English 9: Unit One Vocabulary Review Semester Final Academic
advertisement
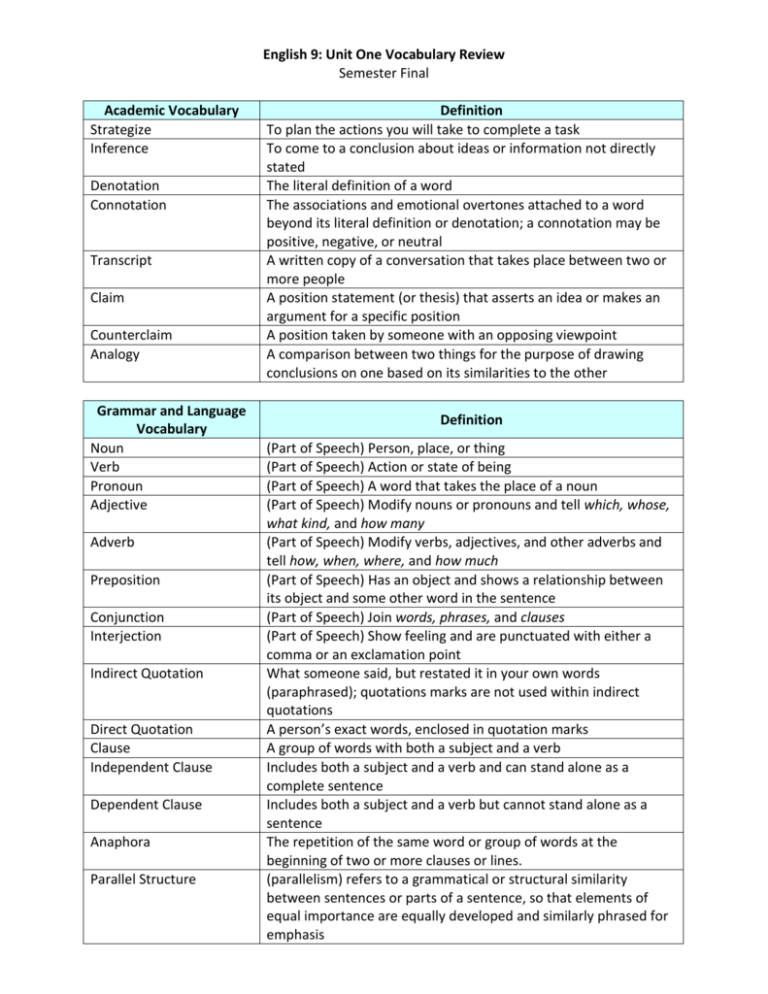
English 9: Unit One Vocabulary Review Semester Final Academic Vocabulary Strategize Inference Denotation Connotation Transcript Claim Counterclaim Analogy Grammar and Language Vocabulary Noun Verb Pronoun Adjective Adverb Preposition Conjunction Interjection Indirect Quotation Direct Quotation Clause Independent Clause Dependent Clause Anaphora Parallel Structure Definition To plan the actions you will take to complete a task To come to a conclusion about ideas or information not directly stated The literal definition of a word The associations and emotional overtones attached to a word beyond its literal definition or denotation; a connotation may be positive, negative, or neutral A written copy of a conversation that takes place between two or more people A position statement (or thesis) that asserts an idea or makes an argument for a specific position A position taken by someone with an opposing viewpoint A comparison between two things for the purpose of drawing conclusions on one based on its similarities to the other Definition (Part of Speech) Person, place, or thing (Part of Speech) Action or state of being (Part of Speech) A word that takes the place of a noun (Part of Speech) Modify nouns or pronouns and tell which, whose, what kind, and how many (Part of Speech) Modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs and tell how, when, where, and how much (Part of Speech) Has an object and shows a relationship between its object and some other word in the sentence (Part of Speech) Join words, phrases, and clauses (Part of Speech) Show feeling and are punctuated with either a comma or an exclamation point What someone said, but restated it in your own words (paraphrased); quotations marks are not used within indirect quotations A person’s exact words, enclosed in quotation marks A group of words with both a subject and a verb Includes both a subject and a verb and can stand alone as a complete sentence Includes both a subject and a verb but cannot stand alone as a sentence The repetition of the same word or group of words at the beginning of two or more clauses or lines. (parallelism) refers to a grammatical or structural similarity between sentences or parts of a sentence, so that elements of equal importance are equally developed and similarly phrased for emphasis English 9: Unit One Vocabulary Review Semester Final Literary Elements Voice Tone Narrative Narrator Diction Juxtaposition Prose Rhetorical Appeals Rhetorical Question Logos Ethos Pathos Syntax Imagery Symbol Metaphor Allusion Foreshadowing Definition The way a writer or speaker uses word and tone to express ideas as well as his/her persona/personality A writer’s or speaker’s attitude toward a subject, character, or audience A story about a series of events that includes character development, plot structure, and theme; can be a work of fiction or non-fiction The person telling the story The writer’s choice of words; a stylistic element that helps convey voice and tone The arrangement of two or more things for the purpose of comparison Ordinary written or spoken language, using sentences and paragraphs, without deliberate or regular meter or rhyme; not poetry or song The use of emotional, ethical, and logical arguments to persuade in writing or speaking A question that is asked for effect or one for which the answer is obvious (logical appeal) a rhetorical appeal that uses factual evidence and logic to appeal to the audience’s sense of reason (ethical appeal) a rhetorical appeal that focuses on ethics, or the character or qualifications of the speaker (emotional appeal) a rhetorical appeal to the reader’s or listener’s sense of emotions The arrangement of words and the order of grammatical elements in a sentence; the way in which words are put together to make meaningful elements such as phrases, clauses, and sentences The verbal expression of sensory experience; descriptive or figurative language used to create word pictures; imagery is created by details that appeal to one or more of the five senses Anything (object, animal, event, person, or place) that represents itself but also stands for something else on a figurative level A comparison between two unlike things in which one thing is spoken of as if it were another, for example, the moon was a crisp white cracker A reference made to a well-known person, event, or place from history, music, art, or another literary work The use of hints or clues in a narrative to suggest future actions











