Body+system+Chart+Answers
advertisement

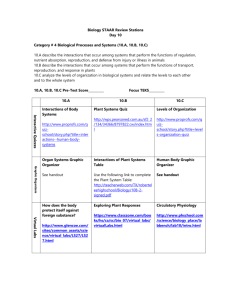
1 Human Body Systems Mega Chart Body system Parts What they do What other systems they interact Integumentary Oil glands Produce sebum to make the skin waterproof and resistant to invasion by bacteria Immune Sweat glands Produce sweat to cool body and maintain homeostasis; nitrogen waste is in the sweat Excretory Hairs & hair follicles Follicles contain the hair; hair raises up to catch a layer of warm air to warm the body Sensory nerves Receive information from the external environment & pass it to the brain Nervous Musculatory Smooth muscle Circulatory, digestive, nervous, excretory, respiratory, & reproductive Remember, muscles can’t push, they can only pull. Striated muscle Spindle shaped; lines all the “tubes” of the body to regulate the passage of liquids & solids through the body & light into the eye Found in arteries, digestive tract, air tubes, urinary tract, & reproductive structures Striped, moves muscles, usually voluntary, though diaphragm also moves involuntarily Cardiac muscle Striped & branched; muscle tissue of the heart, only Circulatory Tendons Heavy fibers that tie muscles to bones so muscles can move bones Skeletal Compact bone Heavy layers of bone that cover spongy bone & make up the middle of the long bones; give strength to the bone; contains yellow marrow Channels through compact bone that carry blood vessels & nerves to feed, clean, and give sensation to bones & bone cells Lies at ends of long bones & in cuboidal & flat bones, covered by compact bone; contains the red marrow Produces red & white blood cells & platelets Musculatory Skeletal Haversian canals Spongy bone Red marrow Yellow marrow Nutrient rich fat found in the core of the long bones; storage Epiphyses Ends of long bones where the bond grows Ligaments Heavy fibers that tie bones to bones Joints- ball & socket Hip & shoulder; knob of one bone fits into a socket made by other bones &/or muscles - pivot Head on top of spine; allows head to swivel to give animal greater field of view - hinge Elbow, knee, finger joints; allows two bones to move against each other -gliding Vertebrae in spine; gives great flexibility to the spine - saddle Thumb; allows greater range of motion with the thumb Skeletal & Respiratory Nervous & Circulatory Circulatory & Immune Circulatory & Immune 2 Respiratory Digestive Excretory Nose Takes in, filters & warms air Pharynx Throat, passes air to larynx Larynx Voice box, protected from food by the epiglottis, passes air to trachea Trachea “Wind pipe,” passes air to bronchi Bronchi Trachea splits into two tubes going to the two lungs; bronchi pass air to bronchioles Bronchioles Smaller tubes that will branch & branch again until they carry air to the alveoli Alveoli Millions of little air bags where CO2 & O2 are exchanged. Mouth Takes in food & begins breaking it down by chewing & with saliva Pharynx Throat- carries food to esophagus Esophagus Long muscular tube down through neck & chest to stomach Stomach Muscular bag that squishes & grinds food while adding digestive acids & enzymes Small intestine Absorbs fats, proteins, and other nutrients Large intestine Absorbs water Liver Makes some of the digestive chemicals including bile- for digesting protein; also cleans the blood of toxins Pancreas Makes insulin & glucagon to control the levels of sugar in the blood Renal arteries & veins Carry “dirty” blood to the kidneys and clean, filtered blood away Kidney Principal organ for removing nitrogen waste from the blood Nephron- makes urine Thousands of these tubular filtering systems are found in the kidney to filter the blood & remove waste, excess salt, & excess water from bloodfunctional unit of the kidney Ureter Drains the kidney into the bladder Urinary bladder Stores the urine Urethra Drains the bladder to the outside Immune- barrier defense Respiratory Digestive & circulatory circulatory 3 Reproductive Ovaries Produce eggs & hormones to maintain a pregnancy or bring on the menses Fallopian tube Carries released egg from the body cavity to the uterus; fertilization occurs here Uterus Muscular organ where the embryo may implant itself & grow to maturity; contractions of the uterus cause birth Neck of the uterus; stays closed during pregnancy, but thins out to permit birth Cervix Nervous Vagina Birth canal- stretches to allow baby to be born; also receives sperm Testes Male gonad- produces hormones & sperm Brain Runs the body; made up of white matter & grey matter & 3 kinds of nerves, covered by three membranes Runs down the vertebral column through openings in each vertebrae, carries nerve tracts for both incoming & out going nerves Receive info from internal & external environment & carry it to the spinal cord & brain Spinal cord Sensory nerves Motor nerves Receive commands from the brain & run to a muscle or gland to activate it to do the command Interneurons In spinal cord & brain; connect incoming to outgoing nerves so the signal may pass in as many directions as needed Nerve cells consisting of cell bodies, incoming dendrite fibers, & an outgoing axon fiber Neurons Circulatory Heart Pumps blood Atria Receives blood from body or lungs & pumps it to a ventricle; Humans have 2 of them Ventricle receives blood from atria and pumps it to the heart or lungs; humans have 2 of them Ventricles Arteries Carry blood away from heart to lungs or body parts (organs, muscles, etc.), largest is the aorta Arterioles Smaller, blood vessels carry blood to capillaries Capillaries Tiny blood vessels with walls one cell thick that feed & clean cells Venules Blood vessels that drain capillary beds into larger & larger veins going back to heart Veins Drain blood from body or lungs into heart, largest veins are the Vena Cavae Endocrine Endocrine 4 Immune Barrier defenses B cells T cells Make antiviral compounds like cytokinins & interferons; attack cancers Spleen Stores “extra” blood & Lymph nodes Stores B-cells & T-cells, especially B-memory cells. Pathogens are brought to it so that B&T cells can start the attack! Lymph nodes that surround the throat; there are 3 kinds Tonsils Endocrine Lining of alimentary canal & respiratory, reproductive & excretory systems; Skin; tears & conjunctiva of the eye Make antibodies to attack & kill bacteria, remember virus & bacteria; give immunity Hypothalamus Pituitary Thyroid “Master gland” controls other glands, also triggers gonads to start puberty, regulates growth, birth, and many other processes Is controlled by hypothalamus, sends chemical messages to other glands & triggers gonads to start puberty, regulates growth, birth, and many other processes Stimulates & controls metabolism Raises blood calcium levels Parathyroid Lowers blood calcium levels Adrenal Produces epinephrine& norepinephrine to manage emergency responses Ovary Controls female secondary sex characteristics and reproduction; produces eggs, helps maintain pregnancy or start menses Controls male secondary sex characteristics and reproduction; produces sperm Testes Pineal Controls biorhythms Thymus Functions in immune response- helps children develop immunity Pancreas Insulin & glucagon to control blood sugar levels Respiratory, digestive, reproductive, & excretory systems