Part of Speech: noun
advertisement

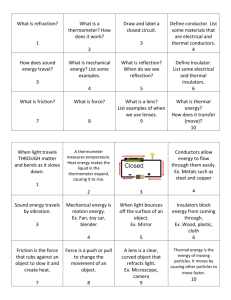
rd 3 Grade Thermodynamics Workbook Name ______________ Dictionary Use this dictionary to find the spelling, pronunciation, and part of speech of each vocabulary word. On the lines, write a sentence using each word. 1. average Pronunciation: (av-( -)rij) Part of Speech: noun Definition: the solution you get when you add numbers together and divide them by the total amount of numbers _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 2. boiling point Pronunciation: (b i( )l ing p int) Part of Speech: noun Definition: the temperature at which water forms into a gas (100° Celsius or 212° Fahrenheit) _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 3. degrees Celsius Pronunciation: (di- gr s sel-s - s) Part of Speech: noun Definition: the basic unit for measuring temperature in the metric system. Water freezes at 0 °Celsius and 100 °Celsius. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 4. combine Pronunciation: (k m- b n) Part of Speech: verb Definition: to bring or mix two things together _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 5. conductor Pronunciation: (k n- d k-t r) 2 Part of Speech: noun Definition: material that is good at transferring energy from one source to another _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _ 6. cool Pronunciation: (kül) Part of Speech: verb Definition: to become or make less warm _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _ 7. decrease Pronunciation: (di- kr s) Part of Speech: verb Definition: to make or become smaller _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _ 8. energy Pronunciation: (en- r-j ) Part of Speech: noun Definition: usable power _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _ 9. energy transfer Pronunciation: (en- r-j tran(t)s- f r) Part of Speech: noun Definition: when energy moves from one place to another _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 10. degrees Fahrenheit Pronunciation: (di- gr s far- n- h t) Part of Speech: noun Definition: the scale for measuring temperature that is used in the U.S. 3 _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _ 11. freezing point Pronunciation: (fr z ing p int) Part of Speech: noun Definition: the temperature when water becomes a solid (ice). (0°C or 32 °F) _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _ 12. heat energy Pronunciation: (h t en- r-j ) Part of Speech: noun Definition: how fast molecules are moving _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _ 13. increase Pronunciation: (in- kr s) Part of Speech: verb Definition: to make or become greater _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _ 14. insulator Pronunciation: (in(t)-s - l t- r) Part of Speech: noun Definition: slows the transfer of energy from one source to another _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 15. measure Pronunciation: (mezh-( -)ri ) Part of Speech: verb Definition: to find out the size or amount of something _____________________________________________________________________ 4 _____________________________________________________________________ _ 16. melt Pronunciation: (melt) Part of Speech: adjective Definition: to change from a solid to a liquid state as a result of warming _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _ 17. meteorologist Pronunciation: (m t- - - räl- -j st) Part of Speech: noun Definition: a person who studies the weather _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _ 18. molecule Pronunciation: (mäl-i- kyü( )l) Part of Speech: noun Definition: the smallest particle of a substance _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _ 19. prevent Pronunciation: (pri- vent) Part of Speech: verb Definition: to hold or keep back _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 5 20. range Pronunciation: (r nj) Part of Speech: noun Definition: a scale between limits _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _ 21. speed Pronunciation: (sp d) Part of Speech: noun Definition: the act of moving swiftly _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _ 22. surface area Pronunciation: (s r-f s ar- - ) Part of Speech: noun Definition: the area of liquid exposed to or touching the air _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _ 23. temperature Pronunciation: (tem-p (r)- ch r) Part of Speech: noun Definition: the measure of how much heat energy an object has _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _ 24. thermometer Pronunciation: (th (r)- mäm- t- r) Part of Speech: noun Definition: a scientific tool for measuring temperature _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 25. transfer Pronunciation: (tran(t)s- f r) 6 Part of Speech: verb Definition: to move to a different place _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 26. volume Pronunciation: (väl-y m) Part of Speech: noun Definition: how much space something takes up _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 7 Thermodynamics Crossword Across 2. lets energy flow 5. person who studies the weather 6. the act of moving swiftly 8. the space something takes up 9. to make bigger 10. move to a different place 11. area exposed to air 12. speed of molecules 13. usable power 15. 0°Celsius or 32°Fahrenheit 16. a scale between limits 17. to make smaller 20. measure of heat energy 22. find the size of something 23. 100°Celsius or 212°Fahrenheit 24. tool to measure temperature Down 1. mix two things together 2. to make less warm 3. unit for temperature in the U.S. 4. movement of energy 5. smallest particle of a substance 7. metric unit for temperature 14. blocks the flow of energy 18. sum divided by the total 19. to hold back 21. solid to liquid 8 Fill in the Blanks Use the words from the word bank to fill each blank. boiling point Celsius conductor cooled decrease Fahrenheit freezing point increases melt meteorologist temperature thermometer transfer _________________ tells people how hot or cold something is. People sometimes touch things to check temperature. Bread from the oven feels hot. Ice cream from the freezer feels cold. Some things are too hot or too cold to touch. People should be careful about what they touch. Temperatures can change. Hot things are _________________ by air and water. Cold things get warmer in sunlight or over a fire. A camper heats soup over a fire. The temperature of the soup rises until it reaches its _________________. Temperature changes can make things change form. Hot temperatures can _________________ things. Butter melts on a hot ear of corn. Cold temperatures can freeze things. Grape juice changes from a liquid to a solid in the freezer. The _________________ is 32 Fahrenheit. Frozen juice makes a good treat. Heated air expands and rises. A hot air balloon _________________ the temperature of the air with burners. The hot air lifts the balloon into the sky. Heat travels through objects that allow the _________________ of energy. Metal is a good _________________ of heat. A metal spoon warms up in hot chocolate. Temperatures change the weather. A _________________ studies the weather. Sunlight heats the air. Thunderstorms can happen when warm, wet air meets cool, dry air. Rain changes to snow or ice when temperatures _________________ below the freezing point. A _________________ is a tool that measures temperatures. They can measure the temperatures of air, food, and people. Thermometers use _________________ and _________________ to measure temperature. These scales help people know how hot or cold something is. 9 Reading a Thermometer Write the temperature of each thermometer on the lines below. °C °C °C °C °C 10 Write the temperature of each thermometer on the lines below. °C °C °C °C °C 11 °F °C °C °C °F 12 °F °F °C °F °C 13 Match the thermometer to the temperature. Write the letter of the matching thermometer on the line. 1. Which thermometer shows 46°F? ___ 6. Which thermometer shows 39°F? ___ 2. Which thermometer shows 66°F? ___ 7. Which thermometer shows 96°F? ___ 3. Which thermometer shows 75°F? ___ 8. Which thermometer shows 62°F? ___ 4. Which thermometer shows 96°F? ___ 9. Which thermometer shows 4°F? ___ 5. Which thermometer shows 23°F? ___ 10. Which thermometer shows 29°F? __ 14 Shade in the thermometers to the correct temperatures. 15 Shade in the thermometers to the appropriate temperatures. 46°C 20°F 55°C 16 Determine the difference in the temperatures for the following thermometers. °C °C °C °C °C °C °C °C °C °C °C °C 17 °C °C °C °C °C °C °C °C °C °C °C °C 18 Measuring Temperature The thermometer is the most common tool for measuring temperature. Many thermometers use two different temperature scales: Fahrenheit and Celsius. You may have wondered how they relate to each other. Both scales were invented in the 1700’s and are named after their inventors. The Fahrenheit scale was invented by Gabriel Fahrenheit. He set the boiling point for water at 212°, and the freezing point at 32°. Temperatures are measured all along the scale, much like a number line or ruler. The unit of measurement for temperature is a degree, instead of an inch on a ruler. Anders Celsius invented the Celsius scale after the Fahrenheit scale. He kept Fahrenheit’s anchor points. The anchor points are the temperatures at which water would freeze or boil. Celsius however, changed the numbers of his temperature scale. Under the Celsius scale, water freezes at 0° and boils at 100°. This numbering scale has been adopted for most scientific purposes. It works well with the metric system. Many thermometers work because liquid changes its volume, or the amount of space it takes up, based on its temperature. When a liquid is cold, it takes up less space than it does when it is warm. Many of the changes in a temperature are very small. Thermometers use a large bulb filled with liquid and a very narrow tube to show the changes. The markings on the thermometer are based on the freezing point and boiling point of water. Why? Because Gabriel Fahrenheit chose them as conditions that are easy to recreate. Anders Celsius agreed. Sometimes, inventors set the standard for everyone. 19 Answer the following questions based on the passage you just read. 1. Which scale came first: Fahrenheit or Celsius? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 2. Why do scientists use the Celsius scale? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 3. Why do many thermometers use liquid? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 4. What is the unit of measurement for temperature? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 5. Which temperature would be more comfortable for most people: 80°Fahrenheit or 80°Celsius? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 20 Surface Area Ms. Gosselin loves to bake. She made 5 different sized cakes. She wants to put icing on each of her cakes, but she has to wait for the cakes to cool down. Order the cakes, 1-5, by the time it would take to cool: 1= takes the shortest amount of time to cool, 5 = takes the longest amount of time to cool. How did you determine the speed at which each cake will cool? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 21 Insulators and Conductors #1 Materials that let heat pass through them are called thermal conductors. Metals are great thermal conductors, though the best thermal conductor is a diamond. Diamonds are crystals made of carbon. Glass, water, wood, and air are poor thermal conductors. Materials that are poor conductors of heat are called thermal insulators. Some types of materials are better thermal insulators than others. Five cups with 60°C were each wrapped in different types of materials. After 10 minutes, the water temperature in each cup was recorded. The results are shown in the table below. Material around the cup Uncovered Temperature after 10 minutes 20°C Aluminum 30°C Cardboard 40°C Cotton 50°C Styrofoam 55°C What material is the best thermal conductor? How do you know? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ What material is the best thermal insulator? How do you know? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ If you wanted to keep your tea hot for a long period of time, which material would you choose to wrap your cup? Why? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 22 Insulators and Conductors #2 Some materials, such as metal, feel cold when you touch them because they take heat away from your hand. When heat is taken away from you, you feel cooler. These materials are said to be good thermal conductors, as they are able to conduct heat. Other materials, such as wood, do not feel cold to the touch. They do not take heat away from your hand. These materials are thermal insulators. They are poor conductors of heat. Five spoons made of different materials were placed in a bowl. Five different scholars held a spoon while hot water was poured into the bowl. The amount of time it took each scholar to feel the heat is recorded in the data table below. Plastic Spoon Time it took to feel the heat 1 minute Steel Spoon 15 seconds Wooden Spoon Never Porcelain Spoon 2 minutes Aluminum Spoon 30 seconds Type of Spoon Which spoon is the best thermal conductor? How do you know? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Which spoon is the best thermal insulator? How do you know? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Which spoon would you use to stir a pot of hot soup? Why? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 23



![Temperature Notes [9/22/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006907012_1-3fc2d93efdacd086a05519765259a482-300x300.png)