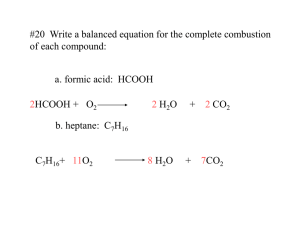
Chapter One: Matter and Change What is the difference between a
advertisement

Chapter One: Matter and Change 1. What is the difference between a physical and a chemical property? 2. List 4 evidences of a chemical change: 3. Classify the following as either a chemical or physical change: Ice melting: Wood burning: Formation of a precipitate: Milk sours: Water being absorbed by a sponge: 4. Fill out the following chart: Volume Forces of Attraction Diffuse Rates Solid Liquid Gas 5. Identify whether the following is an intensive or extensive property: -Color: -Mass: -Volume: -Melting/ Freezing point: -Conductivity: Chapter 2: Measurements and Calculations Questions/Problems Page 1. What is the volume, in cubic centimeters, of an object that is .52 cm long, 6.3 cm wide, and 4.8 cm high? 2. How many significant figures are in each of the following: a. 74513 b. 5690 c. 0.365 d. 0.0004 e. 6789.0 f. 7.00120 3. Write the following numbers in scientific notation. a. 0.000623 b. 5.00000 c. 0.00000000459 4. Find the density of a block of wood that has a mass of 3.49 g and occupies 7.43 mL. (Use significant figures.) 5. a. Find the number of kilometers in 93.72 m. b. Find the number of mL in .625 L. Chapter 3 1. Using John Dalton’s Law of Multiple Proportions, what is the whole number ratio of masses for oxygen between H2O and H2O2? 2. Atoms cannot be __________, ___________, or ___________. 3. Explain the set up for Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment and the conclusions he came to. 4. What is the atomic number, mass number, and element name of the following element? 5. Calculate the average atomic mass of Cesium if: 75% of 133 Cs 20% of 132 Cs 5% of 134 Cs Chapter 4 – there are no questions for this section Chapter 5: The Periodic Law 1. Label the trends on the following periodic table.(Hint there are a total of 6) a. Describe the properties of Copper (at least four), then include the Noble Gas Configuration. 2. Place the following elements in order from highest ionization energy to lowest: (K,Al,Se,O,Fr,I,F) 3. Why does atomic radii decrease as you move from left to right across a periodic table? Why does it increase as you move down a period? 4. Determine the number of Valance Electrons below. Xenon_____ Barium_____ Sulfur______ Iron________ Iodine____ Zinc______ Fluorine___ Mercury___ 5. For each of the following questions tell whether electrons will be gained or lost in a formation of a compound and give number of the amount of electrons involved. Group 18_____ # of e-__ Group 14______ # of e-__ Group 16_____ # of e-__ Group 1_______ # of e-__ Group 2______ # of e-__ Group 13______ # of e-__ Important Info: Periodic law Periodic table Transition elements Main-group elements Lanthanide Period Metals,Non-Metals,Metalloids Halogens Atomic Radius Cation Anion Actinide Electron and Noble Gas Configuration Metallic Behavior Valence Electrons Electronegativity Dmitri Mendeleev Henry Moseley Group S,P,D,F Blocks Reactivity Periodicity Ion Ionization Alkali metals Alkali-earth metals Ionization Energy Electron Affinity Ch. 6: Covalent Bonding Questions/Problems 1. 1. Why 2. 2. List 3. 3. How 4. 4. Identify 5. are noble gases known for being the least reactive elements? the four exceptions to the octet rule including the # of pairs of electrons needed to bond. 5. Draw many electrons are shared in a single, double and triple bond? each compound as ionic, covalent or both. a. MgO: c. BaSO4: b. HCl: d. H2O: Lewis Dot Structures for the following compounds a. CO2: c. CH4: b. N2: d. BF3: Chapter 6: Chemical Bonding; Ionic 1. What is the difference between Ionic bonding and Covalent bonding? 2. Draw the electron configuration for the following: a. F b. K c. Cl d. Al 3. Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for the following: a. Ammonium,NH3 b. Hydrogen Sulfide,H2S 4. Use VSEPR theory to predict the molecular geometry of the following: a. CH4 b.BeF2 5. What are the four types of Intermolecular forces? Chapter 6 Metallic Bonding – there are no questions for this section. Chapter 7 Questions - Covalent 1. Write the chemical name for Si2Br6 2. Write the chemical name for SbBr3 3. Write the chemical formula for Dinitrogen Trioxide 4. Write the chemical formula for Hydrogen Iodide 5. What do the subscripts in a chemical formula for a covalent compound indicate? Chapter 7 – Chemical Formulas and Chemical Compounds; ionic 1. What is the formula for Magnesium Phosphate? 2. What is the name for the compound NH4 OH? 3. Find the formula mass of Potassium Nitrate, KNO3. 4. Find the percentage composition of Copper (I) Oxide. 5. A 10 gram sample of a compound contains 7.22 grams of magnesium and 2.78 grams of nitrogen. What is its empirical formula? Chapter 8 Problems 1. Balance the following equations a) __ CaCl2 + __ H2O __ CaO + __ HCl b) __ Al + __ Pb(NO3)2 __ Al(NO3)3 + __Pb c) __Cu2S + __O2 __ Cu2O + __ SO2 d) __ C2H6 + __O2 __CO2 + __ H20 2. Write the formula equation from the word equation and classify the reaction type. Calcium phosphate and aluminum sulfate yields aluminum phosphate and calcium sulfate 3. Write the word equation as a formula equation and balance. Indicate reaction type. Potassium chlorate when heated yields potassium chloride + oxygen gas 4. Name the following compounds and indicate their bond type. a) H2S b) C3H6 c) CuSO4 d) P4O10 5. Predict the products of the word equation. Write the balanced formula equation with states of matter. (S= Synthesis D= Decomposition DD= Double Displacement SD= single displacement) a) _______ Mercury(II) and oxygen b) _______ Zinc carbonate is heated c) _______ Sodium bromide and silver nitrate d) _______ Aluminum metal and hydrochloric acid Chapter 9: Stoichiometry – there are no questions currently for this section Chapter 10 - States of Matter 1. Explain why the water in a graduated cylinder forms a meniscus? 2. As temperature increases, kinetic energy_________. As temperature decreases, kinetic energy________. In conclusion temperature and kinetic energy are _________ related. 3. Determine whether the following describes a real gas, ideal gas, or cannot be determined: a. ___________This substance has hydrogen bonding forces, but not london dispersion forces b. ___________ A theoretical gas (doesn’t actually exist) c. ___________ There is no net loss of energy when this substances gas particles collide d. ___________ The substance is under extremely high pressure and has a low temperature e. ___________ The gases particles move at a high speed f. ___________ The substance contains lots of particles that are spaced far apart relative to their size 4. Refer to the graph while reading the following directions and answering the following questions: a. Label the critical point, where the supercritical fluid exists, and triple point b. Fill in the boxes with the correct phase changes c. ___________ What state of matter is A? d. ___________ What state of matter is B? e. ___________ What state of matter is C? f. ___________ As pressure increases does the substance freeze or melt? 2 B Pressure (Atmosphere) A C 0 Temperature (°C) 5. Refer to the graph to answer the following questions a. Label the following stages on the graph: liquid, gas, solid, heat of vaporization, heat of fusion, and also label the boiling point and melting point b. __________ Is this a heating or a cooling curve? 100 0 6. How do you differentiate between a chemical change and a phase change. (Include all of the signs of a chemical change.) Chapter 11:Gases 1. A gas occupies a volume of 17.0 L of pressure at 21.0 mm Hg. What is the volume when pressure is increased to 42.0 mm Hg? 2. If you increased the volume in the container, does the gas increase or decrease? Why? 3. A container holds three gases: hydrogen, helium, and nitrogen. The partial pressures are 7.00 atm, 8.00 atm, and 9.00 atm. What is the total pressure inside the container? 4. A gas has a volume of 135 ml when its temperature is 53 degrees Celsius. What change in temperature reduces its volume to 117 ml? (In Kelvin) 5. Some hydrogen occupies .450 L when its pressure is 720 torr. How many ml will it occupy when its pressure is 750 torr? CHAPTER 12: SOLUTIONS 1. How can you tell if a reaction is small or weak? 2. Fill in the chart below: Solutions Type of Mixture (homo/heterogeneous) Colloids Suspensions Particle Size Separation of components? Can it be filtered? Tyndall Effect? Are the properties Uniform or Non-uniform throughout? 3. What happens to the solubility of a gas when the temperature increases? When the pressure increases? When the volume decreases? 4. How many moles of solute are present in the following solutions a. 700 mL of a .40 M CuSO4 solution b. 800 mL of a .20 M NaCl solution 5. Find the molality of the following solutions a. 5.0 moles of NaCl is dissolved in 2 Kg of water b. 20 grams of I2 dissolved in 200 grams of alcohol Chapter 13: Colligative Properties – there are currently no questions for this section Chapter 14: Acids and Bases – there are currently no questions for this section Chapter 15 Acid-Base Titrations and pH - there are currently no questions for this section Chapter 16 Reaction Energy Review 1.) If a 3.00g sample of water at 10.0 oC absorbed 32.7J of heat, what will the final temperature be? 2.) Calculate H for the reaction 2Al(s) + 3Cl2(g) -> 2AlCl3(s) from the data given. 2Al(s) + 6HCl(aq) -> 2AlCl3(aq) + 3H2(g) H= -1049kJ HCl(g) -> HCl(aq) H= -74.8kJ H2(g) + Cl2(g) -> 2HCl(g) H= -1845kJ AlCl3(s) -> AlCl3(aq) H= -323kJ 3.) a.) What is the freezing point of the substance? b.) What is the melting point of the substance? c.) What is the boiling point of the substance? d.) Which number represents the solid being warmed? e.) Which number represents the gas being warmed? f.) Which number represents the liquid being warmed? g.) Which numbers indicate the change in kinetic energy? h.) Which numbers indicate the change in potential energy? Important Values Cp H2O (s) = 2.06 J/g oC Cp H2O (l) = 4.18 J/g oC Cp H2O (g) = 1.84 J/g oC For H2O Hfus = 6.00 kJ/mol Hvap = 40.6 kJ/mol T = T - Tinitial 4.) Calculate thefinal total amount of heat energy necessary to change 95 g of ice at -5oC into steam at 125oC . Show and label all calculations. Water freezes at 0 oC and boils at 100 oC. Steps Equation Calculation Energy Energy in KJ Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Step 5 Total Heat Energy: 5.) Calculate the value of H. Fe2O3(s)= -824.8 HCl(g)= -92.3 Fe2O3(s) + 6HCl(g) -> 2FeCl3(s) + 3H2O(g) FeCl3(s)= -399.4 H2O(g)= -241.8 Chapter 17 Reaction Rates Questions 1. A rate of reaction is determined by what four factors? 2. What is the formula for rate or reaction? 3. What is the rate of reaction for a substance that’s concentration goes from 150 mol to 180 mol in 15 seconds? 4. H2O -> 2H2 + O2 Find the reaction rate for the reaction above if k= 1.14 and water has a concentration of 2.04M 5. The decomposition a substance at 504 Celsius is first order with a half-life of 1570 seconds. What is the initial amount of substance remains after 4710 seconds? Chapter 18Chemical Equilibrium Review 1. Answer these questions by filling in the blank or with a True or False answer. If false explain why. A reversible reaction is when the products and reactants can both react and form____________. a) True or False: Completion is when all compounds are almost completely removed from the solution. b) Chemical equilibrium is when both reactions react at the same rate and the ________ of the products and reactants are unchanged c) In the general equilibrium expression [C]x [D]y A and B represent ________ and C and B represent ________. [A]n [B]m 2. In the unbalanced reaction below what is the value of K if Ba=17, OH=5.5 and Ba(OH)2=30? Ba (s) + OH (aq) Ba(OH)2 (aq) 3. In the unbalanced reaction below does the reaction favor the products or reactants if Zn=13, HCl=35, ZnCl2=225.5 and H2=4.5 Zn(s) + HCl(aq) ZnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g) 4. In the reaction below answer the questions regarding the Equilibrium Shift based on the changes mentioned. 2Na(s) + I2(g) 2NaI(aq) + 15 Kcal a) Increase Na b) Decrease I2 c) Decrease Temp. 5. In the reaction below, describe the effect on the individual components of the reaction based on the questions below. 30Kcal + 2Al(s) + 6 H(NO3) (aq) 2 Al(NO3)3 (aq) + 3H2 (g) a) If Temperature is increased how will Al(NO3)3 be affected? b) If H2 is decreased how will Al be affected? c) If H(NO3) is increased how will Al be affected? Chapter 19 & 20 Q- What are redox reactions? Identify the atom oxidized, the atom reduced, the oxidizing agent, the reducing agent, the oxidation half reaction, the reduction half reaction P1- Mg + HCl => MgCl2 + H2 P2- Fe + V2O3 => Fe2O3 + VO P3- KMnO4 + KNO2 + H2SO4 => MnSO4 + H2O + KNO3 + K2SO4 P4- K2Cr2O7 + SnCl2 + HCl => CrCl3 + SnCl4 + KCl + H2O Organic Chemistry - Chapter 22 1. What is the numerical formula to determine the amount of Carbons and Hydrogens in an alkyne? For example CNH? 2. What Functional group is this? R-COOH 3. Name this. C4H8 4. What are the first four prefixes used to name an organic compound? For example 5- Pent, 6- Hex 5. 5. Write a 7 carbon alkane