and vehicle. advantages and listening skills Drafted July 1, 2015 basic collaboration tools performance systems. define hydraulics and pneumatics and explain its major operating systems. disadvantages of hydraulic and pneumatics systems can be used to do work. Vocabulary: Compression ratio electrons horsepower Law of Conservation of Energy torque Systems) describe the primary components of a hydraulic and pneumatics system. (Hydraulic and pneumatic systems) prepare and deliver a multi-part service and/or repair project and presentation of mechanical systems. x PST.04: Plan, build and maintain agricultural structures. Students will know… Prior Background Knowledge Required: how to follow architectural and mechanical plans to computer experience construct and/or repair basic Math and ELA skills equipment, buildings and basic speaking and facilities. listening skills the reason for building basic collaboration tools codes. how to select hand tools. Vocabulary: amperes cubic foot multi-meter Ohm’s law power resistance square foot Drafted July 1, 2015 Students will understand that … the amount of current in an electrical circuit is directly proportional to the voltage applied across the circuit and inversely proportional to the resistance of the circuit. concrete is a mixture of coarse aggregate, fine aggregate, portland cement, and water. to calculate the amount of concrete needed convert the length, width, and thickness into feet, multiply them together, and divide by 27. fuels, lubricants, and Students will be able to… identify electricity measurements and make measurement calculations. (Electrical Systems) calculate areas and volumes for coatings. (Structural Plans and Building Codes) measure and calculate materials for concrete, brick, stone or masonry units in agricultural construction. (Structural plans and building codes) measure and calculate glass, rigid plastic panels and film plastics for job requirements. (Structural voltage watts coolants are used in agricultural equipment and have a variety of characteristics. Drafted July 1, 2015 plans and building codes) (Plant propagation) explain the different types of building codes. (Structural Plans and Building Codes) identify and explain how to use layout, cutting, shaping, boring, holding, turning, driving and wrecking tools. (Hand and Power tools) describe the maintenance of fuel, lubricant, and coolant systems in agricultural equipment. (equipment service) (Lubrication) (OSHA) (Equipment Safety and Use) describe how agricultural equipment is calibrated and maintained. (Equipment safety and Use) (Equipment service) (GPS) prepare and deliver a multi-part project and presentation to plan, build, and/or maintain an agricultural structure. PST.05: Apply technology principles in the use of agricultural technical systems. Students will know… Students will understand that … Prior Background Knowledge Required: the irrigation methods used generally, black and red in agriculture. conductors carry “hot” computer experience power or current from the the types of sprayers and basic Math and ELA skills source (SEP) to the devices their components. basic speaking and within the circuit, white is listening skills neutral, and green is Vocabulary: basic collaboration tools ground. Geographic Information the National Electrical System (GIS) Code (NEC) provides the Global Positioning System accepted set of guidelines (GPS) that should be followed GPS receiver system when planning and grid installing electricity. grounded conductor precision farming is a site machinery controller specific crop management precision farming system based on the needs remote sensoring of the land and technology. site-specific farming there are multiple systems of land measurement and legal description used in the United States. precision farming increases production efficiency, promotes sustainable agriculture, and protects the environment. Drafted July 1, 2015 Students will be able to… explain the operating principles of irrigation systems used in agriculture. (irrigation) explain the operation of a sprayer. (irrigation) (Manage insects) (Equipment service) use volt and amp meters and continuity testers to demonstrate electricity principles. (Electrical systems) (energy Sources) identify hazards and safety practices in planning, installing and using mechanical systems. (Energy Sources) (Equipment Safety and Use) (Equipment service) (Hand and Power Tools) (OSHA) explain the purpose of land measurement and legal descriptions. (technological and mathematical mapping) (Cartographic skills) (Measure and survey natural resources) (GPS) identify uses, components and setup of precision technology in agriculture, food and natural resources. Drafted July 1, 2015 (GPS) describe principles of precision agriculture for map-and sensor-based systems. (Cartographic skills) (Measure and survey natural resources) (GPS) (Technological and Mathematical Mapping) explain the safety practices for pneumatics. (Hydraulics and pneumatics) (OSHA) prepare and deliver a multi-part application of technological principals through a project and presentation .