Supplementary material to - Springer Static Content Server
advertisement

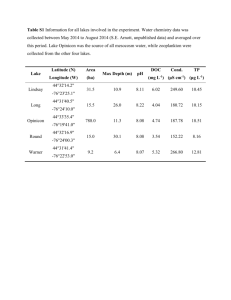
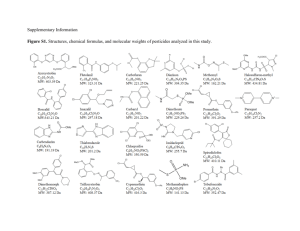
Supplementary material to ‘Understanding the Simultaneous Biodegradation of Thiocyanate and Salicylic Acid by Paracoccus thiocyanatus and Pseudomonas putida ’ Combarros, R.G., Collado, S., Laca, A., Díaz, M* Department of Chemical Engineering and Environmental Technology, University of Oviedo, C/Julián Clavería s/n, E-33071, Oviedo, Spain (10 Pages, 7 Figures, 1 Table) Table of contents 1. Summary of biodegradation conditions and results of interaction effects between P.putida-P. thiocyanatus - SA- SCN- system. (Table S1). 2. Evolution of salicylic acid or thiocyanate concentrations under different culture conditions. (Figure S2). 3. Evolution of salicylic acid in presence of a pure culture of P. putida and growth of P. thiocyanatus. (Figure S3). 4. Evolution of growth curves during the simultaneous biodegradation of both contaminants by a co-culture and by pure culture of P. putida or P. thiocyanatus. (Figure S4). 5. Specific growth rate of suspended biomass in a thiocyanate and salicylic acid solution using a co-culture. (Figure S5). 6. Dot plots representing cFDA fluorescence versus PI fluorescence of co-culture of Paracoccus thiocyanatus and Pseudomonas putida cells during shake-flask fermentation. (Figure S6). 7. Dot plots representing side scatter light (SSC) versus forward scatter light (FSC) signals of co-culture cells during shake-flask simultaneous biodegradation. (Figure S7). 8. Evolution of salicylic acid or thiocyanate concentrations and growth curves during the simultaneous biodegradation of both contaminants by a co-culture of Paracoccus thiocyanatus and Pseudomonas putida. (Figure S8). *Corresponding author’s e-mail: mariodiaz@uniovi.es Phone: +34 985 10 34 39; Fax: +34 985 10 34 34 S 1: Summary of biodegradation conditions and results of interaction effects between P.putida-P. thiocyanatus - SA- SCN- system. Row Mineral medium Culture conditions * Bacteria Substrate 1 PpMM Pp conditions P. putida 500 mg SA L-1 -1 ti (h) Specific degradation rate (mg substrate (h mg cells)-1) μ (h-1) 0 2.5 0.2459 Conversion (reaction time) (%- h) 100% in 22 Volumetric degradation rate (mg substrate (Lh)-1) 31 2 PpMM Pp conditions P. putida 500 mg SA L 500 mg SCN- L-1 0 ----- 0.92 0 0.0007 73% in 140 0% in 140 6.25 0 3 PpMM Pp conditions P. putida 500 mg SCN- L-1 0 0 0 0% in 140 0 4 PtMM Pt conditions P. thiocyanatus 500 mg SCN- L-1 20 0.32 0.0314 100% in 48 20.7 - -1 5 PtMM Pt conditions P. thiocyanatus 500 mg SCN L 500 mg SA L-1 48 ----- 0.35 0 0.0093 100% in 144 0% in 144 6.7 0 6 PtMM Pt conditions P. thiocyanatus 500 mg SA L-1 0 0 0 0% in 144 0 -1 7 PpMM CC conditions P. putida 500 mg SA L 500 mg SCN- L-1 0 ----- 0.99 0 0.2338 96% in 34 0% in 144 13.6 0 8 CCMM CC conditions P. putida 500 mg SA L-1 500 mg SCN- L-1 0 ----- 0.86 0 0.3137 100% in 11 0% in 144 46.1 0 9 PtMM CC conditions P. thiocyanatus 500 mg SCN- L-1 500 mg SA L-1 60 ----- 0.53 0 0.0097 100% in 135 0% in 144 6.67 0 10 CCMM CC conditions P. thiocyanatus 500 mg SCN- L-1 500 mg SA L-1 30 ----- 0.36 0 0.0186 100% in 51 0% in 144 16.7 0 11 CCMM CC conditions P. putida 500 mg SA L-1 12 CCMM CC conditions 13 CCMM CC conditions 14 CCMM CC conditions 15 CCMM CC conditions P. thiocyanatus P. thiocyanatus P. putida P. thiocyanatus P. putida P. thiocyanatus P. putida 0 0.89 0.23 100% in 12 39.3 -1 11 0.68 0.052 100% in 25 32.2 500 mg SCN- L-1 17 0.58 0.027 100% in 40 36.9 500 mg SA L-1 0 0.64 0.091 100% in 14 40 500 mg SCN- L-1 500 mg SA L-1 12 0 0.53 0.39 0.0186 0.3137 100% in 29 100% in 12 35.2 42.1 - 500 mg SCN L * Pp conditions: 200 rpm, 30ºC and 100 mL of mineral medium in 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks; Pt conditions: 250 rpm, 28ºC and 100 mL of mineral medium in 500 mL Erlenmeyer flaks; CC conditions: 30°C, 250 rpm and 100 mL of mineral médium in 500 mL Erlenmeyer flasks 600 600 (a) 400 300 200 100 (b) 500 SCN- (mg/L) SA (mg/L) 500 400 300 200 100 0 0 0 5 10 15 Time (h) 20 0 10 20 30 Time (h) 40 50 S 2: Evolution of salicylic acid or thiocyanate concentrations under different culture conditions. a) Evolution of SA concentration by P. putida (), by P. putida in presence of P. thiocyanatus (■), by P. putida in presence of SCN- () and by P. putida in presence of P. thiocyanatus and SCN- (). b) Evolution of SCN- concentration by P. thiocyanatus (), by P. thiocyanatus in presence of P. putida (■), by P. thiocyanatus in presence of SA () and by P. thiocyanatus in presence of P. putida and SA (). In all cases: CCMM, initial SCN- or SA concentration: 500 mg L-1, 250 rpm, 30 ºC, 100mL in 500 mL Erlenmeyer flasks. 600 4.5E+08 (b) (a) 500 CFU/mL SA (mg/L) 3.5E+08 400 300 200 2.5E+08 1.5E+08 100 5.0E+07 0 0 25 Time (h) 50 75 0 10 20 Time (h) 30 S 3: (a) Evolution of salicylic acid in presence of a pure culture of P. putida. Arrows denote the times at which the bacteria was removed: 4.5 h (), 9.8 h (■) and 22 h (). These media were subsequently inoculated with P thiocyanatus, following its bacterial growth as cfu/mL (b). In all cases: CCMM, initial SA concentration: 500 mg L-1, 250 rpm, 30 ºC, 100mL in 500 mL Erlenmeyer flasks. The arrows indicate the time when P. putida were removed from the medium and P. thiocyanatus were inoculated in that medium. 0.12 C (g/L) 0.1 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.02 0 0 10 20 30 40 Time (h) 50 60 70 S 4: Evolution of growth curves during the simultaneous biodegradation of both contaminants by a co-culture of Paracoccus thiocyanatus and Pseudomonas putida (■) and by pure culture of P. putida () or P. thiocyanatus (). In all cases: CCMM, 30ºC, 250 rpm, inoculum size of 1·107 cfumL-1 of both (a) 0.02 0.01 (b) 0.03 μSCN- (h-1) μSA(h-1) 0.03 0.02 0.01 0 0 0 1000 2000 3000 SA0 (mg L-1) 4000 0 1000 2000 3000 SCN0 (mg L-1) 4000 S 5: Specific growth rate of suspended biomass in a thiocyanate and salicylic acid solution using a co-culture of P. putida and P. thiocyanatus (250-4000 mg L-1). a) P. putida specific growth rate b) P. thiocyanatus ( Experimental data, …… substrate and toxic inhibition model, - - - Teisser model). In all cases: 30ºC, 250 rpm, and inoculum size of 1·107 cfu mL-1 of each bacteria . cFDA fluorescence A D B C E F PI fluorescence S 6: Dot plots representing cFDA fluorescence versus PI fluorescence of co-culture of Paracoccus thiocyanatus and Pseudomonas putida cells during shake-flask fermentation. A, B and C plots correspond to an initial SA and SCN- concentration of 250 mg L-1 at 0, 24 and 31 hours respectively. D, E and F plots correspond to an initial SA and SCN- concentration of 2000 mg L-1 at 0, 48 and 144 hours respectively. 0h 48 h 72 h 168 h 192 h S 7: Dot plots representing side scatter light (SSC) versus forward scatter light (FSC) signals of coculture cells during shake-flask simultaneous biodegradation to an initial SA and SCN- concentration of 3000 mg L-1 at 0, 48, 72, 168 and 192 hours respectively 0.08 500 0.06 400 300 0.04 200 C co-culture (g/L) SA or SCN- (mg/L) 600 0.02 100 0 0 0 10 20 30 Time (h) 40 S 8: Evolution of salicylic acid () or thiocyanate (■) concentrations and growth curves () during the simultaneous biodegradation of both contaminants by a co-culture of Paracoccus thiocyanatus and Pseudomonas putida. Previously to inoculation, the co-culture was acclimated with 4000 mg L-1 of both SCN- and SA during 120 hours. The culture conditions: CCMM, 30ºC, 250 rpm, initial SCNand SA concentrations of 500 mg L-1, and inoculum size of (1·107 cfu mL-1 of both bacteria).