AROMATIC OXAZOLYL AND CARBOXYL FUNCTIONALIZED

FUNCTIONALIZED 1,1-DIPHENYLETHYLENES AS
PRECURSORS FOR INITIATORS IN ATOM TRANSFER
RADICAL POLYMERIZATION: SYNTHESIS OF
AROMATIC
α
-(BIS)OXAZOLYL AND
α
-(BIS)CARBOXYL
FUNCTIONALIZED POLYMERS BY ATOM TRANSFER
RADICAL POLYMERIZATION
Gabriel J Summers, M Patrick Ndawuni, Nomfusi A Mputumana, Rejoice B
Maseko and Carol A Summers
Department of Chemistry, University of South Africa
PO Box 392, UNISA, Pretoria, South Africa, 0003
Contact email address: summegj@unisa.ac.za
The atom transfer radical polymerization of styrene provides an efficient method for the synthesis of polystyrenes with controlled molecular weight, molecular weight distribution, chain functionality, polymer topology and composition. Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization entails the reversible homolytic cleavage of a carbon-halogen bond of an alkyl halide initiator molecule in the presence of a transition metal/halide catalyst complex such as
CuBr/2,2’-dipyridyl, followed by the successive monomer insertion into the carbon halogen bond during the polymerization process 1
The present research involves the application of the ATRP method to the synthesis of chain end functionalized polymers by utilizing functionalized initiators derived from substituted 1,1-diphenylethylene precursors 2 .
For example, by ATRP methods, the initiation of styrene polymerization with the difunctionalized initiator adduct, formed in situ by the reaction of (1bromoethyl)benzene with 1,1-bis[(4,5-dihydro-4,4-dimethyl-2-oxazolyl)- phenyl]ethylene, in the presence of CuBr/bpy catalyst in solution, proceeded in a controlled/living fashion to afford the corresponding aromatic
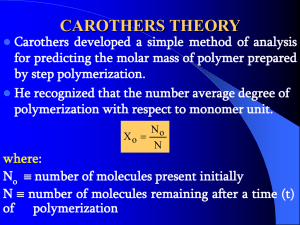
α-(bis)- oxazo lyl functionalized polystyrene. Quantitative yields of α-(bis)oxazolyl polystyrenes with predictable molecular weights and narrow molecular weight distributions were obtained in high initiator efficiency reactions. Deblocking of the oxazolyl groups by successive acid and hydrolysis provides the corresponding aromatic α-(bis)carboxyl functionalized polystyrene in quantitative yields.
O
N
COOH
CH
3
Br
+ i) CuBr / bpy /
DPE / 130 o
C ii) Styrene iii) H / H
2
O
H
3
C CHCH
2
C (CH
2
CH) n
CH
2
CH Br
COOH
O
N
Polymer kinetic measurements show that the polymerization reaction follows first order rate kinetics with respect to monomer consumption and the number average molecular weights increase linearly with monomer conversion.
Similarly, mono- and difunctionalized polystyrenes substituted with the tertiary amine, primary amine, siloxyl and hydroxyl groups were prepared by using the appropriate mono and disubstituted 1,1-diphenylethylene derivatives as precursors in the preparation of functionalized initiators for the atom transfer radical polymerization of styrene.
References
1 Matyjaszewski, K.; Xia, J. Chem. Rev., 2001, 101, 2921.
2 Summers, GJ; Ndawuni, MP; Summers, CA. Polym. Intl. 2003 , 52,158.