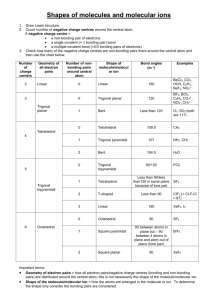
Answers to Practice MC A C C A D E SHORT ANSWERS Answer: (a

Answers to Practice
MC
1) A
2) C
3) C
4) A
5) D
6) E
SHORT ANSWERS
(a)
1.
Answer:
234
94
Pu
2
4
+
230
92
U
Due to a printing error, the student’s answer booklet had the Pu-239 isotope. Therefore, the following is a valid response.
239
94
Pu
2
4
+
235
92
U
(b) This mass defect has been converted into energy.
E =
mc 2
(c) An alpha particle,
or He nuclei, has a 2+ charge and would be attracted to the (-) side of the electric field. A beta particle,
, or electron, has a single negative charge and is attracted to the positive side of the electric field, but since it is much lighter and faster than an alpha it would not be as strongly deflected. Gamma,
, rays are not charged and, therefore, not deflected by the electric field.
(d) The half-life of a radionuclide is independent of its environment. Incineration will neither accelerate its decay nor render it non-radioactive. Half-life is a function of its nucleus, incineration is a function of its electrons.
2. Answer:
In order to have a dipole moment (i.e., to be a polar molecule) a molecule must have polar bonds and must have a molecular geometry which is not symmetrical (i.e., one in which the vector sum of the bond dipoles
0).
In CH
2
F
2
the C-F and C-H bonds are polar and the molecule is not symmetrical; therefore, the molecules is polar and would show a dipole moment.
In CF
4
the C-F bonds are polar, but the molecule is symmetrical; therefore, the molecule is non-polar and would not show a dipole moment.
3. Answer:
B
120_
A B
A
B Example: trigonal planar, BF
3
; trigonal pyramid, NH
3
B B trigonal planar
B trigonal pyramid
For BF
3
, the boron atom is surrounded by three pairs of electrons, the arrangement that will minimize the repulsions is a flat (planar) arrangement with the electron pairs furthest apart at 120º angles. OR
The NH
3
molecule has four pairs of electrons: three bonding pairs and one non-bonding pair. The best arrangement for four electron pairs is a tetrahedral structure (109.5º) with the lone (non-bonding) electron pair at the apex requiring more space than the bonding pairs, compressing the bonding pairs to an angle of 107º. The molecular structure is always based on the positions of the atoms, therefore it is a trigonal pyramid rather than a tetrahedron.
4. Answer:
. . . .
N
. .
. .
. .
. .
P
. .
. .
. .
. .
Describe the sp 3 bonding for NF
3
and the sp 3 d for PF
5
.
Nonexistence of NF
5
because of no low energy d orbital for N.
(a)
:
F
:
F
:
F tetrahedral
: :
:
:
:
F
:
:
Xe
:
:
F
:
:
: :
: :
F
:
: : square planar
:
:
:
F
:
T-shaped
5. Answer:
6. a)
(b)
(c)
(b) CF
4
= 4 bonding pairs around C at corners of regular tetrahedron to minimize repulsion
(maximize bond angles).
XeF
4
= 4 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs give octahedral shape with lone pairs on opposite sides of Xe atom
ClF
3
= 3 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs give trigonal bipyramid with one pairs in equatorial positions 120º apart.
ANSWERS
:
:
:
O
.
N
:
: :
:
O
:
O
:
:
:
N
: :
:
O
:
:
: : : :
:
: NO
2
< NO
2
< NO
2
+
NO
2
- 3 charge centers around N; lone pair of electrons on N
NO
2
- 3 charge centers around N; single electron on N
NO
2
+ - 2 charge centers on N
NO
2
+ is linear, has sp hybridization - or - NO
2
/NO
2
have sp 2 hybridization
7. Answer:
(a)
(ii)
(i) sp 3 .
(iii) pyramidal
:F
:S :
:F:
F:
(iv) smaller than 109.50˚. The lone pair of unbonded electrons occupies more space than the bonded pairs and, therefore, pushed the bonded pairs away and hence, a smaller bond angle than a perfect tetrahedron.
(b)
(ii)
(iii)
(i) sp 3 d 2 square pyrimidal
(iv) S = +4
8) no answer from source
9)