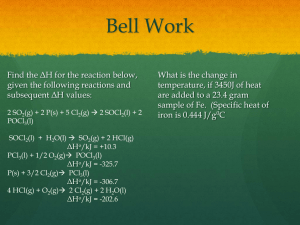
WS 4.1 Key All gas molecules or atoms are always in constant
advertisement

WS 4.1 Key 1. a) All gas molecules or atoms are always in constant, random motion. Collisions between molecules produce pressure without a loss in total energy, (elastic collisions), KE is proportional to Temp. b) Ideal gas molecules have negligible volume and gas molecules don’t attract to each other. NOTE: these postulates are for Ideal Gases only. 𝟑 2. a) 𝑲𝑬𝒂𝒗𝒈 = 𝑹𝑻 𝟑𝑹𝑻 𝓜 b) 𝒖𝒓𝒎𝒔 = √ 3. 4. 5. 6. 𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒆𝒂 𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒆𝒃 = √𝓜𝒃 𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒆𝒂 𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒆𝒃 = √𝓜𝒃 (32𝑠) 4.67 8. 20𝑠 .48 𝓜 ) (274𝐾) = 3415.41 𝐽/𝑚𝑜𝑙 with Sigfigs. 3420 J/mol (𝟑)(𝟖.𝟑𝟏 𝑱/𝒎𝒐𝒍 𝑲)(𝟐𝟕𝟒𝑲) .𝟎𝟐𝟎𝟏𝟖 𝒌𝒈/𝒎𝒐𝒍 = 581.80 𝑚/𝑠 with SigFigs 582 m/s 𝟑𝟐 = √𝟒.𝟎 He effuses 2.8 times faster than O2 𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒆 𝒐𝒇 𝑯𝟐 𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒆 𝒐𝒇 𝑪𝑶𝟐 𝒂 mol∙K 𝒖𝒓𝒎𝒔 = √ 𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒆 𝒐𝒇 𝑯𝒆 𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒆 𝒐𝒇 𝑶𝟐 𝒂 J 𝟐 𝟒𝟒.𝟎𝟏 H2 effuses 4.67 times faster than CO2 = √ 𝟐.𝟎𝟐 = 6.85𝑠 𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒆𝒂 𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒆𝒃 7. ( 𝓜 𝟑 𝑲𝑬𝒂𝒗𝒈 = (8.31 𝟐 𝓜 𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒆 𝒐𝒇 𝑵𝑯𝟑 𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒆 𝒐𝒇 𝑯𝒆 = √𝓜𝒃 𝒂 𝟒.𝟎𝟎𝒈 NH3 compared to He: 0.48 times (slower of course) = √𝟏𝟕.𝟎𝟒𝒈 ) = 𝟒𝟏 𝒔𝒆𝒄 𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒆𝑯𝒆 𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒆𝒖𝒏𝒌𝒏𝒐𝒘𝒏 𝓜𝒃 𝟒.𝟎𝟎 =√ 𝟏 𝟎.𝟐𝟓 𝓜𝒃 𝟒.𝟎𝟎 =√ = 𝟔𝟒 𝒈/𝒎𝒐𝒍 𝟑𝑹𝑻 𝓜 9. a) A is O2 and B is He. O2 is heavier and would have slower speeds compared to He. 𝒖𝒓𝒎𝒔 = √ 𝟑𝑹𝑻 𝓜 b) B is higher temperature. Hotter gas has greater speed than cooler gas. 𝒖𝒓𝒎𝒔 = √ 10. 1.22 𝑎𝑡𝑚 × 1.22𝑎𝑡𝑚 × 1.22𝑎𝑡𝑚 × 760𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔 1𝑎𝑡𝑚 101.325𝑘𝑃𝑎 1𝑎𝑡𝑚 760𝑇𝑜𝑟𝑟 1𝑎𝑡𝑚 = 927.2 𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔 (927𝑠𝑖𝑔𝑓𝑖𝑔) = 123.62 𝑘𝑃𝑎 (124𝑠𝑖𝑔𝑓𝑖𝑔) = 927.2 𝑇𝑜𝑟𝑟 (927𝑠𝑖𝑔𝑓𝑖𝑔) 11. 520𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔 749𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔 − 670𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔 = 79𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔 749𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔 + 103𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔 = 852𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔 12. a) The piston would move upward to double the volume because the greater number of molecules exerts twice the pressure. b) The piston would move upward to double the volume because the faster moving molecules exert twice the pressure. c) The piston would move downward to halve the volume so that molecules are more crowded in order to produce enough collisions to match the pressure. 13. P V n T 2.00 atm 1.00 L 1.500 mol 16.2 K 30.3 kPa 1.250 L 0.0152 mol 27oC 650 torr 11.2 L 0.333 mol 350 K 10.4 atm 585 mL 0.250 mol 295 K 14. a) 𝑃𝑉 = 𝑛𝑅𝑇 b) 0.382𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑂2 × 15. 𝑷𝟏 𝑽𝟏 = 𝒏𝟏 𝑻𝟏 𝑇2 = 16. 𝑚 𝑉 𝑃𝑉 (94.6𝑘𝑃𝑎)(10.0𝐿) = (8.31)(298𝐾) 𝑅𝑇 32.0 𝑔 𝑂2 = 𝟏𝟐. 𝟐 𝒈 𝑶𝟐 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑛= 𝑷𝟐 𝑽𝟐 (𝟕𝟓𝟎𝒕𝒐𝒓𝒓)(𝟑𝟓𝟎𝒎𝑳) 𝒏𝟐 𝑻𝟐 𝒏𝟏 (𝟐𝟖𝟖𝑲) (750𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑟)(450𝑚𝐿)(288𝐾)(𝑛1 ) (750𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑟)(350𝑚𝐿)(𝑛2 ) 𝑃∙ℳ given 𝑅∙𝑇 𝑚 𝑃∙ℳ = 𝑅∙𝑇 𝑉 =𝑑= 17. 𝑑 = 𝑃∙ℳ 𝑅∙𝑇 = = = 𝟎. 𝟑𝟖𝟐 𝒎𝒐𝒍 (𝟕𝟓𝟎𝒕𝒐𝒓𝒓)(𝟒𝟓𝟎𝒎𝑳) 𝒏𝟐 𝑻𝟐 rearrange and solve for T2 = 𝟑𝟕𝟎. 𝟑 𝑲 This is really just Charles Law the information, rearrange solving for molar mass(M) 𝑚𝑅𝑇 𝑃 =ℳ (1𝑎𝑡𝑚)(17.04𝑔/𝑚𝑜𝑙) (.0821)(273) = (4.93𝑔)(.0821)(400𝐾) 1.05𝑎𝑡𝑚 = 𝟏𝟓𝟒. 𝟐𝒈/𝒎𝒐𝒍 = .76 𝑔/𝐿 18. Total Pressure Partial Pressure of He Density Average Kinetic energy per molecule I and III are the same, then II I, II, III III, I, II since T is same avg. KE is same for all 19. a. the number of moles of each gas. n = PV/RT = (265/760)(1.0)/(0.0821)(298) n = 0.014 mol n = PV/RT = (800/760)(1.0)/(0.0821)(298) Ne n = 0.043 mol n = PV/RT = (532/760)(0.5)/(0.0821)(298) H2 n = 0.014 mol b. the total pressure after all stopcocks are opened. P = nRT/V = (0.071)(0.0821)(298)/(2.5) P = 0.695 atm (528 torr) c. the partial pressure of each gas. PN2 = XN2Ptot = (0.014/0.071)(528 torr) N2 PN2 = 104 torr PNe = XNePtot = (0.043/0.071)(528 torr) Ne PNe = 320 torr PH2 = XH2Ptot = (0.014/0.071)(528 torr) H2 PH2 = 104 torr N2 740 = PH2 + 32torr PH2 = 708 torr 20. a) Ptot = PH2 + PH2O b) 𝑃𝑉 = 𝑛𝑅𝑇 𝑛 = 𝑃𝑉 𝑅𝑇 = (0.932𝑎𝑡𝑚)(2.0𝐿) (.0821)(303𝐾) = 𝟕. 𝟓 × 𝟏𝟎−𝟐 𝒎𝒐𝒍 21. a) 𝑛 = b) 𝑛 = c) 𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒆𝒂 𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒆𝒃 𝑃𝑉 𝑅𝑇 𝑃𝑉 𝑅𝑇 = = (0.9489𝑎𝑡𝑚).090𝐿) (.0821)(298𝐾) (0.0313𝑎𝑡𝑚).090𝐿) (.0821)(298𝐾) 𝟏𝟖.𝟎𝟐 𝒈/𝒎𝒐𝒍 =√ 𝟐.𝟎𝟐 𝒈/𝒎𝒐𝒍 = = 𝟑. 𝟒𝟗 × 𝟏𝟎−𝟑 𝒎𝒐𝒍 H2 = 𝟏. 𝟏𝟓 × 𝟏𝟎−𝟒 𝒎𝒐𝒍 then convert to molecules: 6.92 x 1019 molecules H2O H2 is 2.99 times faster d) H2O shows hydrogen bonding which will causes it to deviate from ideal behavior, particularly at low temperatures and high pressures. 22. a) PV=nRT 𝑷 = 𝒏𝑹𝑻 b) 𝑃𝑎 = 𝑋𝑎 ∙ 𝑃𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑽 = (.𝟔𝟎𝒎𝒐𝒍)(.𝟎𝟖𝟐𝟏)(𝟑𝟎𝟎𝑲) (𝟐𝟎𝑳) (𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 𝑓𝑟𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛) 𝑃𝑎 = (. 33) ∙ 74.9𝑘𝑃𝑎 = 𝟐𝟓𝒌𝑷𝒂 = 𝟎. 𝟕𝟑𝟗𝒂𝒕𝒎 𝒐𝒓 𝟕𝟒. 𝟗𝒌𝑷𝒂 𝑋𝑎 = 𝑛𝑎 𝑛𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 = .20𝑚𝑜𝑙 = .33 .60𝑚𝑜𝑙 23. 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 𝑓𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑜𝑓 𝐻𝑒 𝑖𝑠 .978 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 𝑓𝑟𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑜𝑓 𝑂2 𝑖𝑠 0.0218 (𝑛 +𝑛 )𝑅𝑇 𝑃𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 = 𝐻𝑒 𝑂2 = 12.099 atm 𝑉 PHe= XHe Ptotal = 0.978 x 12.099atm = 11.8 atm PO2= XO2 Ptotal = 0.0218 x 12.099atm = 0.264 atm 24. a) All have the same avg. KE because they are at the same temperature and temperature is a measure of KE. b) He because they have the lowest mass. c) He because partial pressure is proportional to the number of moles of gas and the number of moles increases with decreasing molar mass. d) SO2 will deviate because they are the largest, have the greatest LDF interactions and they are also polar molecules so they will have the strongest attractive forces. e) SO2 because its polarity provides higher attractive forces. f) Decreasing the temperature and increasing the pressure.