Cognitive and Quantitative Skills Descriptions for MCAS High
advertisement
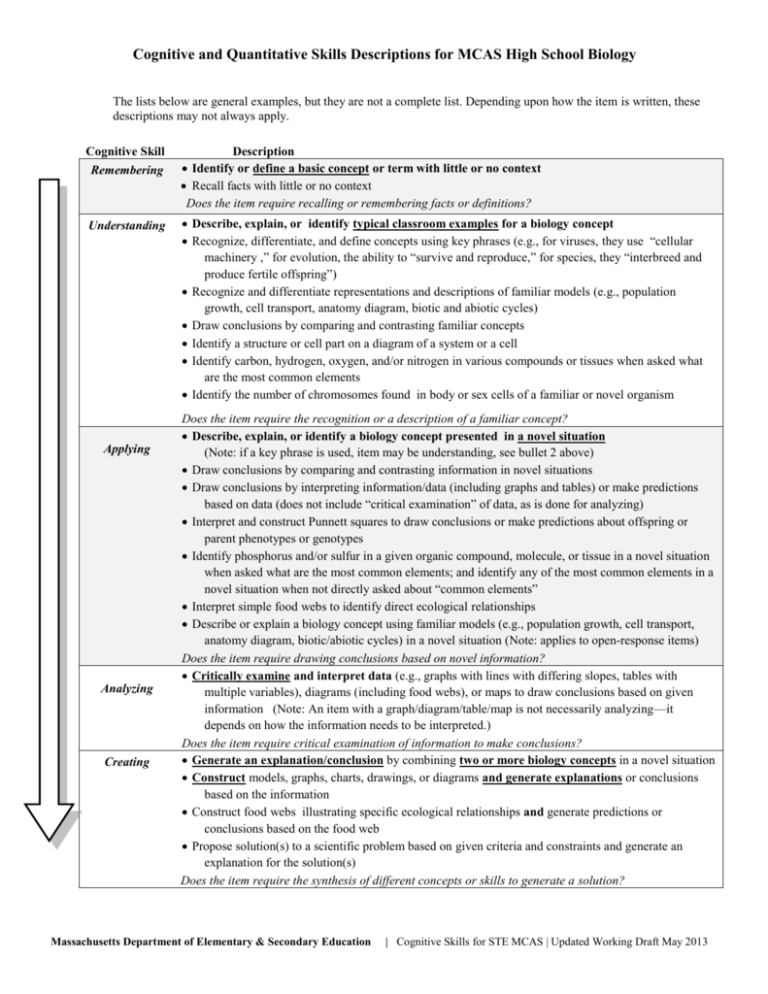
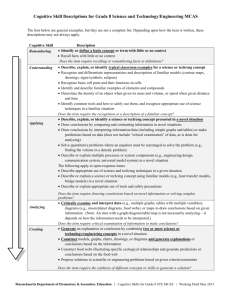
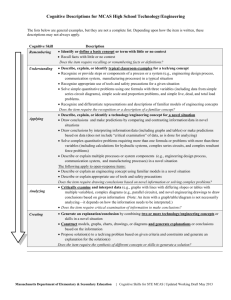
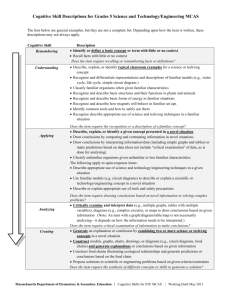
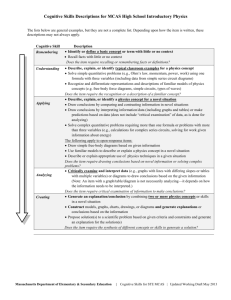
Cognitive and Quantitative Skills Descriptions for MCAS High School Biology The lists below are general examples, but they are not a complete list. Depending upon how the item is written, these descriptions may not always apply. Cognitive Skill Remembering Understanding Applying Analyzing Creating Description Identify or define a basic concept or term with little or no context Recall facts with little or no context Does the item require recalling or remembering facts or definitions? Describe, explain, or identify typical classroom examples for a biology concept Recognize, differentiate, and define concepts using key phrases (e.g., for viruses, they use “cellular machinery ,” for evolution, the ability to “survive and reproduce,” for species, they “interbreed and produce fertile offspring”) Recognize and differentiate representations and descriptions of familiar models (e.g., population growth, cell transport, anatomy diagram, biotic and abiotic cycles) Draw conclusions by comparing and contrasting familiar concepts Identify a structure or cell part on a diagram of a system or a cell Identify carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and/or nitrogen in various compounds or tissues when asked what are the most common elements Identify the number of chromosomes found in body or sex cells of a familiar or novel organism Does the item require the recognition or a description of a familiar concept? Describe, explain, or identify a biology concept presented in a novel situation (Note: if a key phrase is used, item may be understanding, see bullet 2 above) Draw conclusions by comparing and contrasting information in novel situations Draw conclusions by interpreting information/data (including graphs and tables) or make predictions based on data (does not include “critical examination” of data, as is done for analyzing) Interpret and construct Punnett squares to draw conclusions or make predictions about offspring or parent phenotypes or genotypes Identify phosphorus and/or sulfur in a given organic compound, molecule, or tissue in a novel situation when asked what are the most common elements; and identify any of the most common elements in a novel situation when not directly asked about “common elements” Interpret simple food webs to identify direct ecological relationships Describe or explain a biology concept using familiar models (e.g., population growth, cell transport, anatomy diagram, biotic/abiotic cycles) in a novel situation (Note: applies to open-response items) Does the item require drawing conclusions based on novel information? Critically examine and interpret data (e.g., graphs with lines with differing slopes, tables with multiple variables), diagrams (including food webs), or maps to draw conclusions based on given information (Note: An item with a graph/diagram/table/map is not necessarily analyzing—it depends on how the information needs to be interpreted.) Does the item require critical examination of information to make conclusions? Generate an explanation/conclusion by combining two or more biology concepts in a novel situation Construct models, graphs, charts, drawings, or diagrams and generate explanations or conclusions based on the information Construct food webs illustrating specific ecological relationships and generate predictions or conclusions based on the food web Propose solution(s) to a scientific problem based on given criteria and constraints and generate an explanation for the solution(s) Does the item require the synthesis of different concepts or skills to generate a solution? Massachusetts Department of Elementary & Secondary Education | Cognitive Skills for STE MCAS | Updated Working Draft May 2013