Air Pressure and Wind
advertisement

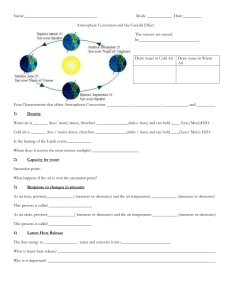
Air Pressure and Wind Main Idea: Differences in air pressure on Earth’s surface cause wind. How Can Air Pressure Change? 1. Volume 2. Height Above Earth’s Surface 3. Temperature 4. Amount of Water Vapor Wind- Air that moves horizontally ( left and right) Updraft- air that rises Downdraft- air that sinks Convection Cells o Warmer air is less dense o Cooler air is more dense o Warm air rises above the denser cool air. o Denser, cool air sinks. o The unequal heating and cooling together causes a circular pattern. o Part of the atmosphere Convection Cell- a circular pattern of air rising, air sinking and wind. o Happen by the water and by mountains. o Cause valley breezes and mountain breezes What are Sea and Land Breezes? Sea breeze- a wind that blows from the sea towards the land. Land breeze- a wind that blows from the land towards water What is the Coriolis Effect? o Coriolis effect- The curving of the path of a moving object caused by Earth’s rotation. In the Northern Hemisphere wind blows to the right. In the Southern Hemisphere winds blow to the left. What are Isobars? Isobar- a line on a map connecting places with equal air pressure. o Help predict how fast air will move.