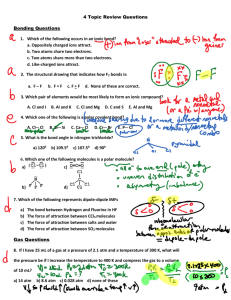
Supplemental methods: equations From the data collected in each
advertisement

Supplemental methods: equations From the data collected in each step calculated values were obtained by the following equations: - the membrane lung (ML) blood flow resistance (Res, mmHg/L/min): Res (mmHg/L/min) = P_in (mmhg) − P_out (mmhg) BF (L/min) where P_in was the blood circuitry pressure at ML blood inlet (Blood_IN) (mmHg), P_out was the blood circuitry pressure at ML blood outlet (Blood_OUT) (mmHg), and BF was the blood flow (L/min); - the oxygen content at Blood_IN (CinO2, mL/dL): CinO2 (mL/dL) = 1.34 × Hb (g/dL) × SinO2 (%) + 0.0031 × p_inO2 (mmHg) 100 where Hb was the hemoglobin (g/dL), SinO2 was the O2 saturation at Blood_IN (%) and p_inO2 was the O2 partial pressure at Blood_IN (mmHg); - the oxygen content at Blood_OUT (CoutO2, mL/dL): CoutO2 (mL/dL) = 1.34 × Hb (g/dL) × SoutO2 (%) + 0.0031 × p_outO2 (mmHg) 100 where Hb was the hemoglobin (g/dL), SoutO2 was the O2 saturation at Blood_OUT (%) and p_outO2 was the O2 partial pressure at Blood_OUT (mmHg); - the ideal hemoglobin “capillary ML blood” saturation (SiO2, %): SiO2 (%) = 100 − COHb (%) − MetHb (%) where COHb is the average between carboxyhemoglobin at Blood_IN and Blood_OUT (%) and MetHb is the average between methemoglobin at Blood_IN and Blood_OUT (%); - the ideal oxygen content of “capillary ML blood” (CiO2, mL/dL): CiO2 (mL/dL) = 1.34 × Hb (g/dL) × SiO2 (%) + 0.0031 × 713 100 where Hb was the hemoglobin (g/dL), SiO2 was the ideal O2 hemoglobin ML saturation (%); - the ML BF shunt fraction (Qs/Qt, %): Qs/Qt (%) = - CiO2 (mL/dL) − CoutO2 (mL/dL) × 100 CiO2 (mL/dL) − CinO2 (mL/dL) the ML oxygen uptake (VO2 , mL/min), according to the Fick equation: VO2 (mL/dL) = (CoutO2 (mL/dL) − CinO2 (mL/dL)) × BF (L/min) × 10 - the ML gas outlet mix carbon dioxide partial pressure (peCO2, mmHg) peCO2 (mmHg) = 713 (mmHg) × [expCO2 ] (ppm) 1000000 where [expCO2] was the CO2 fractional concentration (ppm) measured by CO2 analyzer at the ML gas outlet (Gas_OUT); - the ML dead space (Vd/Vt, %), according to the Bohr method: Vd/Vt (%) = p_outCO2 (mmHg) − peCO2 (mmHg) × 100 p_outCO2 (mmHg) where p_outCO2 was the CO2 pressure at Blood_OUT (mmHg); - the ML carbon dioxide removal (VCO2, mL/min) was calculated: VCO2 (mL/min) = - GF(L/min) × [expCO2 ](ppm) 1000 the ML CO2 removal efficiency ratio (VCO2/CO2in, %) was computed as the ratio between VCO2 and total CO2 content in the ML inlet blood sample: VCO2 /CO2 in (%) = VCO2 (mL/min) 22.41 × inCO2 (mMol/L) × BF(L/min) where in CO2 was the total CO2 at Blood_IN calculated as follows: inCO2 (mMol⁄L) = inHCO− 3 (mMol⁄L) + (0.03 × p_inCO2 (mmHg) ) where inHCO3- and p_inCO2were the bicarbonate ion concentration (mMol/L) and the CO2 partial pressure (mmHg) at Blood_IN, respectively. Supplemental results: tables Baseline GF Patient ML ML day of use (L/min) peCO2 After-RM VCO2 VO2 (mL/min) (mmHg) (mL/min) Vd/Vt (%) peCO2 VCO2 (mmHg) (mL/min) Qs/Qt (%) VO2 (mL/min) Vd/Vt (%) Qs/Qt (%) 1 1 2 5 22.7 159 167 49.2 8.3 24.7 173 158 31.1 7.4 1 1 3 4 19.1 107 168 61.9 7.6 24.5 137 156 45.1 8.0 1 1 8 7 15.4 151 146 60.3 10.7 17.5 172 144 48.9 11.0 1 1 9 6 15.8 133 131 54.5 14.0 19.7 166 132 36.1 11.5 1 1 13 4 18.9 106 103 52.8 23.1 19.8 111 99 49.7 18.8 2 2 1 3 36.4 153 137 8.2 6.0 33.5 141 141 5.6 4.5 2 2 4 4 21.3 120 140 40.9 5.0 20.6 116 146 29.4 6.4 2 3 8 6 17.5 147 150 52.8 5.4 21.2 179 155 27.2 5.1 2 4 2 4 18.1 101 103 47.4 3.8 24.2 136 104 18.2 3.0 3 5 8 7 11.3 111 187 71.7 11.5 17.9 176 207 50.5 9.8 4 6 19 9 13.2 166 137 63.8 10.8 14.0 177 138 58.1 7.4 5 7 2 5 24.4 171 217 52.1 10.5 33.6 235 205 21.2 8.8 5 8 3 7 21.2 208 223 48.0 9.2 24.2 238 214 32.9 8.7 5 9 2 6 21.2 179 145 51.9 7.2 25.5 215 158 23.6 2.4 5 9 4 5 25.8 181 174 44.9 7.3 28.6 201 184 23.5 4.1 5 10 3 6 23.0 194 169 43.1 7.2 27.4 230 183 21.8 4.4 5 11 5 5 24.2 169 137 45.7 5.0 30.4 213 139 20.8 3.9 6 12 6 2 23.2 65 152 47.5 8.0 36.1 101 158 12.5 4.5 7 13 1 4 33.3 187 152 9.3 5.9 32.2 180 159 6.8 4.8 7 13 4 6 19.4 163 165 49.7 9.4 22.5 189 178 29.5 6.3 Table S1. Results of membrane lung (ML) gas exchanges during all tests at Baseline and After-RM steps Hemodynamics p value Baseline After-RM Heart Rate (bpm) 105 ± 12 102 ± 21 0.73 Systolic Arterial Pressure (mmHg) 118 ± 26 115 ± 22 0.31 Diastolic Arterial Pressure (mmHg) 62 ± 12 60 ± 12 0.46 Mean Arterial Pressure (mmHg) 79 ± 15 78 ± 12 0.47 Systolic Pulmonary Pressure (mmHg) 33 ± 6 31 ± 6 0.14 Diastolic Pulmonary Pressure (mmHg) 17 ± 3 16 ± 5 0.97 Mean Pulmonary Pressure (mmHg) 24 ± 3 22 ± 5 0.73 Wedge Pressure (mmHg) 12 ± 4 10 ± 5 0.10 Central Venous Pressure (mmHg) 9±4 8±3 0.34 Cardiac Output (L/min) 7.5 ± 1.3 7.2 ± 1.4 0.35 Internal Temperature (°C) 37.2 ± 0.3 37.2 ± 0.3 0.27 End Tidal CO2 (mmHg) 36 ± 3 34 ± 6 0.10 Pulse Oximeter Saturation (%) 97 ± 2 96 ± 3 0.37 Table S2. Hemodynamics at Baseline and After-RM steps. Data are reported as mean ± standard deviations. No statistical significance was found. Baseline After-RM 1hr-RM 2hr-RM 4hr-RM 6hr-RM ML gas transfer VCO2 (mL/min) VO2 (mL/min) 177 ± 12 A,B 210 ± 15 C 194 ± 16 D 188 ± 16 D,E 180 ± 16 A 171 ± 11 B 158 ± 16 A 168 ± 19 A,B 180 ± 19 B 174 ± 24 A,B 173 ± 21 A,B 164 ± 23 A,B Circuitry Blood Gas Analyses Blood_IN 7.410 ± 0.042 A 7.444 ± 0.041 B 7.467 ± 0.042 B 7.468 ± 0.045 B 7.447 ± 0.035 B 7.436 ± 0.023 A,B pCO2 (mmHg) 55.2 ± 0.4 A 49.1 ± 4.8 B,C 45.7 ± 5.1 C 45.9 ± 4.7 B,C 48.3 ± 4.7 B,C 49.6 ± 4.3 B HCO3- (mMol/L) 34.3 ± 4.9 A 33.2 ± 4.5 A,B 32.4 ± 4.5 B 32.6 ± 4.4 B 32.6 ± 4.0 B 32.5 ± 4.5 B pO2 (mmHg) 45.9 ± 3.4 A 43.1 ± 3.9 A 41.6 ± 3.2 A 43.5 ± 4.3 A 43.3 ± 1.4 A 44.4 ± 2.9 A HbO2 (%) 77.2 ± 3.2 A 76.4 ± 3.1 A 74.8 ± 2.2 A 75.7 ± 3.1 A 74.8 ± 3.1 A 76.6 ± 4.0 A pH Blood_OUT 7.487 ± 0.030 A 7.544 ± 0.032 A,B 7.555 ± 0.038 B 7.548 ± 0.029 B 7.543 ± 0.028 A,B 7.507 ± 0.021 A,B pCO2 (mmHg) 42.9 ± 3.3 A 35.2 ± 2.7 B,C 33.2 ± 2.3 C 34.1 ± 2.8 B,C 36.3 ± 3.8 B,D 38.6 ± 4.0 D HCO3- (mMol/L) 31.4 ± 4.6 A 29.8 ± 4.1 B 29.1 ± 3.7 B 29.2 ± 3.7 B 29.7 ± 3.9 B 30.0 ± 4.0 B 540.2 ± 21.2 B 588.7 ± 25.2 A 578.6 ± 21.1 A,B 569.4 ± 27.8 A,B 547.0 ± 32.5 A,B 539.5 ± 28.5 A,B 97.6 ± 0.2 A 97.6 ± 0.2 A 97.6 ± 0.2 A 97.6 ± 0.2 A 97.5 ± 0.3 A 97.5 ± 0.3 A pH pO2 (mmHg) HbO2 (%) Table S3. RM long-term evaluation: membrane lung (ML) gas transfer and circuitry blood gas analyses. Blood_IN and Blood_OUT are the blood withdrawal at the ML inlet and ML outlet, respectively. Data are reported as mean ± standard deviations. Steps not connected by the same letter are significantly different (p < 0.05). Supplemental results: figure legends Figure S1. Panel A: correlation between membrane lung (ML) dead space fraction (Vd/Vt, %) at Baseline step and ML days of use. Panel B: correlation between Vd/Vt at After-RM step and ML days of use. Figure S2. Panel A: correlation between membrane lung (ML) shunt fraction (Qs/Qt, %) at Baseline step and ML days of use. Panel B: correlation between Qs/Qt at After-RM and ML days of use. Figure S3. Panel A: correlation between membrane lung (ML) dead space fraction (Vd/Vt, %) and ML shunt fraction (Qs/Qt, %) at Baseline step. Panel B: correlation between Vd/Vt and Qs/Qt at After-RM step.