Name: Per: ______ Date: Chapter 11 Test Review: Due Monday
advertisement

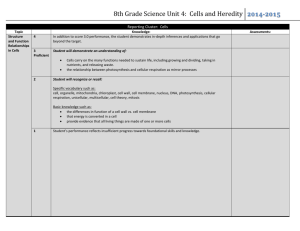
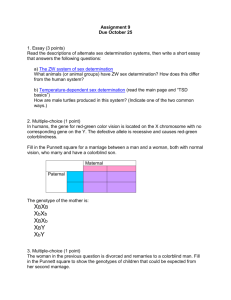
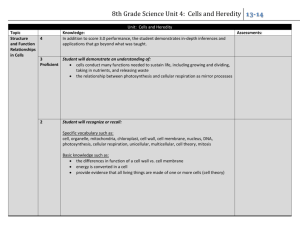
Name: ____________________________________ Per: _____________ Date: ________________________ Chapter 11 Test Review: Due Monday 1. What are two ways that mitosis and meiosis are different? 1. meiosis produces 4 haploid cells, whereas mitosis produces 2 diploid cells 2. mitosis produces body cells, whereas meiosis makes gametes 2. One way mitosis and meiosis are the same? Both go through PMAT, involve interphase (copy DNA), or cytokinesis. 3. What processes increase variation during meiosis? Name two. 1. crossing over 2. segregation 3….independent assortment 4. Identify the number of possible gametes and list them for each genotype: a. Hh: 2; gametes with H or h b. YYKK: 1only type of gamete is YK c. AaTt: 4; can make gametes with AT, At, aT, or at 5. Long tails (L) are dominant over short tails (l) in cats. If two heterozygous long tailed cats (Ll) are mated, there is a 3 long tailed: 1 short tailed ratio seen in offspring. Can these two cats produce 4 kittens with only short tails? Why or why not, explain using probability. Yes it is possible but not probable. The probability of having a short tailed kitten is ¼. So, the probability of having 4 short tailed cats in a row is ¼ x ¼ x ¼ x ¼ which is equal to 1/256. 6. Cystic fibrosis is caused by a recessive allele (cc). a. Set up a Punnett square to show a cross between a dad who is normal (CC) and a mom who has cystic fibrosis (cc). Since dad is CC he can only make gametes with C. Mom has cystic fibrosis so she can only make gametes with c. Therefore, the only genetic combination of the two gametes is Cc b. Identify the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the possible offspring. All (100% or 1/1 or 4/4 ) offspring will have the genotype of Cc. Therefore the phenotype ratio of the kids will be 100% normal, even though they have a gene for cystic fibrosis. c. A child produced from the cross in part a mated with another individual with the same genotype. Show the cross with a Punnett Square. The cross would be Cc x Cc. This will produce a Punnett square with 4 boxes since each “parent” can pass on either a C or a c. This should result in 3:1 ratio of phenotypes. 7. In tigers, a rusty-orange color (R) is dominant to white (r) and brown eyes (B) are dominant to green eyes. a. A tiger that is homozygous dominant for both traits is mated with a white, green-eyed tiger. Show a Punnett square for this cross. Since the tiger that is homozygous dominant for both must have the genotype of RRBB, the only kind of gamete it can produce is RB. The other tiger is white with green eyes; both recessive traits. Therefore, it’s genotype must be rrbb. It can only produce one kind of gamete; rb. As a result, only one type of offspring can result from this cross: when the RB gamete fertilizes the rb gamete only RrBb offspring result. b. What are the genotypes and phenotypes for this cross? See above, since only RrBb offspring result, the genotype ratio is: all (100%) RrBb. The phenotype ratio would be all rust colored fur with brown eyes. c. A tiger who is heterozygous (RrBb) for both traits is mated with a tiger who is recessive for both traits (rrbb). Show this cross using a Punnett square. Heterozygous tigers can produce 4 kinds of gametes: RB, Rb, rB, and rb. The other tiger can only produce one kind of gamete: rb. Therefore, there should only be 4 boxes to a Punnett square. The 4 types of offspring produced are RrBb, Rrbb, rrBb, and rrbb. 8. In horses, white and brown spotted horses are produced by mating a brown horse (BB) with a white horse (WW). a. What type of inheritance is seen when a white and brown spotted horse is produced? This would describe the codominance inheritance pattern. b. Explain how it is possible for two white and brown spotted horses to produce both white and brown offspring. Show a Punnett square. Brown and white horses contain genes for both colors, BW. If two of these are mated, each can produce two types of gametes: B or W. As such, there could be four boxes to a Punnett square. Each possible offspring could be BB, BW, or WW (in a 1:2:1 ratio)