Chapter 6 Vocabulary
advertisement

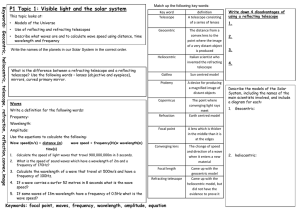
Astronomy: Chapter 6 Vocabulary Glossary Chapter 6 achromatic lens A telescope lens composed of two lenses ground from different kinds of glass and designed to bring two selected colors to the same focus and correct for chromatic aberration. active optics Optical elements whose position or shape is continuously controlled by computers. adaptive optics Computer-controlled telescope mirrors that can at least partially compensate for seeing. alt-azimuth mounting A telescope mounting capable of motion parallel to and perpendicular to the horizon. Angstrom A unit of distance equal to 10-10 m; often used to measure the wavelength of light. atmospheric window Wavelength regions in which Earth's atmosphere is transparent - at visual, infrared, and radio wavelengths. Cassegrain focus The optical design of a reflecting telescope in which the secondary mirror reflects light back down the tube through a hole in the center of the objective mirror. charge-coupled An electronic device consisting of a large array of light-sensitive elements used to record very faint device (CCD) images. chromatic aberration A distortion found in refracting telescopes because lenses focus different colors at slightly different distances. Images are consequently surrounded by color fringes. comparison spectrum A spectrum of known spectral lines used to identify unknown wavelengths in an object's spectrum. cosmic ray A subatomic particle traveling at tremendous velocity that strikes Earth's atmosphere from space. diffraction fringe Blurred fringe surrounding any image caused by the wave properties of light. Because of this, no image detail smaller than the fringe can be seen. electromagnetic Changing electric and magnetic fields that travel through space and transfer energy from one radiation place to another - for example, light, radio waves, etc. equatorial mounting A telescope mounting that allows motion parallel to and perpendicular to the celestial equator. eyepiece A short-focal-length lens used to enlarge the image in a telescope; the lens nearest the eye. false-color image A representation of graphical data in which the colors are altered or added to reveal details. focal length The distance from a lens to the point where it focuses parallel rays of light. frequency The number of times a given event occurs in a given time; for a wave, the number of cycles that pass the observer in 1 second. grating A piece of material in which numerous microscopic parallel lines are scribed; light encountering a grating is dispersed to form a spectrum. infrared radiation Electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths intermediate between visible light and radio waves. interferometry The observing technique in which separated telescopes combine to produce a virtual telescope with the resolution of a much larger diameter telescope. light pollution The illumination of the night sky by waste light from cities and outdoor lighting, which prevents the observation of faint objects. light-gathering power The ability of a telescope to collect light; proportional to the area of the telescope objective lens or mirror. magnifying The ability of a telescope to make an image larger. power nanometer (nm) A unit of length equal to 10-9 m. Newtonian focus The focal arrangement of a reflecting telescope in which a diagonal mirror reflects light out the side of the telescope tube for easier access. objective lens, mirror The main optical element in an astronomical telescope. The large lens at the top of the telescope or large mirror at the bottom. photon A quantum of electromagnetic energy; carries an amount of energy that depends inversely on its wavelength. polar axis The axis around which a celestial body rotates. primary lens, mirror The main optical element in an astronomical telescope. The large lens at the top of the telescope tube or the large mirror at the bottom. prime focus The point at which the objective mirror forms an image in a reflecting telescope. radio interferometer Two or more radio telescopes that combine their signals to achieve the resolving power of a larger telescope. reflecting telescope A telescope that uses a concave mirror to focus light into an image. refracting telescope A telescope that forms images by bending (refracting) light with a lens. resolving power The ability of a telescope to reveal fine detail; depends on the diameter of the telescope objective. SchmidtCassegrain focus The optical design of a reflecting telescope in which a thin correcting lens is placed at the top of a Cassegrain telescope. secondary mirror In a reflecting telescope, the mirror that reflects the light to a point of easy observation. seeing Atmospheric conditions on a given night. When the atmosphere is unsteady, producing blurred images, the seeing is said to be poor. sidereal drive The motor and gears on a telescope that turn it westward to keep it pointed at a star. spectrograph A device that separates light by wavelength to produce a spectrum. ultraviolet radiation Electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than visible light but longer than X rays. wavelength The distance between successive peaks or troughs of a wave; usually represented by