1-1 Early Humans Guided Notes
advertisement

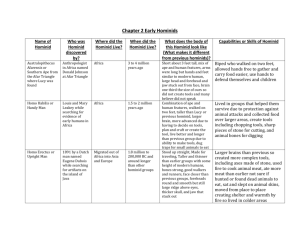
Name: _______________________________________________________ Period: ______ Chapter 1-1 Study Guide: Early Humans Bellringer: 1) _______ 2) _______ 3) _______ 4) _______ 5) _______ Scientists Search for Human Origins Scientists discover clues: Archaeologist – a _________________________ who __________________ the _______________ past by examining the things ________________________ left ____________________. ▪ Artifacts – _______________ and other ____________________ that _________________ made. ▪ Examine the artifacts at archaeological digs Paleontologists – study ____________________, or evidence of early life preserved in _____________. ▪ Give clues on who ancient people were and how they lived Anthropologists – study ___________________, or people’s unique ___________ of ____________. ▪ They make theories about the past based on what they learn from bones and artifacts Often contain small fragments of teeth, skulls, or other bones Archaeologists, anthropologists, paleontologists, and other scientists work as a _______________ to make new discoveries about how _______________________ people lived. Mary Leakey Finds Footprints: Led an expedition to Tanzania in East _______________ Searched for new clues about human ____________________ Found prehistoric ________________________ that resembled those of modern humans in mid-1970s Made by humanlike beings now called ________________________________________ Hominid – _________________ and other ______________________ that walk ___________________ Donald Johanson discovers Lucy: Explored sites in _______________________ 1,100 miles north of ___________________________ Discovered an unusually complete _________________________ of an adult female hominid in 1974 Named her “_____________” She lived around _________________________ years ago – the oldest hominid found to date Hominids in Motion: Lucy and the hominids who left their _______________ in East Africa were species of australopithecines Walking upright helped them __________________ more easily Could spot threatening _____________________ and carry food and children Developed the opposable __________ – means that the tip of the thumb can cross the palm of the hand Australopithecines: Existed __________________ to ______________________ B.C. Found in ___________________ and ___________________ Africa Brain size of _________ cubic centimeters First _______________________ creature to walk ________________________ QuickWrite Activity: Using the quotes and pictures on page 2, respond to the DBQ (document-based question). Provide at least a oneparagraph response of 5-7 sentences. Be sure to include supporting evidence from the quotes and pictures, as well as the information you learned today. Bellringer: Prehistoric and Modern Tools 1. What sorts of functions do you think the pictured prehistoric tools had? 2. What are some common uses of modern tools that prehistoric people might have used their tools for? 3. A _____ B _____ C _____ D _____ E _____ F _____ Arts and Artifacts of Early Humans Australopithecus - was one of the first ____________________ creatures. It could walk upright and had small canine teeth similar to humans. Nicknamed “_______________,” the skeleton is about 3.2 million years old. Footprints in Stone – In 1978 at the Laetoli archaeological site in ___________________, Mary Leakey discovered a set of footprints in hardened volcanic ash. Analysis shows that the footprints were 3.5 million years old and were left by an upright-walking hominid. The Tool-Maker – one of the defining characteristics of our Paleolithic ancestors is that they made tools. They shaped __________________ into various kinds of cutting tools, including knives and axes. The Advent of Art – Paleolithic humans were artists. One of the best proofs of this is the Lascaux Cave in France. The walls are covered with hundreds of painted animals. The paintings are an estimated _________________ years old. Identifying Artifacts Tool #1 How old is this tool? Who made it? What was it used for? Where did it come from? Tool #2 Early Humans and their Environment 1. Out-of-Africa (page 6): 2. The Hunt (page 7): 3. The Ice Age (page 8): 4. The Use of Fire (pages 7-8): 5. Domestication of Plants (page 7): 6. Neolithic Settlements: With sufficient food, humans had more __________________ over their lives. This meant they could give up their nomadic lifestyle and begin to live in _______________________________. These villages appeared in Europe, India, Egypt, China, and Mesoamerica. Video Clip: Before History List 5 facts or contributions mentioned in the video clip. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Progress During the Old Stone Age Paleolithic Age – 2.5 million to 8000 B.C. ______________________________ Oldest stone __________________________________ were created Occurred during the _________________________ Neolithic Age – 8000 B.C. to 3000 B.C. _______________________________ Polished stone _____________, made ________________, grew __________, raised ________________ Homo Habilis: Appeared in _______________________________ Existed ______________________ to _____________________ B.C., after australopithecines Leakey discovered a hominid fossil at ____________________________ in northern Tanzania Means _______________________________ Brain size of ___________ cubic centimeters First to make ________________________________ Homo Erectus: Existed ______________________ to _____________________ B.C. Appeared first in _______________________________ Means ___________________________________ More ________________________ and adaptable species Used intelligence to develop technology – ways of applying ________________________, __________________, and _______________________ to meet their needs Brain size of ______________ cubic centimeters Gradually became skillful ________________ and invented more tools for digging, scraping, and cutting Became first hominids to _____________________ Settled in _______________, China, Southeast Asia, and __________________ First to use _____________ Might also have developed the beginnings of __________________________________ ▪ Named objects, places, animals, plants, exchanged ideas The Dawn of Modern Humans Homo sapiens – the species name for __________________________________ Means _______________________ Had much larger _________________ than homo erectus Neanderthals and Cro-Magnons are included in the early groups Neanderthals: Existed from _______________________ to ____________________ B.C. Found in ____________________ and ____________________Asia _______________________ built – heavy slanted brows, well-developed muscles, and thick bones Brain size of ______________ cubic centimeters Tried to _________________ and control their world First to have _______________ burials Fashioned stone _______________, scrapers, and other tools Cro-Magnons: Existed __________________ to _______________ B.C. Skeletal remains show they are ______________________ to modern humans Planned their __________________ – studied animal habits and stalked their prey Had superior ______________________ strategies, which allowed them to survive more easily Brain size of ______________ cubic centimeters Considered _______________________________________ Created ___________ Advanced skill in _______________ language Recent findings add new knowledge: Constantly changing with new ______________________ Each new scientific discovery helps add further details to the still sketchy picture of human prehistory As time progressed, early humans’ skills and tools for surviving and adapting to their environment became more sophisticated. Helped launch a ________________________ in the way people lived.