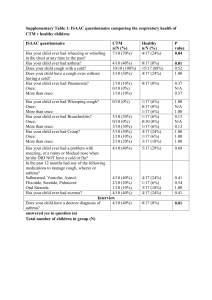
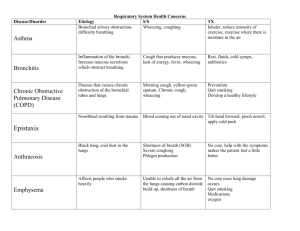
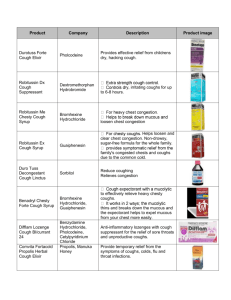
Common Cold
advertisement
Kapaa Pediatrics, LLC Upper Respiratory Infection in Children An upper respiratory infection (URI), also known a COMMON COLD, is usually caused by a virus. URIs are contagious and spread from person to person via contact with droplets from coughing or sneezing. The virus can also be spread with poor hand hygiene. Common Symptoms: Runny nose Fever Cough Sore throat Nasal Congestion Headache Treatment: Most parents and patients seek treatment for URIs because the symptoms are uncomfortable for those that are ill and tiring for parents. Medications such as antibiotics, decongestants, anti-cough, and expectorants do not work for children and are not recommended. Antibiotics Antibiotics treat bacterial infections. The common cold is a viral infection so antibiotics do not work. Antihistamines (e.g., Benadryl, Allegra) Studies show no improvement of cold symptoms in children who have taken antihistamines. Adverse effects have been reported and include stomach upset, blurred vision dry mouth, cardiac effects such as increased heart-rate, irregular heart-rate and heart block, and central nervous system effects such as sedation, respiratory depression, and hallucinations. Decongestants (e.g., Sudafed) Side effects of decongestants can be severe and include headaches, seizures, nausea, vomiting, increased heartrate, irregular heart-rate, nervousness, dystonia (a neurological muscle disorder), and even death have been reported. Antitussives (Cough medicines such as Delsym or Robitussin) Although coughing is one of the most aggravating symptoms of a URI, coughing is the body’s way of ridding the airway of secretions. In some children, suppressing a cough can actually be harmful, such as those with asthma. There is no evidence to support that cough medications work. Cough medication side effect include, altered mental status, neuromuscular abnormalities, respiratory depression, and death. Expectorants (e.g., Mucinex) There are no studies that demonstrate effectiveness in children. What to Expect If your child has a URI, he/she may present with runny nose, cough, sneezing, and nasal congestion. He/she may develop a fever at the beginning of the illness which will usually break within 1-3 days. You may see an increase in fussiness, fatigue, and sleep disturbance during this time. Sore throat and/or headache may also develop. Most children will experience symptoms that get worse through days 4-6, and then slowly get better over the next 1-2 weeks. References: 1. Pappas, DE, Hendley JO. The common cold and decongestant therapy. Pediatrics in Review. 2011;32:47-54 2. Pappas, DE, Hendley JO, Hayden FG, Winther B. Symptom profile of common colds in school-aged children. Pediatr infect Dis J. 2008;27:8-11 3. Smith SM, Schroeder K, Fahey T. Over-the-counter medications for acute cough in children and adults in ambulatory settings. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008;1:CD001831 Kapa’a Pediatrics, LLC ● 4-1461 Kuhio Hwy, Kapa’a HI 96746 ● Ph (808) 634-8011 ● Fax (808) 822-0938