Grade 5: Part of the Tested Curriculum as Identified by TEA Source
advertisement

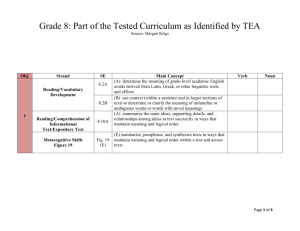
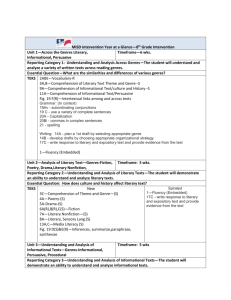
Grade 5: Part of the Tested Curriculum as Identified by TEA Source: Margret Kilgo Obj. Strand SE 5.2A Reading/Vocabulary Development 5.2B 1 Reading /Comprehension of Literary Text/Fiction Reading/Comprehension of Literary Text/Sensory Language Reading/Comprehension of Informational Text/Expository Text Main Concept (A) determine the meaning of grade-level academic English words derived from Latin, Greek, or other linguistic roots and affixes 5.8A 5.11A (A) summarize the main ideas and supporting details in a text in ways that maintain meaning and logical order Metacognitive Skills Figure 19 Fig. 19 (E) Obj. Strand SE 2 Reading/Comprehension of Literary Text/Fiction 5.6A 5.6B Noun meaning words, roots, affixes Verb Noun (B) use context (e.g., in-sentence restatement) to determine or clarify the meaning of unfamiliar or multiple meaning words (A) describe incidents that advance the story or novel, explaining how each incident gives rise to or foreshadows future events (A) evaluate the impact of sensory details, imagery, and figurative language in literary text 5.6A Verb determine (E) summarize and paraphrase texts in ways that maintain meaning and logical order within a text and across texts Main Concept (A) describe incidents that advance the story or novel, explaining how each incident gives rise to or foreshadows future events (B) explain the roles and functions of characters in various plots, including their relationships and conflicts Page 1 of 3 Obj. Strand Reading/Comprehension of Literary Text/Theme and Genre Reading/Comprehension of Literary Text/Fiction Reading/Comprehension of Informational Text/Culture and History 3 Reading/Comprehension of Informational Text/Expository Reading/Comprehension of Informational Text/Persuasive Text Metacognitive Skills Figure 19 SE 5.3A 5.6A Main Concept (A) compare and contrast the themes or moral lessons of several works of fiction from various cultures Verb Noun (A) describe incidents that advance the story or novel, explaining how each incident gives rise to or foreshadows future events (A) draw conclusions from the information presented by an 5.10A author and evaluate how well the author's purpose was achieved (C) analyze how the organizational pattern of a text (e.g., cause-and-effect, compare-and-contrast, sequential order, 5.11C logical order, classification schemes) influences the relationships among the ideas (E) synthesize and make logical connections between ideas 5.11E within a text and across two or three texts representing similar or different genres (A) identify the author's viewpoint or position and explain 5.12A the basic relationships among ideas (e.g., parallelism, comparison, causality) in the argument Fig. 19 (D) make inferences about text and use textual evidence to (D) support understanding (E) summarize and paraphrase texts in ways that maintain Fig. 19 meaning and logical order within a text and across texts (E) (F) make connections (e.g., thematic links, author analysis) Fig. 19 between and across multiple texts of various genres and (F) provide textual evidence Page 2 of 3 Obj. Strand SE Reading/Comprehension of Literary Text/Fiction 5.6 5.11B Reading/Comprehension of Informational Text/Expository Text 4 5.11C 5.11E Reading/Comprehension of 4.12A Informational Text/Persuasive Text Fig. 19 (D) Metacognitve Skills Figure 19 Fig. 19 (F) Main Concept Students understand, make inferences and draw conclusions about the structure and elements of fiction and provide evidence from text to support their understanding Verb Noun (B) determine the facts in text and verify them through established methods (C) analyze how the organizational pattern of a text (e.g., cause-and-effect, compare-and-contrast, sequential order, logical order, classification schemes) influences the relationships among the ideas (E) synthesize and make logical connections between ideas within a text and across two or three texts representing similar or different genres (A) explain how an author uses language to present information to influence what the reader thinks or does (D) make inferences about text and use textual evidence to support understanding (F) make connections (e.g., thematic links, author analysis) between and across multiple texts of various genres and provide textual evidence Page 3 of 3