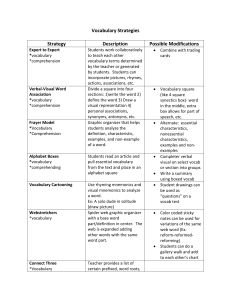
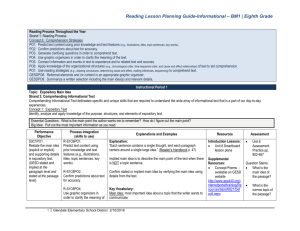
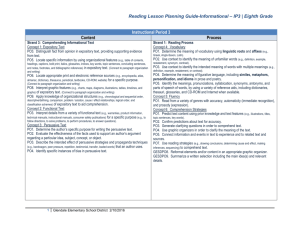
Reading Lesson Planning Guide-Literary
advertisement
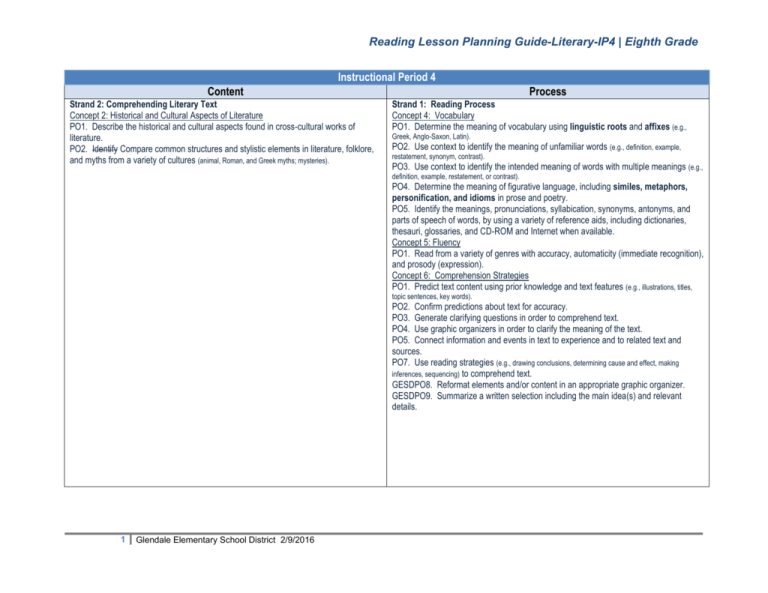
Reading Lesson Planning Guide-Literary-IP4 | Eighth Grade Instructional Period 4 Content Strand 2: Comprehending Literary Text Concept 2: Historical and Cultural Aspects of Literature PO1. Describe the historical and cultural aspects found in cross-cultural works of literature. PO2. Identify Compare common structures and stylistic elements in literature, folklore, and myths from a variety of cultures (animal, Roman, and Greek myths; mysteries). Process Strand 1: Reading Process Concept 4: Vocabulary PO1. Determine the meaning of vocabulary using linguistic roots and affixes (e.g., Greek, Anglo-Saxon, Latin). PO2. Use context to identify the meaning of unfamiliar words (e.g., definition, example, restatement, synonym, contrast). PO3. Use context to identify the intended meaning of words with multiple meanings (e.g., definition, example, restatement, or contrast). PO4. Determine the meaning of figurative language, including similes, metaphors, personification, and idioms in prose and poetry. PO5. Identify the meanings, pronunciations, syllabication, synonyms, antonyms, and parts of speech of words, by using a variety of reference aids, including dictionaries, thesauri, glossaries, and CD-ROM and Internet when available. Concept 5: Fluency PO1. Read from a variety of genres with accuracy, automaticity (immediate recognition), and prosody (expression). Concept 6: Comprehension Strategies PO1. Predict text content using prior knowledge and text features (e.g., illustrations, titles, topic sentences, key words). PO2. Confirm predictions about text for accuracy. PO3. Generate clarifying questions in order to comprehend text. PO4. Use graphic organizers in order to clarify the meaning of the text. PO5. Connect information and events in text to experience and to related text and sources. PO7. Use reading strategies (e.g., drawing conclusions, determining cause and effect, making inferences, sequencing) to comprehend text. GESDPO8. Reformat elements and/or content in an appropriate graphic organizer. GESDPO9. Summarize a written selection including the main idea(s) and relevant details. 1 Glendale Elementary School District 2/9/2016 Reading Lesson Planning Guide-Literary-IP4 | Eighth Grade Reading Process Throughout the Year Strand 1: Reading Process Concept 6: Comprehension Strategies PO1. Predict text content using prior knowledge and text features (e.g., illustrations, titles, topic sentences, key words). PO2. Confirm predictions about text for accuracy. PO3. Generate clarifying questions in order to comprehend text. PO4. Use graphic organizers in order to clarify the meaning of the text. PO5. Connect information and events in text to experience and to related text and sources. PO6. Apply knowledge of the organizational structures (e.g., chronological order, time-sequence order, and cause and effect relationships) of text to aid comprehension. PO7. Use reading strategies (e.g., drawing conclusions, determining cause and effect, making inferences, sequencing) to comprehend text. GESDPO8. Reformat elements and /or content in an appropriate graphic organizer. GESDPO9. Summarize a written selection including the main idea(s) and relevant details. Instructional Period 4 Topic: Historical and Cultural Genres Strand 2: Literacy Text Comprehension Comprehending Literary Text identifies the comprehension strategies that are specific in the study of a variety of literature. Concept 2: Historical and Cultural Aspects of Literature Recognize and apply knowledge of the historical and cultural aspects of American, British, and world literature. Essential Questions: What special qualities do the characters possess? How is this story organized? What is the purpose of the story? What effect does setting play on characters and plot? Big Idea: Stories vary in different cultures. Performance Objective S2C2PO1. Describe the historical and cultural aspects found in crosscultural works of literature. Process Integration (skills to use) R-S1C6PO3. Generate clarifying questions in order to comprehend text. R-S1C6PO4. Use graphic organizers in order to clarify the meaning of the text. R-S1C6PO5. Connect Information and events in text to experience and to related text and sources. 2 Explanations and Examples Explanation: Works of literature may reflect the influence of significant events, scientific discoveries, cultural values or social issues. Resources Read a VARIETY of pieces of literature that pertains to a historical or cultural aspect. Introduction Lessons: Standard Lesson File: Targeted Instruction for Arizona Standards p. 21 Students should be able to compare/contrast the different aspects between cross-cultural pieces of literature. Supplemental Resources: Key Vocabulary: Author’s Background: Story details frequently reflect information about an author’s background. Glendale Elementary School District 2/9/2016 www.ClassZone.com ML Text: Assessment Question Stems: In what literary period was this passage written? How can you tell? Give two reasons supporting your answer. Reading Lesson Planning Guide-Literary-IP4 | Eighth Grade R-S1C6PO6. Apply knowledge of the organizational structures of text to aid comprehension. R-S1C6PO7. Use reading strategies to comprehension. R-S1C5PO1. Read from a variety of genres with accuracy, automaticity and prosody. W-S3C5PO1. Write a response to literature that: a. presents several clear ideas; b. supports inferences and conclusions with examples from the text, personal experience, references to other works, or reference to nonprint media; c. relates own ideas to supporting details in a clear and logical manner; d. provides support adequate to the literary selection (e.g., short poem vs. novel) Historical Context: Understanding historical context makes it easier to appreciate the play, which is set during the 1960’s. Cultural Context: Music, customs, and traditions established the cultural context for a story about life in the Southwest. Author’s Perspective: an author’s view based on surroundings and circumstances. Cause and Effect: One example of cause and effect is not sleeping well and feeling tired the next day. Allusion: reference to a work of literature, famous person, place, event; something with which the reader is likely to be familiar with Example: Show a film clip from Diary of Anne Frank Diary of Anne Frank Historical Content Cultural Context Have student fill out the graphic organizer 3 Glendale Elementary School District 2/9/2016 Civil War Journal p. 327 The First American p. 1006 Letter to Harriet Tubman p. 270 An American Plague: The True and Terrifying Story of 1793 p. 938 A Dream of Freedom p. 859 Reading Lesson Planning Guide-Literary-IP4 | Eighth Grade S2C2PO2. Compare common structures and stylistic elements in literature, folklore, and myths from a variety of cultures. (animal, Roman, and Greek myths; mysteries) R-S1C6PO3. Generate clarifying questions in order to comprehend text. R-S1C6PO4. Use graphic organizers in order to clarify the meaning of the text. R-S1C6PO5. Connect Information and events in text to experience and to related text and sources. R-S1C6PO6. Apply knowledge of the organizational structures of text to aid comprehension. R-S1C6PO7. Use reading strategies to comprehension. R-S1C5PO1. Read from a variety of genres with accuracy, automaticity and prosody. Explanation: Structure in literature is the way it is put together. “The Wise Old Woman”, for example, is structured around the three challenges set forth by Lord Higa. Stylistic Elements in literature refers to how something is written rather than what is said. For example, an author may use sentence fragments, repetition, or figurative language. Analyzing structure & stylistic elements common to Literature Folktales Fables Myths in order to compare literature. Read a VARIETY of literature focusing on: Structure Style This PO is not limited to Folklore, Fables and Myths. All pieces of literature can be analyzed for structure and style. Key Vocabulary: Literature: All pieces of written work Style: The way writers express their ideas; not what they say, but how they say it. Literary devices: Author’s word choice Sentence structure Figurative language Imagery Dialogue Symbols Structure 4 Glendale Elementary School District 2/9/2016 Introduction Lessons: Resource Manager: Unit 7 pp. 1-11 United Streaming: 4 type of folktales Supplemental Resources: ML Textbook: Myths: Pandora’s Box p. 454 Folk Tale: The Old Grandfather and his Little Grandson p. 462 The Wise Old Woman p. 466 A Blind Man Catches a Bird p. 566 Tall Tale Pecos Bill p. 800 Reader’s Handbook p. 396 Reader’s Handbook Student Applications pp. 146-148 Reading Lesson Planning Guide-Literary-IP4 | Eighth Grade Folklore: Passed down from generation to generation by word of mouth Reflects traditional beliefs Mostly set in the past Supernatural events Characters vary from ordinary people to animals or supernatural beings. Myth: Fables: A traditional story Can be about the origins of the world Human or social cultures Mysteries of the earth Can be based on what a group of people in the past believed. A brief tale Teaches a lesson Explains a moral about life Often has animals as major characters Legend: Passed down for many generations Believed to be real events Focus on a hero/heroine Tall tale: Exaggerated story Impossible events Main character is larger than life 5 Glendale Elementary School District 2/9/2016 Reading Lesson Planning Guide-Literary-IP4 | Eighth Grade Example: 1. Begin with an anchor chart, students would fill out this example: 2. As a class, create an anchor chart comparing the essential elements of literature. Fairy Tale Tall Tale Fables Gods/ supernatu ral beings Animals who show that human speak characteri stics Folk Tale Everyday people/ animals with human characteris tics Character Good vs. Evil Hero larger than life Setting Castles Forests Early Where settlemen Gods live ts or visit Theme Justice prevails Courage and ingenuity We are puppets of the Gods The wise triumph over the foolish Treat others as you wish to be treated Solved in humorous ways Reveal the consequen ces of human error Contains a moral Generally teaches a lesson about obedience Occurs in Common 3s/7s Structures Involves magic 6 Myth Glendale Elementary School District 2/9/2016 Country Simple Wildernes village s