Techniques to Analyze Organic and Inorganic Substances
advertisement

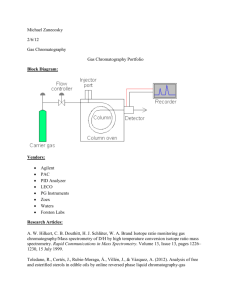
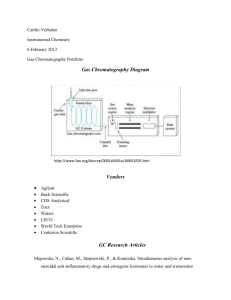
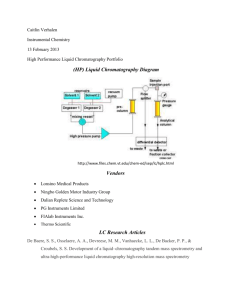
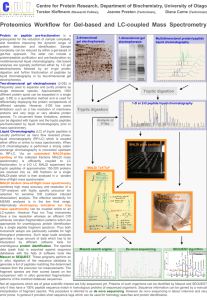
Techniques to Analyze Organic and Inorganic Substances Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry - the electrons of elements absorb specific wavelengths of light, because each element has a different electron configuration, the absorption pattern of each element is different. This one looks like a rainbow with colors missing Atomic Emission Spectrophotometry - once the electrons have absorbed the specific wavelengths of light and jumped up to a higher energy level, they then lose that energy and emit the same wavelengths they once absorbed. This one looks mostly black with random slivers of color. Electrophoresis - also called DNA fingerprinting, is a technique that uses agarose purified from seaweed to make a gel. Small amounts of DNA or proteins are placed in the gel and an electric charge separates the fragments of DNA or protein to be analyzed. Gas Chromatography - vaporizes a substance and then uses a moving gas and a stationary liquid to separate the components of a mixture. Most commonly used in conjunction with mass spectrometry High Performance Liquid Chromatography - uses a pressurized liquid to separate the components of a mixture. Excellent for mixtures that cannot be heated like explosives Mass Spectrometry - shoots electrons at a pure substance to break the molecule apart. The pieces of the molecule are analyzed by their atomic mass to give a unique pattern of molecular fragments. Neutron Activation Analysis - shoots neutrons at a substance in a nuclear reactor to make the substance radioactive and then measures the gamma rays given off by the radioactive isotope. Paper Chromatography - a liquid solvent like water or acetone soaks up paper and as it does, it carries and separates the components in mixtures like ink and dye by their density and solubility. Spectrophotometry - measures the specific wavelengths of infrared, visible, or ultraviolet light being absorbed by a molecule Thin Layer Chromatography - a volatile liquid solvent like acetone or ether soaks up a silica gel plate and separates out the components of a thick organic substance like grease or make-up X-Ray Diffraction - uses X-rays to determine crystalline structure of a molecule by analyzing how the X-rays get deflected by the molecule similar to the way X-rays can be used to analyze broken bones