Important Information
advertisement

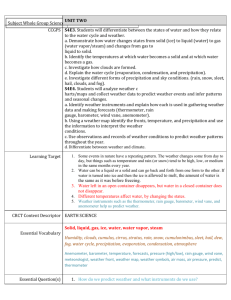
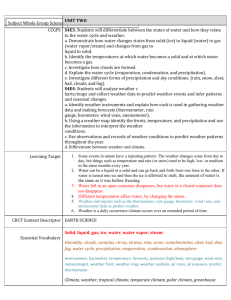
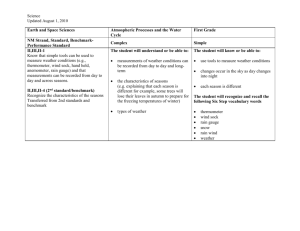
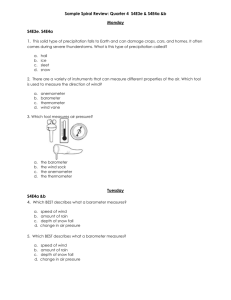
o I can explain that air surrounds us, takes up space, and moves around us as wind. Important Vocabulary Air Oxygen carbon dioxide water vapor thermometer Important Information Air is made up of matter Air is a mixture of gases Life on earth depends on gases in the air Air temperature is measured with a thermometer Textbook pages E10-13 and E38-39 o I can explain that air around us can be measured using barometric pressure. Important Vocabulary Air pressure barometer Important Information Pressing down of air on the earth is air pressure The higher above you are in the atmosphere, the less air is above you Air temperature affects air pressure Rising air pressure usually means drier air and fair weather Falling air pressure usually means moister air is coming – wet weather Barometer measures air pressure o I can identify that water exists in the air as vapor in the form of clouds and fog. o I can describe the type of weather brought upon by each cloud type (cumulus, cumulonimbus, cirrus, and stratus clouds). Important Vocabulary Clouds Fog water vapor condensation Important Information Cirrus clouds – Wispy and see-through – Bring fair weather and a change in weather Cumulus clouds – puffy, like cotton balls – Bring fair, sunny weather Stratus clouds – gray layered – Bring drizzle or rain, if near ground called fog Cumulonimbus – large, mushroom-like – bring thunderstorms, rain, snow and hail When water evaporates into water vapor, it condenses into a cloud Textbook pages E54-57 o I can identify the forms of precipitation (rain, snow, and hail). o I can describe how water changes from one state to another (freezing, melting, condensation, and evaporation). Important Vocabulary Rain Snow Hail rain gauge evaporation condensation precipitation water cycle Important Information Water changing from a liquid to a gas is evaporation Water vapor changing back from a gas to a liquid is condensation Water or snow falling from clouds is precipitation Heat from the sun warms water on the earth, which changes into water vapor through evaporation. When water vapor cools it condenses into clouds. When clouds become too heavy, precipitation falls back to earth. This is the water cycle. Rain is measured with a rain gauge Textbook pages E46-48 o I can describe the weather using the following information: temperature, wind direction, wind speed, precipitation, and barometric pressure o I can describe weather changes over a period of time. o I can record and explain weather data from an investigation. Important Information These I can statements connect to the daily weather data students recorded in the classroom. o I can record local weather information on a calendar or map using weather symbols. o I can recognize that weather generally moves from west to east across the United States. o I can analyze weather data to make an inference about what will most likely occur next. Important Vocabulary Warm front wind Cold front weather map Important Information Meteorologists make and study weather maps Meteorologists forecast the weather by looking at weather instruments and weather data Winds mover over large parts of the earth’s surface – moving weather systems Weather usually moves across the country from west to east. To get a clue about your weather tomorrow, look at the weather to the west of where you live! Meteorologists use weather symbols on a map to show different types of weather Textbook pages E58-63 o I can describe the proper use and placement of scientific tools. Important Vocabulary Thermometer Barometer Wind Vane Anemometer Rain Gauge Beaufort Scale Important Information Thermometer measures air temperature. For accurate measure a thermometer should be placed in the shade because in direct sunlight the thermometer heats up and makes the reading too high. Barometer measures air pressure. For accurate measurement a barometer can be place inside or outside. Wind vane records wind direction For accurate measurement a wind vane should be placed up high or on the roof of a house/building Anemometer measures wind speed For accurate measurement an anemometer should be placed up high with a wind vane. Rain gauge measures the amount of rain fall For accurate measurement a rain gauge should be placed out in the open to collect the amount of rain falling. Beaufort scale is a scale that measures wind speed using 12 different categories. You can use the Beaufort scale when you don’t have an anemometer.