Chemistry 161. Test Three. April 20, 2010. Name R = 0.08206 L atm
advertisement

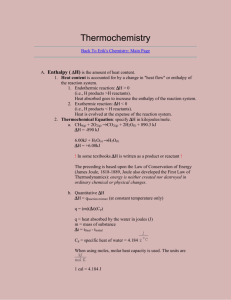
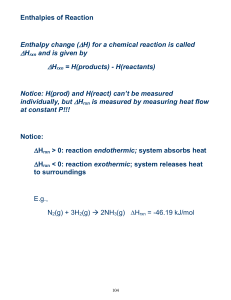
Chemistry 161. Test Three. April 20, 2010. Name ______________________________________________ R = 0.08206 L atm / mol K h = 6.626 x 10-34 J sec c = 3.00 x 108 m/sec Part One. Twenty-five points. _____ 1) The reaction CH4(g) + 2 O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g) Hrxn = -802 kJ. What is the energy for the following 3 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(g) → 3 CH4(g) + 6 O2(g) a- -802 kJ b- +2406 kJ c- -2406 kJ d- +267 kJ _____ 2) A gas occupies 345 mL at 100oC. The volume at 200oC will be a- 437 mL b- 690 mL c- 172 mL d- 345 mL _____ 3) When is a gas is most likely to NOT be ideal a- high temperature and low pressure b- low temperature and high pressure c- low temperature and low pressure d- high temperature and high pressure _____ 4) Sulfur trioxide gas diffuses through a tube at a rate of 22.1 cm/min. A second gas diffuses at the rate of 31.2 cm/min. The second gas is a- CO2 b- H2S c- NO d- Ar _____ 5) A gas occupies 255 mL at 800. torr and -25.6 oC. What is the volume at STP? a- 220 mL b- 268 mL c- 296 mL d- 342 mL _____ 6) A gas mixture is made of 34.5 g of CO2 and 28.7 g of He. The total pressure is 675 mmHg. What is the pressure of the CO 2? a- 66.5 mmHg b- 675 mmHg c- 368 mmHg d- 275 mmHg _____ 7) The average kinetic energy of a mixture of different gas molecules is a- independent of the temperature b- dependent on the molar mass of the individual molecules c- dependent on the type of covalent bonding present d- dependent only on the temperature _____ 8) Which of the following is not a postulate of the Kinetic Molecular Theory of gases a- gas molecule travel in straight lines until they collide or are attracted to another gas molecule b- collisions between gas molecules are elastic c- gas molecules have tiny volumes approaching zero volume d- gas molecules are moving constantly and randomly _____ 9) A two meter tube (sealed at one end) is completely filled with mercury and then inverted into a pan of mercury (no mercury is spilled). The mercury level in the tube will now be a- two meters b- 760 cm c- 760 mm d- cannot be determined _____ 10) What is the energy of a photon of light at 567 nm (green light)? a- 3.76 x 10-31 J b- 3.51 x 10-28 J c- 3.51 x 10-19 J d- 211 kJ _____ 11) Which of the following is the highest energy? a- UV radiation b- visible light c- infrared radiation d- microwave radiation _____ 12) Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle states that we cannot a- accurately know anything about a proton b- know the orbital in which an electron is located c- accurately know both the charge and the position of an electron d- accurately know both the position and the momentum of an electron _____ 13) Which of the following sets of quantum numbers does not exist? a- n = 2, l = 1, ml = -1, ms= +1/2 b- n = 4, l = 2, ml = 3, ms= -1/2 c- n = 3, l = 0, ml = 0, ms= +1/2 d- n = 5, l = 3, ml = -2, ms= +1/2 _____ 14) Which of the following species is the largest? a- Ga b- Si c- Se d- Kr _____ 15) Which of the following atoms has the highest first ionization potential? a- Ge b- Si c- C d- B _____ 16) Which of the following statements about size is correct? a- Fe3+ > Fe2+ b- Ca2+ > Ca0 c- F > F1d- O2- > O _____17) For the angular momentum quantum number, l, we know all of the following except a- the energy of the electron (in conjunction with n) b- the geometric orientation of the orbital c- the number of nodes in the orbitals d- the subshell as s, p, d, or f Part Two. 1) (15 points) Definitions. In Words State function Pressure Pauli exclusion principle Hund’s rule Degenerate electrons 2) (8 points) What is the Hrxn for the following reaction using the information given 2 Pb(s) + 2 C (graphite) + 3 O2 (g) → 2 PbCO3 (s) Pb (s) + ½ O2 (g) → PbO (s) C(graphite) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) Pb (s) + C (graphite) + 1.5 O2 (g) → PbCO3 (s) Hrxn = ____________________ Hrxn = -219 kJ Hrxn = -394 kJ Hrxn = 86 kJ 3) (5 points) From your answer to question 2, how much energy is consumed or released (show the proper sign) in the formation of 4.65 g of PbCO3 (s)? 4) (12 points) Give the complete electronic configurations for each of the following species. No short cuts! In3+ Cr0 Se2Ba0 5) (10 points) Draw (showing the electrons as dots) the Lewis dot structures for each of the following. Show formal charges on the appropriate atoms and state the number of electrons needed (used) for each structure NO31NF3 6) (10 points) A gas comprised of chlorine and oxygen has a density of 2.875 g/ml at 756 mm Hg and 11.0 oC. What is the molecular formula of the gas and what is its most likely molecular formula? 7) (7 points) Oxygen is generated by the thermal decomposition of potassium chlorate by the following equation. How many moles of KClO3 are needed to generate 200.0 L of oxygen at 0.850 atm and 27.0 oC? 2 KClO3(s) → 2 KCl(s) + 3 O2(g)