File - Lanier Bureau of Investigation
advertisement

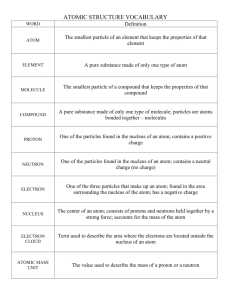
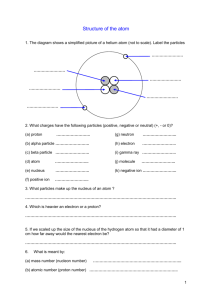
8th Grade Science Vocabulary CRCT Practice a. A 1. D 2. B 3. C 4. the transfer of energy carried by light waves to particles of matter b. the bouncing back of a wave after it strikes a barrier or an object c. the bending of a wave as it passes at an angle from one medium to another DUE TO CHANGE IN SPEED d. the bending of waves around a barrier or through an opening Absorption Diffraction Reflection Refraction C A B D 5. 6. 7. 8. A B AB E C D 9. Wheel & Axle 10. Wedge 11. Incline Plane 12. Lever 13. Screw 14. Pulley a. b. c. d. Acceleration Velocity Speed Time - a. simple machine consisting of two circular objects of different sizes b. a simple machine that is a double inclined plane that moves c. a simple machine that is an inclined plane wrapped in a spiral d. a simple machine consisting of a grooved wheel that holds a rope of a cable e. a simple machine consisting of a bar that pivots at a fixed point, called a fulcrum ab. a simple machine that is a straight, slanted surface a. B D A C AB E B C A D A C D E B 15. 16. 17. 18. Simple Machine Compound Machine Work Power 19. Amplitude 20. Frequency 21. Pitch 22. Sound Energy 23. Light Energy 24. Wavelength 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. Atom Element Compound Mixture Molecule the speed of an object in a particular direction the rate at which an object moves the rate at which velocity changes the rate at which something is done b. c. d. the action that results when a force causes and object to move in the direction of the force the six machines from which all other machines are constructed the rate at which work is done a machine that is made of two or more simple machines a. the energy produced by the vibrations of electrically charged particles b. how high or low a sound is perceived to be c. the energy caused by an object's vibrations d. the distance between one point on a wave and the corresponding point on an adjacent wave in a series of waves e. the number of waves produced in a given amount of time ab. maximum distance a wave vibrates from its rest position a. b. c. d. e. the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still be the same substance a neutral group of atoms held together by covalent bonds a pure substance that cannot be separated or broken down into simpler substances by physical or chemical means a pure substance composed of two or more elements that are chemically combined a combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined 1 D A B C 30. 31. 32. 33. a. b. Atomic Mass Atomic Number Periodic Table Pure Substances c. d. a. E A C D B 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. Groups/Family Period Metal Metalloids Nonmetals C B A D 39. 40. 41. 42. Solid State Liquid State Gas State Plasma State number of protons in the nucleus of an atom an arrangement of elements according to increasing atomic number so that elements with similar properties are in the same column a substance in which there is only one type of particle the weighted average of the masses in the nucleus of all the naturally occurring isotopes of an element, the number of protons plus the number of neutrons b. c. d. e. a horizontal row of elements on the periodic table, same # of electron clouds elements that are dull and are poor conductors of thermal energy and electric current , to the right of the zigzag line elements that are shiny and are good conductors of thermal energy and electric current, left of the zig zag line elements that have properties of both metals and nonmetals, on the zigzag line a column of elements on the periodic table who have similar reactivity and properties a. b. the state in which matter change in both shape and volume the state in which matter takes the shape of its container and has a definite volume the state in which matter has a definite shape and volume the state of matter that does not have a definite shape or volume and whose particles have broken apart c. d. a. C E AB B D A a property of matter that can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the matter b. a change that affects one or more physical properties of a substance c. A physical characteristic where the temperature at which a liquid boils and becomes a gas d. property of matter that describes a substance based on its ability to change into a new substance with different properties e. A physical characteristic where the temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid ab. a change that occurs when one or more substances are changed into entirely new substances with different properties 43. Boiling Point 44. Melting Point 45. Chemical Change 46. Physical Change 47. Chemical Property 48. Physical Property a. C A D B E C D B A 49. Density 50. Combustibility 51. Reactivity 52. Matter 53. Volume 54. Proton 55. Neutron 56. Electron 57. Nucleus b. c. d. e. the chemical property aka flammability (the measure of how easily a substance will burn) the amount of “stuff” in an object the amount of matter in a given space a chemical property that is used to determine how elements react with one another the amount of space an object takes up a. b. c. d. Where the protons and neutrons are located in an atom The particle that is negatively charged in an atom, have relatively no mass, they reside in the electron cloud and is equal to the atomic number The particle that is positively charged in an atom, resides in the nucleus, has a mass of one amu and is equal to the atomic number 2 The particle that has no charge in an atom, reside in the nucleus, have a mass of one amu and is equal to the atomic mass – atomic number D C B AD A AC AE E AB a. b. c. d. 58. Chemical Energy 59. Electrical Energy 60. Kinetic Energy 61. Potential Energy 62. Mechanical Energy 63. Thermal Energy 64. Nuclear Energy 65. Light Energy 66. Sound Energy e. ab. ac. ad. ae. an atom the total energy of motion and position of an object the energy of motion the energy of electric charges the energy of a compound that changes as its atoms are rearranged to form a new compound the energy produced by the vibrations of electrically charged particles the energy caused by an object's vibrations the total energy of the particles that make up an object the energy of position or shape the form of energy associated with changes in the nucleus of a. E D A B C 67. Conduction 68. Convection 69. Radiation 70. Thermal Expansion 71. Temperature b. c. d. e. a. C E D B A 72. Force 73. Mass 74. Weight 75. Gravity 76. Friction b. c. d. e. the transfer of energy through matter or space as electromagnetic waves increase in volume of a substance due to the increase in temperature a measure of how hot (or cold) something is a transfer of thermal energy by the movement of a liquid or a gas a transfer of electrons (electricity) or heat (energy) through direct contact a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are touching a force of attraction between objects that is due to their masses and distance a push or a pull a measure of the gravitational force exerted on an object the amount of matter that something is made of a. C B E AB D A 77. Newton’s First Law 78. Newton’s Second Law 79. Newton’s Third Law 80. Inertia 81. Balanced Forces 82. Unbalanced Forces C D B A AB AC E 83. Law of Conservation of Matter 84. Law of Conservation of Energy 85. Law of Universal Gravitation 86. Watt 87. Joule 88. Heat 89. Heat Transfer the forces on an object that cause the net force to be other than zero, resulting in movement b. the acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the amount of force applied c. an object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion remains in motion at constant speed and in a straight line unless acted on by an unbalanced force d. forces on an object that cause the net force to be zero, resulting in no movement e. whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first ab. the tendency of all object to resist any change in motion a. b. the unit used to express power the law that states that all objects in the universe attract each other through gravitational force c. the law that states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in ordinary chemical and physical changes d. the law that states that energy is neither created nor destroyed e. the transfer of energy between objects that are at different temperatures, HOT TO COLD ab. the unit used to express work and energy ac. energy that is being moved from one object to another 3