Essential Biology 4.1 File
advertisement

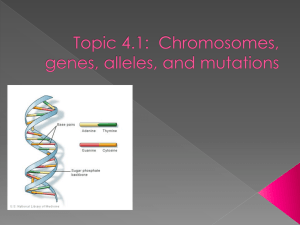
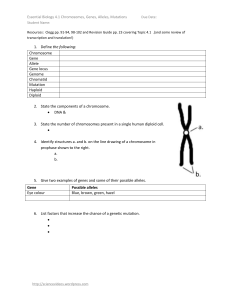
Essential Biology 04.1: Genetics (HL & SL) 4.1 Chromosomes, Genes, Alleles and Mutations 1. DNA structure review: draw and label a section of a DNA molecule. Include sugar-phosphate backbone, bases, double helix shape, complementary base pairing. Label the bond between nucleotides in a strand of DNA and the bond between base pairs. 2. What is a chromosome? 3. What makes up the structure of a chromosome? DNA & ____________ 4. How many chromosomes are present in a diploid human cell? 5. Distinguish between haploid and diploid. 6. Distinguish between chromosomes and chromatids. 7. Define gene. 8. Define genome. 9. What is a gene locus? 10. Define allele. 11. Give two examples of genes and some of their possible alleles. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 04.1: Genetics (HL & SL) 12. Define mutation. 13. What factors can increase the chance of a genetic mutation? 14. Define evolution. 15. How can mutations lead to evolution by natural selection? 16. 17. What is the difference between the two DNA strands above in terms of: a. DNA base sequence? b. Amino acid sequence in the resulting polypeptide? 18. What level of protein structure is affected by a change in amino acid sequence of a polypeptide? Why? Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 04.1: Genetics (HL & SL) 19. Compare the following types of base-substitution mutation. Silent mutation Number of bases substituted Mis-sense mutation Nonsense mutation 1 Stop codon produced early – polypeptide shortened Effect on polypeptide Example illness Sickle cell disease 20. Describe the effects of sickle cell disease on sufferers in terms of: a. Hemoglobin production b. Symptoms and mortality 21. In which parts of the world could a single sickle cell (Hbs) allele be beneficial? Why? 22. How is the spread of the sickle cell gene an example of natural selection in action? 23. How could this be an example of a correlation which has a strong element of causality? Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 04.1: Genetics (HL & SL) 24. Using the NCBI gene database at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=gene , find the gene locus of the HBB (hemoglobin) gene. 25. Human Nutrition and Health link: Using the same database, look for the gene related to the illness PKU (phenylketonuria) a. What is the gene name? b. What is the gene locus of this gene? c. Which enzyme is encoded by this gene? d. What is the consequence of a base-substitution (mis-sense) mutation of this gene? e. How is PKU diagnosed and why must it be diagnosed as early as possible? 26. Stem cells link: Read this article: http://notexactlyrocketscience.wordpress.com/2007/12/08/sickle-cell-micecured-by-stem-cells-reprogrammed-from-their-own-tails/ a. What is an IPS stem cell? b. Outline the use of this technology in treating the mice with sickle cell disease. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com