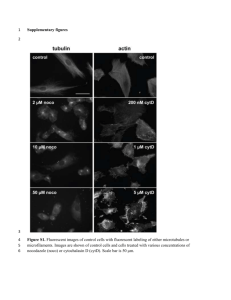
pmic12222-sup-0003-supinfo
advertisement

SUPPORTING INFORMATION Figure S1. Light microscopy of transverse and longitudinal semi-thin sections of gastrocnemius muscles from young (a, c) and aged (b, d) rats. Signs of aging processes are represented by a splitting fiber (b, arrowheads point the invaginated sarcolemma) and an area of myofibrillar degeneration (d, arrow). Toluidine blue staining. Scale bar = 20 µm. Figure S2. Light microscopy of transverse and longitudinal semi-thin sections of triceps muscles from young (a, c) and aged (b, d) rats. Signs of aging processes are represented by internal migration of nuclei (b, arrows), areas of disarray of myofibrils (d, upper fiber) and myofibrillar degeneration (d, arrowheads). Toluidine blue staining. Scale bar = 20 µm. Figure S3. a-d) Electron microscopy images of muscles from aged rats. In the gastrocnemius muscle (a) are evident lamellar formations, parallel arranged and close to the nucleus (at high magnification in the inset). In the triceps muscle (b) are evident small foci of myofibrillar loss (red asterisks). Scale bar = 1 µm; inset scale bar = 0.25 µm. In the gastrocnemius (c) is present a lipofuscin granule (arrow); in the triceps (d) are present lipid droplets (arrowheads). Scale bar = 1 µm. e-h) Electron microscopy images of subsarcolemmal and intermyofibrillar mitochondria. Gastrocnemius (e,f,g) and triceps (h) muscles from aged rats show some age related modifications of mitochondria. In aged gastrocnemius (e), some subsarcolemmal mitochondria, appear larger (arrows) than others. An autophagosome is marked by asterisk. (f) an extended intermyofibrillar network of elongated mitochondria (arrowheads) is evident in this muscle. (g) Evidence of a mitochondrion with crystalloid inclusions, suggestive of morphological changes, between normal myofibrils (higher magnification of a small detail is shown in the inset). (h) Subsarcolemmal accumulation of mitochondria and a lipid droplet (arrowhead) in aged triceps muscle. Scale bar = 1 µm. Figure S4. SDS-PAGE of young (Y) and aged (A) gastrocnemius (Gas) and triceps (Tri) muscle extracts. Samples (50 µg) were loaded on a 6-14% gradient polyacrylamide gel and stained using SYPRO Orange protein gel stain (Molecular probes). Low and High Molecular weight markers (Ge Healthcare) were run in separate lanes. Figure S5. Gastrocnemius (A) and triceps (B) muscles protein profiling by 2D-DIGE. Protein extracts (50 µg) from each set type were labeled with 400 pmol Cy5 dye (CyDye; GE healthcare), while an internal standard, generated by pooling together an aliquot of all the samples, was labeled with the Cy3 dye. Individual samples (40 µg) were combined with an equal amount of internal standard and separated on 24 cm, nonlinear pH 3–10 gradient IPGstrips (first dimension) and on 20 × 25 cm2, 12% T, 2.5% C polyacrylamide gels (second dimension). Protein spots significantly changed (Student’s t-test, p < 0.01) in 22-month-old gastrocnemius and triceps extracts compared with their 3-month-old controls and identified by MALDI-ToF mass spectrometry are indicated in representative 2D maps and numbered accordingly to Supplementary Table S2A and S2B listing. Figure S6. Validation of MALDI-ToF MS identified proteins by immunoblotting. Immunoblotting of selected proteins (identified by proteomic analysis) in gastrocnemius and triceps muscles from aged rats versus their respective young controls. Statistical analysis was performed by Student’s T-Test (n=6; * p<0.05). The data were normalized against the total amount of loaded proteins stained with Sypro Ruby. GAPDH: glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; LDHA: Llactate dehydrogenase A chain; CKM: creatine kinase M-type; ACO2: aconitase 2; ATP5B: ATP synthase subunit beta; CRYAB: alpha-crystallin B chain; CAR3: carbonic anhydrase 3; VDAC1: voltage-dependent ion channel 1. Figure S7. Biochemical analysis of myogenic regulatory transcription factors (MRFs). Upper panel: Representative immunoblot images of Pax7, MyoD and myogenin in gastrocnemius (Gas) and triceps (Tri) muscles of aged rats (A) and young controls (Y). Lower panel: Histograms of protein expression (normalized to their respective controls) in gastrocnemius and triceps muscles of aged rats (mean ± SD). *Significant differences (Student’s t-test, n = 3, p < 0.05) of aged vs. control rats. Table S1. MIAPE Standards Data MIAPE-GE Gel Electrophoresis Supplementary Information General Features • 22-month-old (aged) and 3-month-old (young) Sprague-Dawley male rats (Charles River, Calco, Italy) were used in this study. All the procedures involving animals and their care were conducted in conformity with the institutional procedures in compliance with national (D.L. No. 116, G.U. Suppl. 40, Feb. 18, 1992, Circolare No. 8, G.U., 14 Luglio 1994) and international regulations (EEC Council Directive 86/609, OJ L 358, 1 DEC.12, 1987; NIH Guide for the Care and use of Laboratory Animals, U.S. National Research Council, 1996). • Experiments conducted at the Università degli Studi di Milano, Dipartimento di Scienze Biomediche per la Salute, Segrate (MI), Italia. • Electrophoresis type: 2-D DIGE. • Images: available upon request. • Image analysis software: DeCyder version 6.5 (GE Healthcare). • Statistical analysis software: EDA module version 1.0 (GE Healthcare). Gel analysis design • Animals: 12 male rats (6 young and 6 aged). • Samples: gastrocnemius and triceps muscles from left and right fore- and hind-limbs. • Sample preparation: an aliquot of each frozen muscle was suspended in lysis buffer (urea 7M, thiourea 2M, CHAPS 4%, Tris 30mM, and PMSF 1mM) and solubilized by sonication on ice. Proteins were selectively precipitated using PlusOne 2D-Clean-up kit (GE Healthcare) in order to remove nonprotein impurities and re-suspended in lysis buffer. Protein extract was adjusted to pH 8.5 by the addition of NaOH 1M solution, and sample concentrations were determined using PlusOne 2-D Quant kit (GE Healthcare). • Experimental groups: 4 (aged gastrocnemius, aged triceps, young gastrocnemius, young triceps) – 12 samples for each experimental group. 6 aged and 6 young samples for each muscle type were used for DIGE analysis. Each sample was Cy5-labelled and run in duplicate. • Internal standard: Cy3-labelled pool of equal protein amounts from all samples run on each analytic gel. Image pre-processing • Type: Images were scanned on the Typhoon 9200 Imager (GE Healthcare). • Software: ImageQuant TL (GE Healthcare). Settings: • • • Analytic (quantitative) gels: laser voltages were optimized for each fluorophore prior to scanning to avoid signal saturation. Identical laser settings were then used to scan each gel. Preparative (picking/protein identification) gel: fixed with ethanol/acetic acid and poststained with Deep Purple, scanned independently from analytic gels. All gels were scanned at 100μm resolution. Data extraction process • Input images: available upon request. • Feature detection: DeCyder version 6.5, DIA module (GE Healthcare) • Automatic detection with estimation of 5000 protein spots • Exclusion filter applied to spots with the following features • Slope > 1.2 • Area < 200 • Volume < 10000 • • • • • • • • DIA workspaces were manually edited to eliminate gel artefacts and to reinclude any incorrectly excluded spots. Matching algorithm: DeCyder version 6.5, BVA module (GE Healthcare) Automatic matching with 50 manually identified landmark protein spots per gel Spot matches were manually edited Match on 90% of gels required. Feature quantitation: Decyder version 6.5 Background subtraction: DeCyder version 6.5 Normalization: DeCyder version 6.5. Data analysis • PCA: DeCyder EDA module version 1.0. • Statistical analysis: DeCyder EDA module version 1.0. • Type: Student’s T-test (p<0.05); input data: log standardized abundance. • Power analysis: Lenth power tool; input data: biological variance calculated from standardized spots volumes. MIAPE MS Supplementary Information General features • Instrument used: MALDI ULTRAFLEX III (Bruker Daltonics). • Software used: FlexAnalysis v. 3.0 (Bruker Daltonics); MASCOT v 2.2 database Input data and parameters • Type of MS data: MS spectra. • Databases queried: MASCOT v2.2, NCBInr 20090430 database (8483808 sequences; 2914572939 residues). • Taxonomical restrictions: Rodentia. • Cleavage agent: Trypsin. • Allowed number of missed cleavages: 1. • Permissible amino acid modifications: oxidation (variable) and carbamidomethylation (fixed). • Mass exclusion tolerance: 30 ppm. The output from the procedure • Data for identified proteins: See Supporting Information Table S2A, S2B and annotated spectra of identified proteins. Protein identification methods Spots of interest were excised from gel using the Ettan spot picker robotic system (GE Healthcare), destained in 50% methanol/50mM ammonium bicarbonate (AMBIC), reduced, alkylated and incubated with 30 µL of 6 ng/µL trypsin (Promega) dissolved in 10 mM AMBIC for 16 h at 37°C. Released peptides were subjected to reversed-phase chromatography (ZipTip C18 micro, Millipore), eluted with 50%ACN/1% formic acid. Peptides mixture (1 µL) was diluted in an equal volume of 10 mg/mL CHCA matrix dissolved in 70% ACN/30% citric acid and processed on a Ultraflex III MALDI-ToF/ToF (Bruker Daltonics) mass spectrometer. MS was performed at an accelerating voltage of 25 kV and spectra were externally calibrated using Peptide Mix calibration mixture (Bruker Daltonics); 1000 laser shots were taken per spectrum. Spectra were processed by the FlexAnalysis software v. 3.0 (Bruker Daltonics) setting the signal-to-noise threshold value to 6 and search was carried out by correlation of uninterpreted spectra to Rodentia entries in NCBInr 20090430 database (8.483.808 sequences; 2.914.572.939 residues). Proteins were identified by comparing the digest peaks with a computer-generated database of tryptic peptides from known proteins using MASCOT, which utilizes a robust probabilistic scoring algorithm. With regard to MASCOT parameters, the significance threshold was set at p-value<0.05. One missed cleavage per peptide was allowed and carbamidomethylation was set as a fixed modification while methionine oxidation as a variable modification. Mass tolerance was set at 30 ppm. Table S2. Protein Identification by MALDI-ToF MS in gastrocnemius (A) and triceps (B) muscles. For each identified spot, characterized by a unique spot number assigned during the matching process by the DeCyder software, mass spectrometry parameters (theoretical MW and pI, MASCOT score, protein coverage, n° matched over searched peaks) and statistical analysis parameters (t-test pvalue, average ratio aged/young, % variation) are reported, along with recommended protein name, gene symbol, and UniProt Knowledgebase accession number. Table S2A. List of changed proteins in aged vs. young gastrocnemius muscle, identified by MALDI-ToF MS. 2D map reference Protein Gene name UniProtKB entry Theoretical MW Theorecical pI Mascot Coverage Matched/Searched Peptides T-test p-value Av. Ratio % variation Anaerobic metabolism: 1 Aldehyde reductase 1 Akr1b1 P07943 35,8 6,3 112 32,9 9/21 1,90E-05 -1,43 -30 2 Alpha enolase Eno1 P04764 47,1 6,2 93 23 10/20 0,00015 -1,51 -34 3 Beta enolase Eno3 P15429 47 6,9 93 21 7/16 4,60E-05 -1,37 -27 4 Beta enolase Eno3 P15429 47 7,8 148 39,2 13/21 4,60E-05 -1,39 -28 5 Beta enolase Eno3 P15429 47 7,8 138 32,9 12/32 2,10E-05 -1,35 -26 6 Beta enolase Eno3 P15429 47 7,8 188 38,2 16/27 3,60E-05 -1,37 -27 7 Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase A Aldoa P05065 39,3 9,2 202 38,5 16/34 0,00083 -1,29 -22 8 Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase A Aldoa P05065 39,3 9,2 248 55,2 18/32 0,0049 -1,27 -21 9 Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase Gapdh P04797 35,8 9 157 35,1 10/15 2,60E-06 -1,82 -45 10 Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase Gapdh P04797 35,8 9 100 29,7 8/22 2,40E-07 -1,83 -45 11 Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase Gapdh P04797 35,8 9 113 39,6 11/28 2,40E-05 -1,89 -47 12 Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase Gapdh P04797 35,8 9 95 30,6 9/26 0,00036 -1,37 -27 13 Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase [NAD+], cytoplasmic Gpd1 O35077 37,4 6,2 119 29,8 11/19 0,0028 -1,17 -15 14 Glycogen phosphorylase, muscle form Pygm P09812 97,2 6,7 200 25,9 19/26 0,0002 -1,5 -33 15 Glycogen phosphorylase, muscle form Pygm P09812 97,2 6,7 151 20,5 18/30 6,30E-05 -1,53 -35 16 Glycogen phosphorylase, muscle form Pygm P09812 97,2 6,7 304 38,4 26/32 0,0001 -1,57 -36 17 L-lactate dehydrogenase A chain Ldha P04642 36,4 9,3 181 41 18/26 8,70E-05 -1,53 -35 18 L-lactate dehydrogenase A chain Ldha P04642 36,4 9,3 178 36,4 15/22 5,50E-05 -1,57 -36 19 L-lactate dehydrogenase A chain Ldha P04642 36,4 9,3 180 37 14/19 0,0019 -1,58 -37 20 Phosphoglucomutase Pgm1 P38652 61,4 6,1 113 26,3 12/27 5,50E-05 -1,41 -29 21 Phosphoglycerate mutase 2 Pgam2 P16290 28,7 9,5 157 48,2 12/22 0,0064 -1,29 -22 22 Phosphoglycerate mutase 2 Pgam2 P16290 28,7 9,5 151 44,3 11/20 3,40E-05 -1,38 -28 23 Phosphoglycerate mutase 2 Pgam2 P16290 28,7 9,5 153 44,3 12/22 5,00E-05 -1,39 -28 24 Pyruvate Kinase, isozymes M1/M2 Pkm P11980 57,8 6,7 130 28,2 12/23 0,0006 -1,39 -28 25 Triosephosphate isomerase Tpi1 P48500 26,8 7,7 161 51 11/22 0,00011 -1,14 -12 26 Creatine kinase, M chain Ckm P00564 43 6,6 223 38,3 18/22 0,0026 -1,27 -21 27 Creatine kinase, M chain Ckm P00564 43 6,6 100 31,2 9/24 0,00079 -1,32 -24 28 Creatine kinase, sarcomeric mitochondrial Ckmt2 P09605 47,4 9,5 199 42,5 19/30 5,80E-05 -1,19 -16 29 Adenylate kinase isoenzyme 1 Ak1 P39069 21,6 8,8 140 52,6 12/23 0,0011 -1,29 -22 30 Nucleoside diphosphate kinase B Nme2 P19804 17,3 7,8 186 84,2 11/18 0,0031 -1,16 -14 Energy balance: TCA cycle: 31 Aconitate hydratase, mitochondrial, Aco2 Q9ER34 85,4 8,7 117 22,6 14/36 0,00011 1,49 49 32 Aconitate hydratase, mitochondrial, Aco2 Q9ER34 85,4 8,7 373 51,9 33/58 5,00E-06 1,34 34 33 Aconitate hydratase, mitochondrial, Aco2 Q9ER34 85,4 8,7 134 23,3 17/45 0,001 1,24 24 34 Aconitate hydratase, mitochondrial, Aco2 Q9ER34 85,4 8,7 252 34,7 25/43 0,00025 1,29 29 35 Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase, mitochondrial Dld Q6P6R2 54 9 154 26,9 14/33 0,0001 1,23 23 36 Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex Dlat P08461 53,2 9,3 85 16,6 9/15 0,001 1,21 21 37 Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NAD] subunit alpha, mitochondrial precursor Idh3a Q99NA5 39,6 6,5 155 34,4 17/41 9,10E-06 1,29 29 38 Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NAD] subunit alpha, mitochondrial precursor Idh3a Q99NA5 39,6 6,5 81 23 9/26 0,00066 1,17 17 39 Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NADP], mitochondrial [precursor] Idh2 P56574 50,9 9,6 214 45,4 22/49 0,0003 1,5 50 40 Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component beta subunit, mitochondrial Pdhb P49432 39 6,2 130 41,5 13/26 0,00056 1,34 34 41 Succinyl-CoA ligase [ADP-forming] beta-chain, mitochondrial, [precursor], Sucla2 F1LM47 46,2 5,6 92 22,3 11/27 0,0021 1,19 19 42 Succinyl-CoA: 3-ketoacid-coenzyme A transferserase 1, mitochondrial [precursor] Oxct1 B2GV06 56 9,5 116 29 11/21 0,00018 1,29 29 43 ATP synthase alpha chain, mitochondrial Atp5a1 P15999 59,7 9,7 92 22,2 11/26 5,60E-06 1,34 34 44 ATP synthase alpha chain, mitochondrial Atp5a1 P15999 59,7 9,7 266 42,2 20/24 1,20E-05 1,27 27 45 ATP synthase beta chain, mitochondrial Atp5b P10719 56,1 5,1 161 36,1 15/29 9,70E-05 1,32 32 46 ATP synthase beta chain, mitochondrial Atp5b P10719 56,1 5,1 261 53,9 27/40 1,40E-05 1,36 36 47 ATP synthase D chain, mitochondrial Atp5h P31399 18,8 5,7 103 59,6 9/39 0,0021 1,41 41 48 Ubiquinol-cytochrome C reductase complex co. protein I, mitochondrial Uqcrc1 Q9CZ13 52,8 5,5 170 24,4 11/16 0,00031 1,52 52 49 Actin, alpha skeletal muscle Acta1 P68136 37,8 5,4 145 36,3 13/24 0,00025 1,26 26 50 Cofilin, muscle isoform Cfl2 M0RC65 18,7 8,8 76 31,3 5/8 0,0053 1,64 64 51 Desmin Des P48675 53,4 5,1 325 49 28/39 5,50E-05 1,42 42 52 Desmin Des P48675 53,4 5,1 309 52 30/46 0,0049 1,28 28 53 Desmin Des P48675 53,4 5,1 307 58 29/57 0,0021 1,29 29 54 Myosin binding protein C, fast-type Mybpc2 D3ZA38 127,2 6 135 17,2 16/25 1,10E-05 -1,28 -22 55 Myosin binding protein C, fast-type Mybpc2 D3ZA38 127,2 6 126 17,4 16/30 1,40E-05 -1,31 -24 56 Myosin binding protein C, slow type Mybpc1 Q63518 126,1 5,6 251 22,8 29/36 0,00011 1,64 64 57 Myosin binding protein C, slow type Mybpc1 Q63518 126,1 5,6 141 16,2 17/25 7,50E-05 1,7 70 58 Myosin heavy chain IIB [Fragment] Myh4 Q9JHR4 61 5,3 286 44,6 26/37 0,0027 -1,43 -30 59 Myosin heavy chain IIB [Fragment] Myh4 Q9JHR4 61 5,3 201 32,5 16/19 0,0002 -1,68 -40 60 Myosin light chain 1, skeletal muscle isoform Myl1 P02600 20,7 4,8 183 63,5 14/25 0,00045 -1,45 -31 61 Myosin-binding protein H Mybph O88599 52,6 6 113 33,5 12/38 0,00084 -1,53 -35 62 Myosin-binding protein H Mybph O88599 52,6 6 73 18,4 7/19 3,50E-05 -1,57 -36 63 Myozenin-1 Myoz1 D4A7U8 31,4 9,1 110 34,5 9/12 0,00029 -1,23 -19 64 PDZ-LIM protein cypher 2s Ldb3 Q5XIG1 35,1 9,6 187 47,4 16/30 0,00041 -1,15 -13 65 PDZ-LIM protein cypher 2s Ldb3 Q5XIG1 35,1 9,6 143 35,5 13/27 0,0066 -1,19 -16 Respiratory chain: Structural proteins: 66 Skeletal muscle-specific alpha-actinin 3 Actn3 Q8R4I6 102,9 5,2 361 41,1 37/49 67 Tropomyosin 1 alpha chain 68 Tubulin beta-2C chain 69 70 0,001 -1,09 -8 Tpm1 P04692 32,7 4,6 Tubb4b Q6P9T8 49,8 4,6 189 44 246 33,7 17/35 0,0042 -1,3 -23 23/26 6,80E-05 1,9 90 Myoglobin Mb Q9QZ76 17,1 Myoglobin Mb Q9QZ76 17,1 8,9 127 8,9 159 55,2 8/11 0,0031 1,43 43 63 11/20 0,0039 1,35 35 71 Serotransferrin Tf P12346 72 Serotransferrin Tf P12346 76,3 7,2 76,3 7,2 266 28,9 19/21 0,00018 1,44 44 182 30,2 17/28 0,00012 1,33 73 Serum albumin Alb P02770 68,7 33 6,1 180 33,9 18/37 3,00E-06 1,61 74 Serum albumin Alb P02770 61 68,7 6,1 334 54,3 29/49 5,70E-06 1,77 77 0,0024 1,16 16 Transport proteins: Cell Signaling and Stress Proteins: 75 14-3-3 protein gamma-subtype Ywhag P61983 28,3 4,7 110 27,5 10/14 76 Alpha crystallin B chain Cryab P23928 19,9 6,9 169 62,6 12/26 0,00018 3,17 217 77 Carbonic anhydrase III Car3 P14141 29,4 7,1 197 54,2 14/25 1,50E-06 7,02 602 78 Stress-70 protein, mitochondrial precursor Hspa9 P48721 73,8 5,9 205 43,2 24/47 0,00042 1,94 94 79 Mitochondrial inner membrane protein Immt Q3KR86 67,1 5,5 322 43,3 29/45 0,0025 1,21 21 80 Mitochondrial inner membrane protein Immt Q3KR86 67,1 5,5 154 17,4 11/14 0,00012 1,93 93 81 Ppp2r1a protein Ppp2r1a Q5XI34 65,3 4,9 107 19,2 11/18 0,0055 1,22 22 82 Prohibitin [Mus musculus] Phb P67779 29,8 5,5 178 58,1 12/22 0,004 4,7 370 83 Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 1 Vdac1 Q9Z2L0 30,7 8,6 185 52,7 14/33 0,00017 1,39 39 84 Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 1 Vdac1 Q9Z2L0 30,7 8,6 106 38,2 9/31 0,00027 1,26 26 85 Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 2 Vdac2 P81155 31,7 8,7 96 29,2 6/11 1,00E-05 1,81 81 86 Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 2 Vdac2 P81155 31,7 8,7 91 29,2 7/18 3,80E-05 1,41 41 Table S2B. List of changed proteins in aged vs. young triceps muscle, identified by MALDI-ToF MS. 2D map reference Protein Gene name UniProtKB entry Theoretical MW Theorecical pI Mascot Coverage Matched/Searched Peptides T-test Av. Ratio % variation Anaerobic metabolism: 1 Aldehyde reductase 1 Akr1b1 P07943 35,7 6,9 91 34,5 8/28 1,85E-03 -1,22 -18 2 Alpha enolase Eno1 P04764 47,1 6,2 142 40,3 15/30 3,10E-04 -3,41 -71 3 Beta enolase Eno3 P15429 47 6,9 87 23,7 9/24 4,80E-05 -1,26 -21 4 Beta enolase Eno3 P15429 47 6,9 217 50,9 19/27 1,81E-05 -1,36 -26 5 Beta enolase Eno3 P15429 47 6,9 220 53,3 19/30 9,52E-05 -1,25 -20 6 Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase A Aldoa P05065 39,3 9,2 221 52,5 18/31 7,62E-05 -1,22 -18 7 Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase A Aldoa P05065 39,3 9,2 132 49,2 13/33 1,21E-04 -1,32 -24 8 Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase Gapdh P04797 35,8 9 126 34,5 10/24 8,76E-04 -1,33 -25 9 Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase Gapdh P04797 35,8 9 113 39 13/38 2,64E-04 -1,22 -18 10 Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase [NAD+], cytoplasmic Gpd1 O35077 37,4 6,2 192 48,1 17/24 7,99E-05 -1,34 -25 11 Phosphoglycerate mutase 2 Pgam2 P16290 28,7 9,5 166 52,2 13/35 1,20E-04 1,35 35 12 Phosphoglycerate mutase 2 Pgam2 P16290 28,7 9,5 117 39,9 10/24 3,58E-03 1,25 25 13 Pyruvate Kinase, isozymes M1/M2 Pkm P11980 57,8 6,7 249 44,4 22/32 1,66E-04 -1,27 -21 14 Triosephosphate isomerase Tpi1 P48500 26,8 7,7 160 51 11/25 2,83E-05 1,41 41 15 Creatine kinase, M chain Ckm P00564 43 6,6 238 53,8 19/36 9,62E-05 -1,28 -22 16 Creatine kinase, M chain Ckm P00564 43 6,6 217 42 15/20 2,30E-05 -1,3 -23 17 Adenylate kinase isoenzyme 1 Ak1 P39069 21,6 8,8 120 47,9 9/16 0,0000112 -1,21 -17 18 Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex Dlat P08461 49 9,9 135 31,9 14/26 9,77E-06 3,61 261 ATP synthase D chain, mitochondrial Atp5h P31399 18,8 5,7 93 49,7 7/21 1,20E-04 1,28 28 20 Actin, alpha skeletal muscle Acta1 P68136 37,8 5,4 158 45,2 14/27 2,90E-04 1,44 44 21 F-actin-capping protein subunit alpha-2 Capza2 Q3T1K5 32,9 5,5 176 52,4 10/15 0,0000716 -1,27 -21 22 Myosin binding protein C, fast-type Mybpc2 D3ZA38 127,2 6 148 18,1 17/25 0,0000393 -2,49 -60 23 Myosin binding protein C, fast-type Mybpc2 D3ZA38 127,2 6 104 16,4 16/32 0,0000877 -2,16 -54 24 Myosin binding protein C, slow type Mybpc1 Q63518 126 5,6 258 24,2 29/37 0,00104 1,2 20 25 Myosin binding protein C, slow type Mybpc1 Q63518 126,1 5,6 154 14,3 18/27 0,000351 1,28 28 Energy balance: TCA cycle: Respiratory chain: 19 Structural proteins: 26 Myosin heavy chain IIB [Fragment] Myh4 Q9JHR4 61 5,3 143 23,5 13/18 2,41E-05 3,46 246 27 Myosin-binding protein H 28 Myozenin-1 Mybph O88599 Myoz1 D4A7U8 52,6 6 109 31,6 31,4 9,1 70 20,6 11/32 1,00E-04 -2,02 -50 8/12 0,000033 -1,28 29 Skeletal muscle-specific alpha-actinin 3 Actn3 Q8R4I6 102,9 5,2 286 -22 41,3 36/66 2,29E-05 2,01 101 30 Tropomyosin 1 alpha chain 31 Tropomyosin beta chain Tpm1 P04692 32,7 4,6 Tpm2 P58775 32,8 4,5 225 56,3 21/46 1,45E-06 4,39 339 124 34,9 14/41 0,00000426 3,69 32 Tubulin beta-2C chain Tubb4b Q6P9T8 49,8 269 4,6 262 50,8 26/56 0,00416 -1,23 -19 33 Myoglobin Mb Q9QZ76 34 Myoglobin Mb Q9QZ76 17,1 8,9 163 63,6 12/27 2,83E-05 4,31 331 17,1 8,9 156 72,7 11/21 1,97E-05 5,19 419 35 Serotransferrin Tf 36 Serotransferrin Tf P12346 76,3 7,8 340 36,5 24/25 1,86E-04 1,32 32 P12346 76,3 7,8 337 41,8 26/32 1,17E-04 1,45 37 Serum albumin 45 Alb P02770 68,7 6,1 227 40,3 21/37 2,28E-05 -1,28 -22 38 Serum albumin Alb P02770 68,7 6,1 383 51,3 30/41 7,58E-05 -1,27 -21 Transport proteins: Cell Signaling and Stress Proteins: 39 Alpha crystallin B chain Cryab P23928 19,9 6,9 141 47,7 11/28 2,50E-03 1,36 36 40 Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein Hspa8 P63018 70,8 5,2 226 30,2 17/20 0,00000525 -1,2 -17 41 Tripartite motif-containing protein 72 Trim72 A0JPQ4 52,8 5,8 173 36,9 14/21 0,000394 -1,25 -20 42 Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 1 Vdac1 Q9Z2L0 30,6 8,6 118 34,4 8/16 3,75E-03 -1,68 -40 43 Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 2 Vdac2 P81155 31,7 8,7 119 36,9 8/15 2,64E-04 -1,31 -24 44 Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 2 Vdac2 P81155 31,7 8,7 100 29,2 7/14 3,14E-04 -1,29 -22