Mathematical Competenc Science and Technology (edited)
advertisement

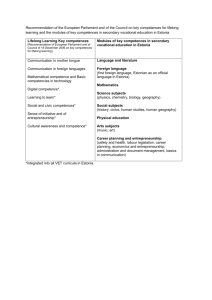
Mathematical competence and basic competences in Science and Technology 1. Theoretical Part There are lots of real uses of Mathematical competence and basic competences in science and technology in our life. Today almost all businesses are based on those skills. From early age children are familiar with numbers and as they get older they realize that almost everything in their lives is connected to Mathematical competence and basic competences in science and technology. When someone goes shopping, calculations are needed.Even people who suffer from math-related anxieties or phobias cannot escape from math everyday presence in their lives. Math is everywhere,it exists from home, to school, to work and places in-between. Whether using measurements in a recipe, or deciding if half a tank of gas will make the destination, we all use math. It is a good, therefore, for reluctant math learners to use real world examples to ignite a spark of practical interest. Math is a part of our lives, wherever we go, whatever we do, we are using math daily without even realizing it. Some people aren't even out of bed before encountering Mathematical competence in our life. The use of setting an alarm and hitting snooze, assumes this skill. Baking and cooking requires some mathematical skill as well. Every ingredient has to be measured so as to get the exact amount we need. Even gardening requires skills in math in order to count the holes and the plants that have to be planted. If we think deeper we will realize that almost everything is based on Mathematical competence in our life: the house we live in, the decoration that we chose for our house, the distance and the time that is needed for our work, our children’s programme in school, bank transactions, travelling. Numbers and digits surround our lives every minute. Competence in science refers to the ability and willingness to use the body of knowledge and methodology employed to explain the natural world, in order to identify questions and to draw evidence-based conclusions. Competence in science and technology involves an understanding of the changes caused by human activity and responsibility as an individual citizen. Also many jobs are related by their activities to science, environment protection, social issues etc, where ideas developed by science are used into practice and researches and scientific findings are integrated into those jobs. 1.1 Analysing Structure & Objectives of Key Skills Mathematical competence is used in differentfacets in our lives. In sports, athletes and fans have to record the time, to use statistics so as to calculate win-loss ratios. We need to know numbers and how they work, and with today's technology we can do almost everything by our mobile phone, from talking and faxing to surfing on the Internet. The use of math is also required in arts. Whether someone is a sculptor, a painter, a dancer or even just doing a collage for fun, math is necessary to measure, count and apply basic math to it. Summarizing we conclude that math is a skill that is so essential to people and the absence of math- thinking means the presence of many obstacles in people daily lives. The competence of knowledge of science and technology involves interaction with the natural environment and the natural world, and the ability to understand facts, predict the consequences and the impact that they have on human health and environmental sustainability. It is the ability of people to interact with the physical world, both in its natural aspects and those generated by human activity, so as to allow the understanding of events, predict consequences and actions that lead to improvement and the maintenance of conditions of life, of other people and other living beings. In short, it is the competence that one has so that he can incorporate skills to deal appropriately with autonomy and personal initiative in various spheres of life (health, productive activities, consumption, science, technological processes, etc.) and to interpret the world, applying concepts and principles that allow the analysis of phenomena from different fields of scientific knowledge. By obtaining those skills, one will have the opportunity to take an active and responsible role in his daily life, in community and workplaces. 1.2 Strategy and procedure to acquire the competence There are several ways so as to acquire skills on Mathematical competence and basic competences in science and technology. We learn to count in early age using fingers, fact that in some occasions enables people lacking in math skills. People lacking on math skills and basic competences in science and technology could ask for assistance and we can use all available resources, i. e notes from previous lessons, talk with friends who have knowledge and are eager to help so as to find a solution to a problem or that already know the process to solve it. Thus at school or during lessons one can so as to improve his math skills : Ask for explanations for the implicit rules so as to make the complex definitions understandable. Interrupt the course at regular intervals to make sure that he gets the meaning of what is being discussed. Discuss the results of calculations to help understand and develop learning skills. Take advantage of the time that teachers dedicate to students at school for the personal improvement. Use pencil and paper, when studying. When someone writes down notes or reading text from a book, it is a good idea to use a pencil and a clean sheet of paper in which he can write his own ideas and evaluations. This will help to get mathematical thinking. Use a calculator to check the results calculated. Generally one should outline the objective that wishes to achieve whenever he starts dealing with a new area of scientific interest, before analyzing the process step by step. 1.3 Benefits Benefits of having mathematical skill and basic competences in science and technology are essential in the hectic pace of everyday life. We can separate the benefits in the following different facets: Science Mathematical competence and basic competences in science and technology are intimately connected to science, particularly in fields such as chemistry, astronomy and physics. Students who can not master basic arithmetic skills will struggle to read scientific charts and graphs. More complex math, such as geometry, algebra and calculus, can help students solve chemistry problems, understand the movements of the planets and analyze scientific studies. Math is also important in practical sciences, such as engineering and computer science. Thus, students may have to solve equations when writing programs. Social studies Social studies classes, such as history, often require students to review charts and graphs that provide historical data or information on ethnic groups. In geography classes, students might need to understandhow the elevation of an area affects its population or chart the extent to which different populations have different average life spans. Knowledge of basic mathematical terms and formulas in science and technology make statistical information accessible. Arts People interested in pursuing careers in theater, music, dance or art can benefit from basic mathematical knowledge. Musical rhythm often follows complex mathematical series, and math can help people learn the basic rhythms of dances used in ballet and theater performances. Art thrives on geometry, and people who understand basic geometric formulas can craft impressive art pieces. Poetry Mastering basic arithmetic can enable people to better understand poetry. The meter of poetry, the number of words to include in a line and the effect that certain rhythms have on the reader are all products of mathematical calculations. At a more mundane level, math can help people’s plan reading assignments in literature classes by discerning their average reading time and estimating how long it will take them to read a particular work. At home Doubling up on recipes is an easy way to “earn” time from weekly cooking schedule. A slow cooker has to know how to use math in order to “handle” time. So it is necessary to schedule time in the morning and start the meal. Thus all shopping needs the existence of basic math skills. It's always best to stick with your grocery list when shopping and avoid temptation to purchase impulse items. However, when it comes to discount items, it's not always wise to pass up the purchase. If a particular ingredient someone frequently uses is on sale, then he should grab the chance. Academic subjects Mathematical competence and basic competences in science and technology are also relevant to a wide variety of academic subjects, which means that a student who has no competence in this skill ends up struggling in other subjects. Bank transactions Banks, payments, bills and so many other transactions assume the existence of Mathematical competence and basic competences in science and technology. Work The most important benefit by the existence of Mathematical competence and basic competences in science and technology is mostly obvious at work. No business transaction can take place without those skills. 2. Examples 2.1 Analysing structure and objectives of Key Skill George is a young Greek who has just finished his studies at economics. He also has a master degree in information systems and he attended the course in a foreign country. He participates in the final phase of the selection process that conducts a large multinational company so as to employtwoof them in the financial section. He has previously worked during his practice in different sectors such as the accounting, financial planning, marketing and sales. During his practice, he gained practical knowledge on financial management, the marketing mix that is applied by business and the production technology (although it is not relevant to his degree). Literature http://europa.eu/legislation_summaries/education_training_youth/lifelong_learnin g/c11090_en.htm https://www.youthpass.eu/en/youthpass/for/youthinitiatives/learn/information/kcdigital/ http://everydaylife.globalpost.com/mathematics-used-other-subjects-10114.html http://everydaylife.globalpost.com/use-mathematics-everyday-life-14225.html http://www.mathworksheetscenter.com/mathtips/everydaymath.html http://www.usnews.com/opinion/articles/2011/09/27/why-math-and-scienceeducation-means-more-jobs https://student.societyforscience.org/topic/tech-math Recommendation of the European Parliament and of the Council of 18 December 2006 on key competences for lifelong learning. The Key Competences for Lifelong Learning – A European Framework- Official Journal of the European Union on 30 December 2006/L394. Youth in Action mobilising the potential of young Europeans stronger backing for youth projects. Mathematics, Science, and Technology in Secondary Schools: Do Gender and Region Make a Difference?, Qing Li, Canadian Journal of Learning and Technology, Volume 33(1) Winter / hiver 2007. Integration of Technology, Science, and Mathematics in the Middle Grades: A Teacher Preparation Program, ALFINIO FLORES, JONATHAN E. KNAUP, JAMES A. MIDDLETON, AND FREDERICK A. STALEY, Arizona State University. Preparing the 21st century workforce: A new reform in science and technology education, Rodger W. Bybee and Bruce Fuchs.