File - Follett Science
advertisement

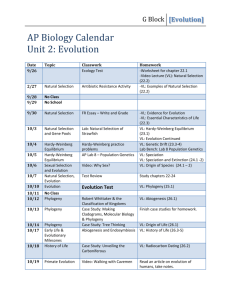
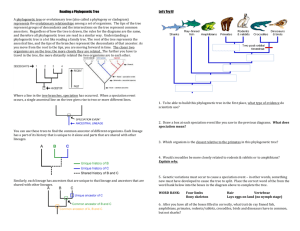
AP Biology Final Study Guide Plants: Chapters: 29.1, 29.3, 30.1, 30.3-4, 35.1-2, 36.1-4, 38.1, 39.2-3 Characteristics of bryophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms, and angiosperms Phototropism details and experiments Water potential and transpiration Pollination vs. fertilization Ecology: Chapters: 52.1, 51.1-3, 53.1-5, 54.1-4, 55.1-5, 56.1, 56.4 Energetic hypothesis vs. dynamic stability hypothesis Rule of 10’s Types of symbiotic relationships (i.e. mutualism, parasitism, commensalism, predator/prey) Behaviors: sign stimulus, taxis/kinesis, learning, imprinting, etc Patterns of dispersion Competitive exclusion principle Population equations (logistic equation) Hardy-Weinberg Equations Invasive species (why are they successful???) Energy pyramids (be able to explain) Evolution: Chapters: 22.2, 22.3, 23.1-4, 24.1-2, 24.4, 25.1, 25.3-4, 26.1, 26.3, 26.6 Natural Selection: define and apply Arrange from most inclusive to least: intrasexual selection, evolution, microevolution, natural selection, sexual selection. Speciation: Pre and post zygotic barriers to reproduction What is the general progression of evolution (what event happens first to eventually lead to speciation) Natural selection directly acts upon________ and indirectly acts upon_________ Know how to read and interpret phylogenetic trees (terms: monophyletic, paraphyletic, polyphyletic) Be able to apply maximum parsimony to find most likely explanation for phylogenetic trees Biochemistry: Chapters: 3.1-3, 4.1, 5.1-5, 8.1-5 Molarity/mole calculations Polarity Properties of water (adhesion, cohesion, specific heat) pH-know scale and examples of each (how is H+ ion involved?) role of buffers in body Enzymes: substrate and enzyme concentration and rates of reaction Enzyme inhibitors (types) Exergonic vs. endergonic reactions and Gibbs free energy Hydrolysis and dehydration reactions ATP coupling Protein structure and function Cell Function: Chapters: 6.2-5, 7.1-5, 11.1-5, 9.1-5, 10.1-3 Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes: endosymbiotic theory/evidence Fluid mosaic model (what are the parts) Hydrophilic/hydrophobic regions of lipid bilayer RE-DOX reactions Photosynthesis: equation, steps, reactants, and products Cellular respiration: equation, steps, reactants, and products Steps of cell signaling Phosphorylation cascades Practice Free Response Directions: Question 1 long free-response question that should require about 20 minutes to answer. Read each question carefully and write your response on a separate piece of paper. Only material written on the piece of paper will be scored. Answers must be written out. Outline form is not acceptable. It is important that you read each question completely before you begin to write. 1. Phylogeny reflects the evolutionary history of organisms. (a) Discuss TWO mechanisms of speciation that lead to the development of separate species from a common ancestor. (b) Explain THREE methods that have been used to investigate the phylogeny of organisms. Describe a strength or weakness of each method. (c) The two phylogenetic trees represent the relationship of whales to six other mammals. All of the organisms shown to have a pulley-shaped astragalus bone in the ankle except for the whale. • For each tree, describe a monophyletic group, the closest relative to the whale, and the point at which the pulley astragalus was lost or gained. • Based on the principle fo parsimony (the simplest explanation is the best) and the genomic information in the table shown, identify which tree is the best representation of the evolutionary relationship of these animals, and justify your answer.