LangArts.Lang.3
advertisement

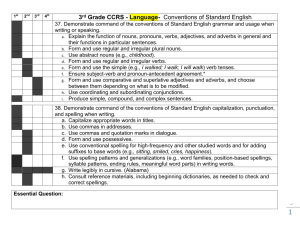
Content Area Standard Language Arts 3.3 Grade 3 Strand L. Language Content Statement CPI# Cumulative Progress Indicator (CPI) ACSSSD Objectives Conventions of Standard English 3.L.3.1 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. a. Explain the function of nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs in general and their functions in particular sentences. b. Form and use regular and irregular plural nouns. c. Use abstract nouns (e.g., childhood). d. Form and use regular and irregular verbs. e. Form and use the simple (e.g., I walked; I walk; I will walk) verb tenses. f. Ensure subject-verb and pronounantecedent agreement.* 1. Identify nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs in sentences. 2. Combine nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs in a grammatically correct order when writing or speaking. 1. Identify a noun. 2. Classify nouns as singular or plural. 3. Form plural nouns when writing or speaking. 1. Identify nouns. 2. Recognize that abstract nouns are words associated with feelings (e.g., childhood). 1. Identify verbs. 2. Form regular and irregular verbs when writing or speaking. 1. Identify verbs. 2. Classify sentences as past, present, or future based on verb tense (e.g., I walked; I walk; I will walk). 3. Form and use appropriate verb tense when writing or speaking. 1. Identify words as subject, verb, pronoun. 2. Form sentences that include subject/verb agreement and pronouns when writing or speaking. g. h. i. 3.L.3.2 Form and use comparative and superlative adjectives and adverbs, and choose between them depending on what is to be modified. 1. Identify adjectives. 2. Identify adverbs. 3. Form adverbs when writing and speaking (e.g., add -ly to adjective: quiet, quietly). Use coordinating and subordinating 1. Classify coordinating (e.g., and, but, conjunctions. or, yet, so…) and subordinating (e.g., after, if, though, because…) conjunctions. 2. Use coordinating and subordinating conjunctions when writing or speaking. Produce simple, compound, and complex 1. Combine nouns, pronouns, verbs, sentences. adjectives, and adverbs in a grammatically correct order when writing or speaking to produce simple, compound, and complex sentences. Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing. a. Capitalize appropriate words in titles. b. Use commas in addresses. c. Use commas and quotation marks in dialogue. d. Form and use possessives. 1. Locate capital letters in a name or sentence. 2. Capitalize proper nouns when writing. 1. Identify commas. 2. Locate commas in addresses. 3. Use commas in approximate place. 1. Identify commas. 2. Identify quotation marks. 3. Identify dialogue in writing. 4. Approximate the use of commas and quotation marks when writing. 1. Identify nouns. 2. Form possessive with nouns to show belonging to, or ownership by adding ‘s. e. f. g. Use conventional spelling for highfrequency and other studied words and for adding suffixes to base words (e.g., sitting, smiled, cries, happiness). Use spelling patterns and generalizations (e.g., word families, position-based spellings, syllable patterns, ending rules, meaningful word parts) in writing words. Consult reference materials, including beginning dictionaries, as needed to check and correct spellings. 1. Spell familiar words with letter-sound matches. 1. Demonstrate ability to spell using conventional spelling by segmenting and sounding-out strategies. 2. Use specific spelling strategies when writing (e.g., word wall, partner sharing, dictionary). 1. Identify guide words and their purpose. 2. Find specific words in a dictionary using the guide words. 3. Use a dictionary to look up word spellings, or to define unfamiliar words. Knowledge of Language 3.L.3.3 Use knowledge of language and its conventions when writing, speaking, reading, or listening. a. Choose words and phrases for effect. b. Recognize and observe differences between the conventions of spoken and written standard English. 1. Use language to communicate an idea when writing, speaking, reading or listening. 2. Choose appropriate words and phrases to convey an idea when writing or speaking. 1. Understand formal and informal uses of English (e.g., They are going to the storeformal; They’re going to the storeinformal). Vocabulary Acquisition and Use 3.L.3.4 Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiple-meaning word and phrases based on grade 3 reading and content, choosing flexibly from a range of strategies. a. b. c. d. 3.L.3.5 a. b. c. 3.L.3.6 Use sentence-level context as a clue to the meaning of a word or phrase. 1. Using pictures or objects, match a word to its definition. 2. Identify the relevant context clues for the meaning of a word. 3. Given a word in a sentence or passage, identify the correct meaning for the word. Determine the meaning of the new word 1. Identify root words. formed when a known affix is added to a 2. Identify affixes. known word (e.g., agreeable/disagreeable, 3. Identify the meanings of affixes (e.g., comfortable/uncomfortable, care/careless, dis-,un-,pre-,-less). heat/preheat). 4. Identify the meaning of words when a known affix is added (e.g., care/careless). Use a known root word as a clue to the 1. Identify root words. meaning of an unknown word with the 2. Use acquired knowledge to determine same root the meaning of an unknown word containing a familiar root word. Use glossaries or beginning dictionaries, 1. Use glossaries to determine the both print and digital, to determine or meaning of unknown words. clarify the precise meaning of key words and phrases. Demonstrate understanding of figurative language, word relationships and nuances in word meanings. Distinguish the literal and nonliteral meanings of words and phrases in context (e.g., take steps). Identify real-life connections between words and their use (e.g., describe people who are friendly or helpful). Distinguish shades of meaning among related words that describe states of mind or degrees of certainty (e.g., knew, believed, suspected, heard, wondered). Acquire and use accurately gradeappropriate conversational, general academic, and domain-specific words and 1. Identify the meaning of simple figurative language (e.g., similes and metaphors). 1. Use common known words to make real-life connections. 1. Identify figurative language. 1. Use words acquired through conversation and domain specific words when speaking or writing. phrases, including those that signal spatial and temporal relationships (e.g., After dinner that night we went looking for them).