Fall 2014 Semester Final Review
advertisement
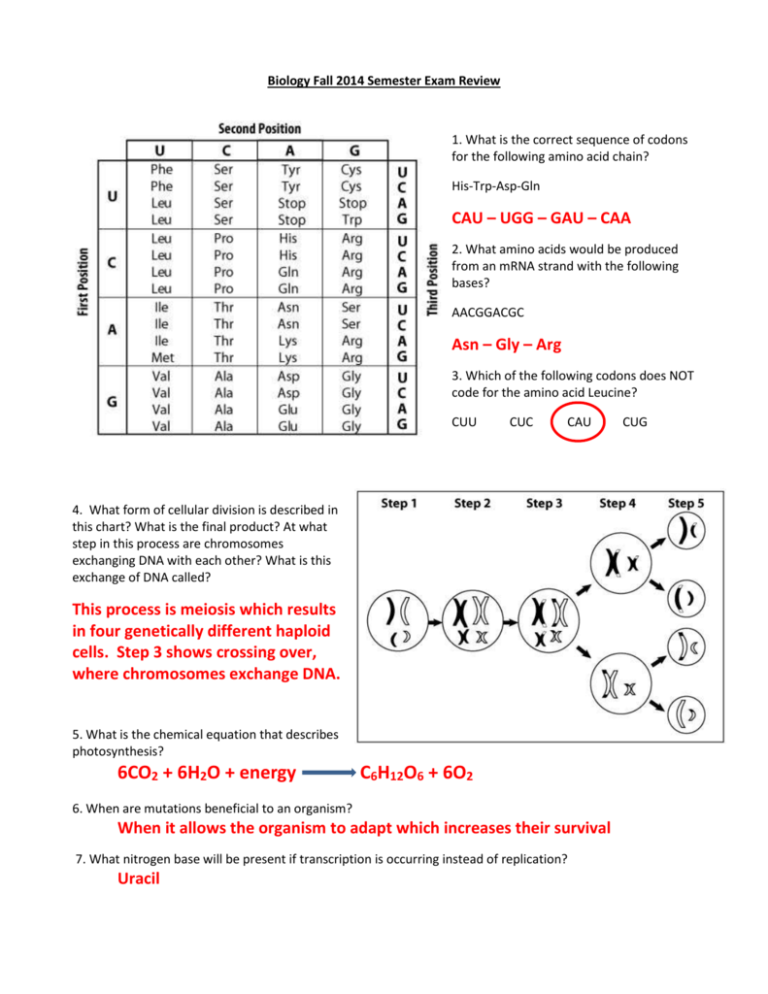
Biology Fall 2014 Semester Exam Review 1. What is the correct sequence of codons for the following amino acid chain? His-Trp-Asp-Gln CAU – UGG – GAU – CAA 2. What amino acids would be produced from an mRNA strand with the following bases? AACGGACGC Asn – Gly – Arg 3. Which of the following codons does NOT code for the amino acid Leucine? CUU CUC CAU 4. What form of cellular division is described in this chart? What is the final product? At what step in this process are chromosomes exchanging DNA with each other? What is this exchange of DNA called? This process is meiosis which results in four genetically different haploid cells. Step 3 shows crossing over, where chromosomes exchange DNA. 5. What is the chemical equation that describes photosynthesis? 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 6. When are mutations beneficial to an organism? When it allows the organism to adapt which increases their survival 7. What nitrogen base will be present if transcription is occurring instead of replication? Uracil CUG 8. Which part of this diagram represents codons being translated? Part 3 9. Which part of this diagram represents transcription taking place? Part 2 10. What process does this diagram describe? Protein Synthesis 11. Find and circle the cell undergoing Anaphase in this picture. 12. If a cross is done between two pea plants with the genotypes TTYy and Ttyy, what is the expected phenotype ratio? 8:8:0:0 TY Ty TY Ty Ty TTYy TTyy TTYy TTyy Ty TTYy TTyy TTYy TTyy ty TtYy Ttyy TtYy Ttyy ty TtYy Ttyy TtYy Ttyy 25% TTYy 25% TTyy 25% TtYy 25% Ttyy 13. What are two things that can alter the function of an enzyme? How acidic or basic something is (pH) or temperature RR RR Rr Rr 14. Cystic Fibrosis is a recessive disorder, where an individual has the disease if they are homozygous recessive. If a male carrier for the disease has children with a female that is homozygous dominant, what percentage of their offspring could have the disease? Male: Rr Female: RR 0% 15. What are produced from meiosis? Gametes 16. What molecule starts the process of cellular respiration in the cytoplasm and mitochondria? Glucose 17. What are the genotype and phenotype ratios for this Punnett Square? Genotypes: BB: o – 0% Bb: 2 – 50% bb: 2 – 50% Phenotypes: Bouncy: 2 – 50% Not Bouncy: 2 – 50% 18. What does the arrow indicate on this DNA model? The hydrogen bond between bases 19. What does the process of crossing over create for a species? Genetic variation 20. What is doubled in the cell after the synthesis stage of interphase? The amount of DNA 21. In this model of transcription, what occurs after the DNA molecule has been unzipped? DNA bases pair up with complimentary RNA bases. 22. A female parent is a carrier for a recessive sex linked trait. The male parent does not carry the trait. What percentage of their female offspring will have the trait? What percentage of their male offspring will have it? H h H Female: X X Male: X Y Female offspring: 0% Male offspring: 50% XHXH XHXh XHY XhY 23. What are the products of the light dependent reactions? ATP, NADPH, H+, and O2 24. What are the differences between RNA and DNA? RNA is only a single strand of nucleotides and is used only for protein synthesis 25. An mRNA has the codon 5’-AGG-3’. What would be the anticodon that matches up with it? 3’ – UCC – 5’ 26. What part of the DNA molecule is responsible for the expression of traits? The Nitrogenous bases 27. What occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle? DNA is replicated so two new cells can be formed 28. If this polymer is a protein, then what are the subunits, or monomers called? Amino acids 29. Changes in cellular reproduction can lead to disease. These changes affect what process? Mitosis 30. How many chromosomes do the reproductive cells have in comparison to the body cells? What terms describe the two types of cell in terms of chromosome number? Reproductive cells have half as many strands of DNA. 31. A cell with 14 chromosomes undergoes mitosis. How many chromosomes will the daughter cells have? 14 32. What kind of biomolecule is this? Fatty acid (AKA: Lipid) 33. How do you know this is DNA instead of RNA? The molecule is double stranded 34. What will be the result in offspring in comparison to parents in species that reproduce sexually? Parents and offspring will have different acquired traits 35. What is the primary difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells? Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus 36. What provides the genetic material for all living things? DNA 37. How do complex, multicellular organisms arise from a single fertilized cell? Cells differentiate as they divide making different types of cells, then forming different types of tissues and organs DD Dd Dd dd 38. If two parents are heterozygous for dimples Dd, what will be the expected genotype and phenotype ratios? Genotypes: DD: 1 – 25% Dd: 2 – 50% dd: 1 - 25% Phenotypes: Dimples: 3 – 75% No dimples: 1 – 25% 39. What will be the expected genotype and phenotype ratios for offspring with parents who are homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive for freckles? The alleles are: F (freckles), and f (no freckles). Genotypes: FF: 0 – 0% Ff: 4 – 100% ff: 0 - 0% Phenotypes: Freckles: 4 – 100% No freckles: 0 – 0% Ff Ff Ff Ff 40. What are the genotype and phenotype ratios for a cross between Bb and bb? Bb bb Bb bb Genotypes: BB: 0 – 0% Bb: 2 – 50% bb: 2 - 50% Phenotypes: Trait: 2 – 50% No trait: 2 – 50% 41. How many chromosomes does cell 1 have in comparison to cell 2? Cell 1 has twice as many chromosomes as cell 2 42. What process stores energy in carbohydrate molecules? 43. What is the only form of life that has prokaryotic cells? Photosynthesis Bacteria 44. Which part of the DNA molecule causes variation among organisms? Part 3 – the Nitrogenous bases 45. Arctic foxes are dominant for thick fur (T). Foxes can also be black (B), or white (b). During winter, what genotypes of foxes would survive? TTbb or Ttbb 46. Why can this pedigree chart not be for a sex-linked trait? An affected male has an unaffected female offspring 47. Where does replication and transcription take place in this cell? Part 1 48. Where would mutations in gametes show up? In the offspring of that organism (AKA: in the kids) 49. What disease are cells that cannot enter G0 likely to cause? What will they continuously do? These cells can cause cancer. The cells will repeat the cell cycle continuously. 50. What will occur next? Sister chromatids will be pulled apart to opposite ends of the cell. (AKA: Anaphase II) 51. What would be some possible gamete combinations from this diploid cell’s chromosomes? A1, B2, C1 OR A2, B1, C1 Any combination that includes ONE of each 52. What biochemicals are responsible for breaking down or digesting chemicals? Enzymes 53. What are the reactants and products of the Calvin Cycle? Carbon Dioxide is the reactant for the Calvin Cycle – Glucose is the product of Photosynthesis 54. How many alleles can a parent give to their offspring for a trait? Each parent can only give one trait (in the gamete) to their offspring (the zygote) 55. What are the monomers for proteins? For carbohydrates? Proteins are formed from amino acids – Polysaccharides are formed from sugars 56. Where are gametes formed? What process forms them? Meiosis forms gametes in the reproductive organs of multicellular organisms 57. Describe what happens in the mitochondria during cellular respiration. Energy from the glucose is transferred into the energy form of ATP 58. What is the expected phenotype ratio for a dihybrid heterozygous cross? 9:3:3:1