Cell Organelles Chart: Functions & Cell Types
advertisement
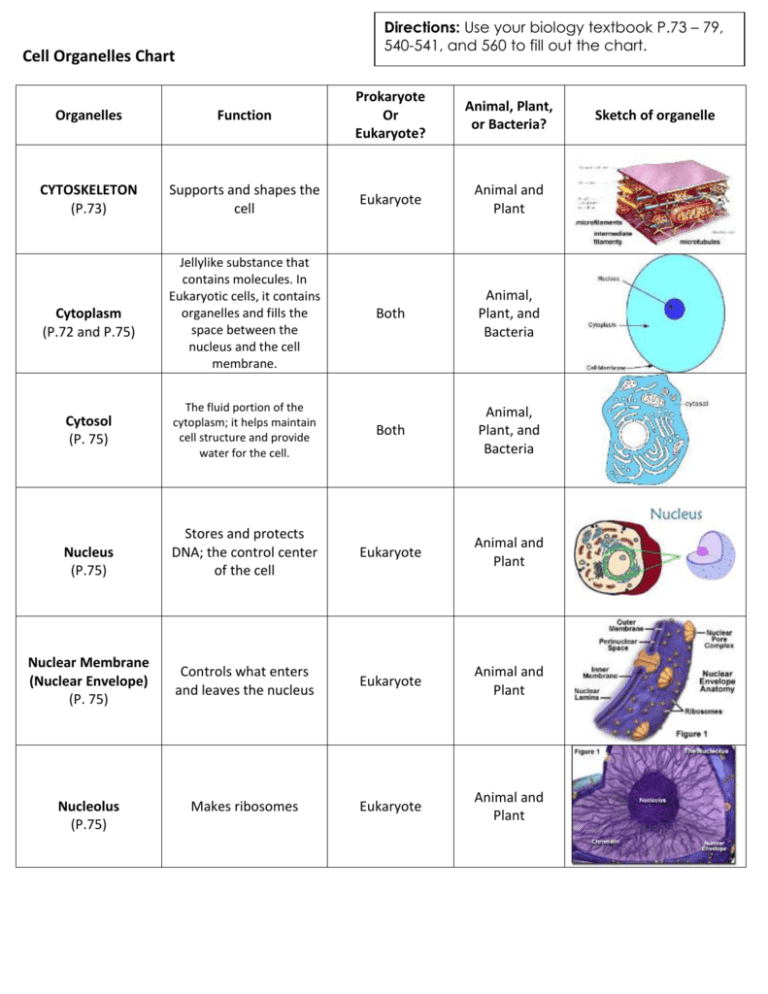
Directions: Use your biology textbook P.73 – 79, 540-541, and 560 to fill out the chart. Cell Organelles Chart Organelles Function Prokaryote Or Eukaryote? Animal, Plant, or Bacteria? CYTOSKELETON (P.73) Supports and shapes the cell Eukaryote Animal and Plant Jellylike substance that contains molecules. In Eukaryotic cells, it contains organelles and fills the space between the nucleus and the cell membrane. Both Animal, Plant, and Bacteria The fluid portion of the cytoplasm; it helps maintain cell structure and provide water for the cell. Both Animal, Plant, and Bacteria Stores and protects DNA; the control center of the cell Eukaryote Animal and Plant Controls what enters and leaves the nucleus Eukaryote Animal and Plant Makes ribosomes Eukaryote Animal and Plant Cytoplasm (P.72 and P.75) Cytosol (P. 75) Nucleus (P.75) Nuclear Membrane (Nuclear Envelope) (P. 75) Nucleolus (P.75) Sketch of organelle Prokaryote and Eukaryote Animal, Plant, and Bacteria Eukaryote Animal and Plant Eukaryote Animal and Plant Golgi Apparatus (P.76) Sorts, modifies, packages, and transports material such as proteins Eukaryote Animal and Plant Vesicles (P. 77) Isolate and transport specific molecules Eukaryote Animal and Plant Generate energy (ATP) for the cell Eukaryote Ribosomes (P.76) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (P. 76) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (P. 76) Mitochondria (P. 77) Makes proteins Help make protein Makes lipids Animal and Plant Vacuole (P. 77) Central Vacuole (P. 77) Lysosome (P. 78) Centriole (P. 78) Flagellum, Flagella (P. 78, 540, 541) Cilia (P. 78, 560) Pilus, Pili (P. 540, 541) Stores materials needed by the cell Eukaryote Animal and Plant Strengthens and supports plant cell; stores materials including waste Eukaryote Plant Eukaryote Animal Eukaryote Animal Prokaryote and Eukaryote Animal, Plant(rare), and Bacteria Eukaryote Animal and Plant(rare) Prokaryote Bacteria Breaks down bacteria, virus, and worn out cell parts with enzymes. Divides DNA during cell division; organizes microtubules Whip or tail that help the cell move Helps organism swim and capture food Helps stick to other surfaces Cell Wall (Page 79, 541) Rigid layer that gives protection, support, and shape to the cell Prokaryote and Eukaryote Plant and Bacteria Chloroplast (Page 79) Converts solar energy into chemical energy through photosynthesis Eukaryote Plant Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane) (P. 72, 81) Controls what goes into and out of the cell Prokaryote and Eukaryote Animal, Plant, and Bacteria Chromatin (p. 135) Grainy material made of DNA; in the cytoplasm of bacteria; in the nucleus of Eukaryotes Prokaryote and Eukaryote Animal, Plant, and Bacteria









