Bellwork #25 DNA vs. RNA

Bellwork #25 DNA vs. RNA
1 ___________________________ contains the instructions that cells need in order to make every
2 ____________ required to carry out their activities and surv i ve . It is made of two strands of monomers called 3 _______________ , and the two strands are said to be 4 _______________ to each other because the bases on one strand match up with their partner on the other strand.
5 _______________ is made of 6 _____________ , and is essential in the process of 7 _ _ ________ synthesis. One way it differs from other nucleic acids is that it uses the base 8 ____________ instead of
9 ____________ . A gene's instructions for making a protein are coded in the sequence of 1 0 _________ bases in the DNA.
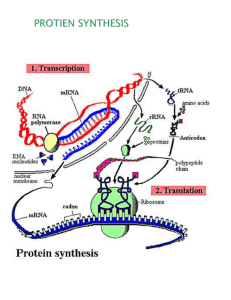
The instructions for making a protein are transferred from a 1 1 _________________ to an
RNA molecule in a process called 12 _______________________ . During this step, an enzyme called
1 3 ___________________ opens the double heli x at a promoter region , and adds complementary RNA nucleotides until it reaches a stop signal.
This form of RNA , called 1 4 ____________ , travels out of the nucleus to the 1 5 ___________ .
There , the transcript is "read" by another type of RNA called 16 _______________ . The ribosome moves along the transcript three nucleotide bases at a time. These three-base sequences are called
17 ____________ and correspond with one particular 1 8 _____________ . A third type of RNA called
1 9 _____________ has a region called the 2 0 ____________ that is complementary to the transcript.
Each of these clover-shaped RNAs carry with it a particular 2 1 _________________ , according to the
2 2 ______________ . The ribosome assists in assembling the amino acids in sequence , thus producing a
2 3 ____________ . This process of reading the transcript and resulting in a chain of amino acids is called 2 4 ________________ .
_______________________________________________ WORD BANK __________________________________________________ a. anticodon e. codons b. genetic code c. protein (x3) d. RNA polymerase f. messenger RNA g. ribonucleic acid h. transcription i. complementary j. nucleotide(s) (x3) k. ribosomal RNA l. transfer RNA m. uracil q. thymine n. translation r. cytoplasm o. gene
s. amino acid (x2)
p. deoxyribonucleic acid