25.3 – The Universe I. Galaxies A. Spiral Galaxies 1. usually disk
advertisement

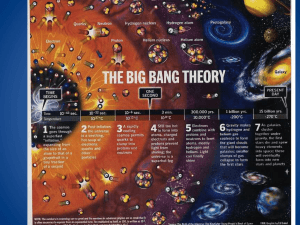
25.3 – The Universe I. Galaxies A. Spiral Galaxies 1. usually disk-shaped, with a somewhat greater concentration of stars near their centers 2. arms extend from a central nucleus i. 3. young and old stars with the youngest located in the arms 4. Barred Spiral Galaxies i. B. C. II. outermost stars of the arms rotate most slowly, giving the galaxy the appearance of a pinwheel a type of spiral galaxy where its stars extend from the nucleus in opposite directions in the shape of a bar, which rotates as a rigid system. Attached to each end of these bars are curved spiral arms. Elliptical Galaxies 1. 60% of galaxies are classified as elliptical galaxies. 2. Range in shape from oval to round 3. most are small, but the largest known galaxies are elliptical 4. contain old stars Irregular Galaxies 1. composed mostly of young stars 2. irregular in shape The expanding universe A. Doppler effect 1. Large Doppler shifts indicate higher speeds 2. Smaller Doppler shifts indicate lower speeds 3. Red shifts = longer wave-lengths 4. Blue shifts = shorter wave-lengths B. III. Red Shifts 1. Observations completed by Edwin Hubble allowed him to discover in 1929 that most galaxies have Doppler shifts toward the red end of the spectrum. 2. Red shift occurs because light waves are “stretched,” which shows the Earth and the source are moving away from each other. 3. The red shifts of distant galaxies indicate that the universe is expanding. The Big Bang – theory that the universe began as a violent explosion from which the universe continues to expand, evolve, and cool. A. B. Supporting evidence 1. The big bang theory states that at one time, the entire universe was confined to a dense, hot supermassive ball. Then, about 13.7 billion years ago, a violent explosion occurred, hurling this material in all directions. 2. Red shifts 3. Cosmic background radiation – scientists believe this radiation was produced during the big bang. The big crunch? 1. The belief that the outward flight of the galaxies will slow and eventually stop. Gravitational contraction would follow, causing the galaxies to collide and combine into the high-energy, high-density mass from which the universe began.