Study Guide
advertisement

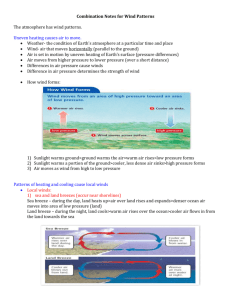
Heat Transfer Study Guide Conduction- transfer of heat through direct contact. Examples: Burning your hand after touching a hot plate Frying bacon in a frying pan Stepping on the hot pavement with bare feet Convection- the movement caused within a fluid by the tendency of hotter and therefore less dense material to rise, and colder, denser material to sink under the influence of gravity, which consequently results in transfer of heat. Examples: Boiling water Hot air balloon Warm weather and Bodies of Water- Weather is largely affected by convection, as air creates breezes over land masses located next to large bodies of water like lakes or oceans. Water has a higher heat capacity than earth, so it holds its heat better. That means it also takes longer to change the water's temperature in either direction. At daytime, the air over the body of water will be a lower temperature than the air over land, creating a low pressure area over the land and a higher pressure area over the water. This movement of air molecules from one pressure system and temperature to the other causes breezes to blow from water to land, altering the temperature. The opposite scenario occurs at night when the sun goes down and the water cools off more slowly than the land. Radiation- the transfer of energy through electromagnetic waves Examples: Being warmed while lying in the sun Cooking in the microwave Heat from a fire Heat from a light bulb