Supplementary figure legends - Springer Static Content Server
advertisement

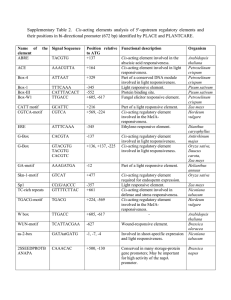
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Fig. S1. Screening of the CaCcs promoter from Capsicum genomic library. A. Hybridization signal with 32P-CaCcs full-length cDNA on 1st plaque screening. B. Hybridization signal with 32P-CaCcs full-length cDNA on 2nd plaque screening. C. Three restriction enzyme digest patterns of a putative CaCcs genomic clone. D. Southern hybridization of a putative CaCcs genomic clone with a 32P-0.2 kb fragment of N-terminal region of CaCcs cDNA. Lane 1, EcoRI; Lane 2, HincII; Lane 3, HpaI. The resulting EcoRIdigested 2.5-kb fragment containing 2.3 kb of 5′ proximal promoter and 0.2 kb of the Nterminal coding region of the CaCcs gene was subcloned into pSK as pSK-CaCcs-G-2.5kb. Supplementary Fig. S2. DNA sequences of the 5’-proximal promoter region for CaCcs and schematic illustration of deletion vector constructs for driving Gus gene expression. A. DNA sequence of a 2,555-bp EcoRI fragment containing 2,309 bp of the 5' promoter (upper case) and 246 bp of N-terminal coding region (lower case) of CaCcs. Restriction enzyme sites used for 5'-deletion series of CaCcs promoter are indicated in blue above the nucleotide sequences. Nucleotides shown in red indicate the transcriptional (+1) and translational (methionine) start sites. B. Scheme for subcloning the CaCcs promoter (CaCcsP6) and its 5′deletion fragments (CaCcs-P5, P4, P3, P2, P1) into pBluescript (pKS) and fusion with a βglucuronidase gene (Gus) and Nos terminator (Tnos). C. Size confirmation of the full-length CaCcs promoter and its deletion fragments by restriction enzyme digestion. Common 2.2-kb fragments indicated in all six lanes are Gus:Tnos fragments. Supplementary data Table S1. Scan results of predicted cis-acting motifs in the region of –367 to +30 of the Capsicum Ccs promoter. No. Motif name Signal sequence Number of signal Species origin Promoter origin Binding protein Spatial specificity Stress-regulator chloroplast blue, white or UV-A light 1 -10PE TATTCT 1 Barley psbD 2 ARR1 NGATT 4 Arabidopsis NSHB 3 CAAT box1 CAAT 7 Pea legA 4 CACT motif YACT 7 Flaveria trinervia ppcA1 5 CArG motif CWWWWWWWWG 6 Arabidopsis 6 CCAAT box1 CCAAT 2 Soybean 7 GATA box GATA 2 CaMV, petunia, Arabidopsis , rice CaMV 35S, petunia Cab22 8 GT-1 consensus GRWAAW 2 Pea, oat, rice, tobacco, Arabidopsis , spinach, bean many rbcS et al. 9 GT-1 GAAAAA 1 Soybean SCaM-4 10 GT-1 motif KWGTGRWAAWRW 1 Pea rbcS-3A 11 GTGA motif GTGA 5 Tobacco g10 12 INR element YTCANTYY 3 Tobacco psaDb 13 MYB1 element GTTAGTT 1 Arabidopsis , tomato Pti4(ERF) 14 MYB2 TAACTG 1 Arabidopsis 15 MYB2 consensus YAACKG 1 Arabidopsis 16 MYB core CNGTTR 1 Arabidopsis , petunia 17 NODCON2/ OSE2ROOTNODULE CTCTT 2 Soybean, Vicia faba Ibc3, N23, VfLb29 18 POLLEN1 AGAAA 6 Tomato lat52, LeMAN5 19 RAV1A CAACA 1 Arabidopsis 20 ROOT motif ATATT 2 Agrobacterium rolD 21 SEF4 motif RTTTTTR 3 Soybean 7S globulin SEF4 embryo (seed) 22 TAAAG motif TAAAG 1 Potato KST1 StDof1 guard cell 23 T box ACTTTG 1 Arabidopsis GAPB Supplementary Fig. S1 ARR1 cytokinin-regulated seed mesophyll AGL15 heat shock protein flower flowering ASF-2 light light pathogen and salt GT-1 light pollen light defense ATMYB2 water stress (dehydration) rd22 water stress (dehydration) ATMYB1, ATMYB2 petal epidermiss water stress (dehydration) root nodule anther, pollen RAV1 rosette leaves, roots root light