Types of Chemical Reactions
advertisement

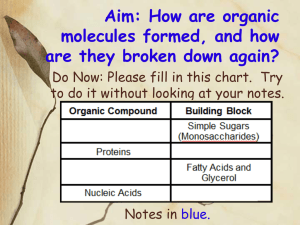
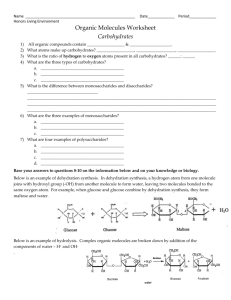
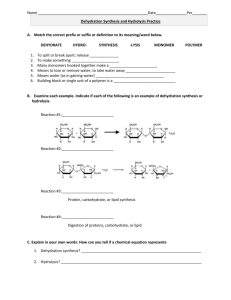
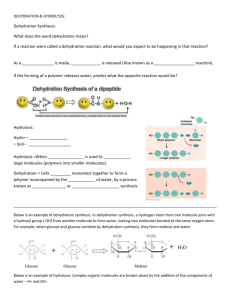
CHEMICAL REACTIONS METABOLISM • Your metabolism is the sum of all the chemical reactions that take place within you. (There are literally thousands of them going on at any given moment!) • Every chemical reaction involves the breaking of bonds within the reactants and the rearranging of atoms and formation of new bonds in the products. • There are four major types of chemical reactions that are common in biology. 1. Dehydration Synthesis 2. Hydrolysis 3. Neutralization 4. REDOX DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS • AKA: Condensation Reaction • In a dehydration synthesis reaction, subunits of a larger molecule are joined together by the removal of water. • We see these reactions all the time in biochemistry. They are use to construct carbohydrates, lipids and proteins. HYDROLYSIS • Hydrolysis is a reaction in which water is used as a reactant to split a larger molecule into smaller subunits. • Hydrolysis is the exact opposite of dehydration synthesis. • ”Dehydration Makes!…Hydrolysis Breaks!” • Digestion of many materials depends greatly upon hydrolysis. NEUTRALIZATION • A neutralization reaction occurs between an acid and a base. • These opposing chemicals nullify each others properties and form water and a salt. ACID + BASE WATER + SALT • Your body has a number of areas that must maintain a specific pH level if function is to be maintained so your body has a series of buffer systems in place that use acids and/or bases to do this. REDOX • REDOX reactions involve the movement of electrons from one substance to another. It is also known as am electron transfer reaction. • Oxidation involves the loss of electrons by a substance. • Reduction involves the gain of electrons by a substance. • Each reaction will have a reducing agent and an oxidizing agent…the reducing agent gives up the electrons and the oxidizing agent receives the electrons…sounds backwards but it ain’t! • We see REDOX reactions quite commonly when there is energy transfer within the cell. REDOX FIN