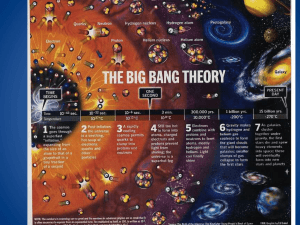
Evidence that Supports the Big Bang Theory
advertisement

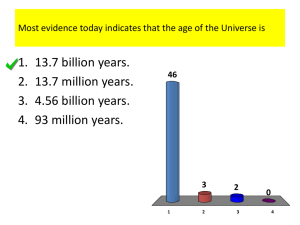
Evidence to support the... But first, what’s a scientific theory? • The term “theory” in science has a different meaning than in our everyday language. • A scientific theory is NOT a guess or a shot in the dark explanation for something • A scientific theory is a plausible explanation for phenomena in nature supported by evidence and builds upon scientific laws. • Scientific law describes a relationship between factors or what should occur in a certain situation because of previous repeated observation. ex. Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation • Scientific theory will try to explain why we repeatedly see these relationships and observations through experimental evidence. ex. Einstein’s Theory of Relativity What is the Big Bang Theory? 13.7 billion years ago the universe formed when an infinitely dense point suddenly and rapidly expanded in a single moment. Evidence to Support the Theory 1.Redshift Spectra and Hubble’s Law • Edwin Hubble observed the line spectra from many different galaxies in the sky • most of the spectra for the galaxies were shifted towards the red end of the spectrum – a redshift • Hubble concluded that if most of the galaxies were redshifted, they must be receding in all directions and the universe is expanding from a single point – BIG BANG Evidence to Support the Theory 2.Cosmic Background Radiation In 1965 Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson were using a new microwave antenna with the intention of using it for telecommunication. What they picked up was microwave radiation from the sky in all directions, not just from stars But what did that mean? Evidence to Support the Theory Cosmic Background Radiation Penzias and Wilson unintentionally discovered cosmic background radiation. It is believed that this is leftover radiation from the initial big bang. Penzias and Wilson later won a Nobel Prize for their serendipitous find. Evidence to Support the Theory 3. Radiation Mapping Cosmic Background Explorer (COBE) satellite created detailed maps of the background radiation from distant parts of the universe in 1992. Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) in 2006 provided even more precise measurements of the radiation. Evidence to Support the Theory Radiation Mapping analysis of temperature differences and microwave polarization from these maps provided the point of inflation Inflation is the idea that the universe expanded many trillion times its size faster than a snap of the fingers at the outset of the Big Bang This breakthrough that enabled scientists to analyze what happened less than a trillionth of a trillionth of a second after the Big Bang. Evidence to Support the Theory 4.Proportion of Matter in Stars • Simplest atoms, hydrogen, gets cooked into heavier elements at a high enough temperature and density (such as the cores of stars). • In the early hot and expanding universe only enough time to fuse hydrogen to helium before expansion and cooling shuts it down. Isotopes of Hydrogen Evidence to Support the Theory Proportion of Matter in Stars The theory is 12:1 ratio hydrogen to helium by number, or 75% 25% by mass, from the Big Bang. Most matter detected from the universe fits this composition supporting the Big Bang Theory. Evidence to Support the Theory 5. Observation of Distant Galaxies and Stars An expanding universe is evolving over time. If we look at the early universe, it should appear different. Distant galaxies therefore appear as they did in a less evolved universe. These early galaxies are more disturbed because of collisions with other galaxies, smaller and contain fewer heavy elements Evidence to Support the Theory 6. Expanding Dynamic Universe According to Einstein, space-time of the universe is expanding and because of it the galaxies are drifting apart. Evidence to Support the Theory Expanding Dynamic UniverseRaisin Bread Analogy Where do we go from here? Dark Energy The unknown energy that is causing the acceleration of the expansion of the universe. Supernovae in distant galaxies are further (so dimmer) than they should be, thanks to an accelerating universe. They are traveling faster than predicted by their redshift spectrum according to Hubble’s Law. Through the study of light from these distant supernovae, it was determined that the slowing universe started to speed up again 5 billion years ago. Where do we go from here? Dark Matter • 90% of matter in and between galaxies is of an unknown form that does not emit or absorb light (so we can’t see it). • It can be detected through its gravity by the way it affects objects we can see. • Without dark matter, normal matter would have been unable to clump and form stars and galaxies - and us. “Normal Matter” 4% Dark Energy 73% Dark Matter 23% CERN HADRON COLLIDER http://www.youtube.com/user/CER NTV?blend=9&ob=5#p/c/C193B03B 29D263DE/0/UDoIzvKumGI • The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is a gigantic scientific instrument near Geneva, where it spans the border between Switzerland and France about 100 m underground • It is a particle accelerator used by physicists to study the smallest known particles – the fundamental building blocks of all things • It will revolutionise our understanding, from the minuscule world deep within atoms to the vastness of the Universe.