Oceans Study Guide
advertisement

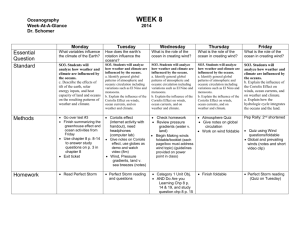
OCEANS STUDY GUIDE AND CHECKLIST NAME ______________________ Here is what you need to do to prepare for the test: 1) Study the old quizzes. 2) Fill out the matching for the geo-words below: 3) Discuss the questions below regarding the Main Concepts with your lab partners: 1) _______thermocline 2) _______pycnocline 3) _______oceanographer 4) _______Coriolis effect 5) _______Hadley Cell 6) _______wind 7) _______air current 8) _______trade winds 9) _______westerlies 10) _______polar easterlies 11) _______doldrums 12) _______salinity 13) _______gyre 14) _______upwelling 15) _______surface ocean currents 16) _______Gulf Stream 17) _______California stream 18) _______ocean conveyor 19) _______thermohaline current 20) _______El Nino 21) _______Southern Oscillation 22) _______Walker Circulation Cell 23) _______La Nina 24) _______weather 25) _______climate 26) _______ meteorologist 27) _______climatologist 28 _______ anomalies 29) _______isotherm 30) _______precipitation 31) _______phytoplankton 32) _______zooplankton A. circular motion of ocean water due to winds B. scientist who studies the weather C. scientist who studies the climate D. microscopic plants living in the ocean E. rainfall, snowfall, hail.. F. microscopic animals living in the ocean G. reversal in air pressure in the equatorial Pacific H. zone of rapid change in ocean temperature with depth I. area in the tropics with no steady winds J. curving of the winds due to the earth’s rotation K. irregularities L. lateral air convection current in the equatorial Pacific M. prevailing winds in North America N. “normal” climate and ocean conditions in the Pacific O. zone of rapid change in ocean density with depth P. salt concentration of water Q. scientist who studies the ocean R. prevailing winds in the polar regions S. vertical motion of air columns T. circulation cell between the equatorial low and subtropical high U. colder water from the bottom flowing upwards V. movement of air from high pressure to low pressure areas W. current controlled by temperature and salinity X. warm surface current on the east coast of America Y. a line that connects areas with similar temperatures Z. tropical easterlies a. currents controlled mostly by the winds and Coriolis force b. climate phenomenon where the trade winds reverse direction c. deep ocean current regulated by water density d. long-term atmospheric conditions e. short-term daily atmospheric conditions f. cold surface current on the west coast of North America MAIN CONCEPTS: 1) Activity 1(# 111 in binder): In which direction does the earth rotate? _____________________________________________________________________________ 2) # 112 in binder: What causes wind? _____________________________________________________________________________ 3) # 112 in binder: What air mass has a higher pressure – cool or warm air? _____________________________________________________________________________ 4) # 112 in binder: Draw a convection cell. _____________________________________________________________________________ 5) # 113 in binder: In the space below, draw the global wind patterns. Include all arrows and label all winds, including the Hadley Circulation Cell. 6) Activity 3 (# 121): How do the global wind patterns and the Coriolis force affect the surface ocean currents? Explain how the gyres rotate in the different hemispheres. 7) Activity 3 (# 121): In which direction does the warmer water tend to flow? Towards or away from the equator? What about the cooler water currents? _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 8) Activity 2 (# 117): What two factors control the circulation of the deep ocean current? _____________________________________________________________________________ 9) Activity 2 (# 117): Why is the ocean conveyor so important in regulating the climate of the earth? _____________________________________________________________________________ 10) Activity 4 (# 123):What is the difference between El Nino and La Nina? _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 11) Activity 4 (# 123): Explain El Nino in terms of wind direction and water movement. ____________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 13) Activity 5 (#124): How is North America affected by El Nino? 14) # 123: What type of data does the satellite TOPEX/Poseidon provide? 15) Activity 5 (# 124): How does El Nino affect Colorado? _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 16) Activity 6 (# 125): Explain the relationship between El Nino, cold water upwelling, phytoplankton, and the fishing industry in Peru. _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________