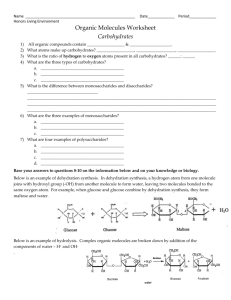
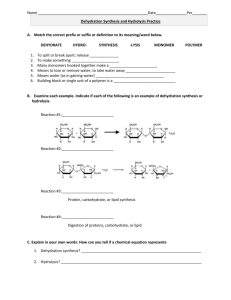
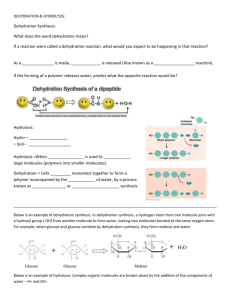
Unit I Study Guide KEY
advertisement

Unit II Study Guide KEY 1. a. 15 d. ~ 31 b. 16 e. 15 c. 15 2. a. isotopes b. # protons, # electrons, atomic number are same; # neutrons, atomic mass are different 3. Polar = unequal sharing of electrons 4. cohesion, adhesion Allows water to move up from roots to leaves 5. Heat is absorbed, released when hydrogen bonds break, form; allows water to be relatively unaffected by temperature change 6. High heat of vaporization Cooling effect of perspiration 7. Hydrogen bonds in solid ice hold water molecules further apart; less dense as solid Protects aquatic life, insulates 8. Universal solvent Polar water molecules “pull apart” other polar, ionic substances 9. coffee 10. Orange juice has 100X more H+ than coffee 11. 10 -3 3 acid 12. 10 -6 8 base 13. 10 -1 10 -13 acid 14. 10 -7 7 neutral 15. a. H2CO3 ↔ H+ + HCO3 – b. To the right; [H+ ] will increase to decrease pH c. 7.4 16. Dehydration synthesis 17. Hydrolysis 18. Dehydration synthesis 19. Dehydration synthesis 20. Hydrolysis 21. Dehydration synthesis 22. Structural = cellulose – cell walls of plant cells chitin – cell walls of fungal cells; insect exoskeleton peptidoglycan – cell walls of Eubacteria 23. Storage = glycogen – animals starch - plants 24. a. Sucrose or lactose or maltose b. disaccharide d. sucrose = glu + fru lactose = glu + galac maltose = glu + glu e. dehydration synthesis 25. hydroxyl 26. carbonyl – aldehyde 27. amino + carbonyl 28. amino 29. carboxyl 30. carbohydrate – monosaccharide 31. lipid - saturated 32. nucleic acid 33. carbohydrate – polysaccharide 34. nucleic acid (nucleotide) 35. lipid (fatty acid) – saturated 36. b. lactose c. glucose and galactose d. hydrolysis e. Induced fit refers to the slight “hug” that occurs when the substrate fits into the active site. This is important because it either stresses the bonds slight to allow for break down, or holds substrates closely together to facilitate bonding f. competitive inhibitor – takes up active site, physically blocking substrate non-competitve inhibitor – changes shape of active site by binding with enzyme at another location g. regulation of enzyme activity in which protein’s function at one site is affected by the binding of a regulatory molecule at another site; may result in stimulation or inhibition of enzyme 37. non-polar 38. basic 39. basic 40. polar 41. polar 45. 2° 46. 3° 47. 2° a. phosphate group c. nucleotide b. deoxyribose d. adenine – purine DNA is a double helix; RNA is a single helix. The sugar in DNA is dexoyribose; ribose is found in RNA In RNA, uracil replaces thymine. 42. 2° 43. 4° 44. 1° 48. e. guanine – purine f. thymine - pyrimidine g. cytosine - pyrimidine