Technologies that Use Light The Invention of the Telescope Hans
advertisement

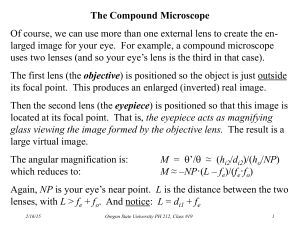
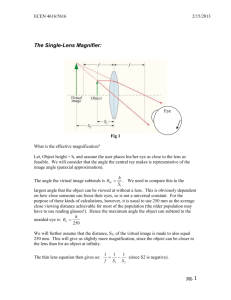
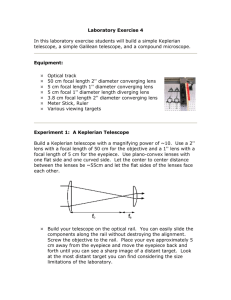
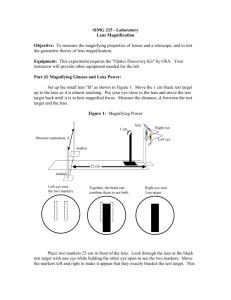
Technologies that Use Light The Invention of the Telescope Hans Lippershey invented the telescope Galileo improved the design and built the most powerful telescope in the world; he was able to see Jupiter (magnified up to 30X) Isaac Newton had designed a telescope in which the large convex lens that was normally placed at the front of the telescope was replaced by a large concave mirror placed at the back of the telescope, therefore making it lighter Telescope Telescope - is an optical device that provides enlarged images of distant objects Refracting Telescope – is similar in design to a microscope in that they both have two lenses; one on each end of a long tube. Unlike a microscope, the objective lens in a telescope is the larger lens. Binoculars – are composed of 2 short refracting telescopes attached together How does one see an object? - light enters the objective lens, reflects off the reflective prisms and makes its way out to through the fixed eye piece Reflecting Telescope – lights enter from one end of a tube and then reflects off a concave mirror to a small plane mirror. Then the small mirror reflects the light into the eyepiece. This telescope has an advantage of being a lot lighter. Microscope Antonie van Leeuwenhoek – discovered the microscope Compound microscope – a pair of convex lenses causes a small object to appear magnified when viewed through the eyepiece Confocal microscope – is a type of microscope that uses light which uses a laser beam to light the specimen. The image of the specimen is then digitally enhanced so it can be viewed on a computer. Cameras Parts of a Camera Camera –light proof box with a lens at one end to form a real, inverted image on a film Shutter – controls the length of time light is allowed in Diaphragm – the part of the camera that controls the aperture Aperture- the opening that the light passes through Camera diaphragm aperture Film Human Eye iris Pupil Retina Types of Lenses Telephoto lens - increases the amount of light that is collected and magnifies a distant object - has a long focal length, that is why it protrudes so far out from the camera Wide Angle Lens – captures a wider angle of view (e.g. trying to take a picture of a bedroom for real estate) Pixels – tiny picture elements; when pixels are combined, a continuous image is produced -the greater the number of pixels, the more closely the image resembles the original object Digital Image Manipulation Red Eyes – light from the camera flash passes into the eye, reflects off the red blood vessels inside of the eye, and then passes out again through the pupil Lasers Laser - an optical device that produces a form of light in which all the light rays are almost perfectly parallel -often used in communications, bar code readers, DVD players etc. -all lasers are bright enough to do permanent damage to your retina, which is why you never look directly into a laser beam -very little energy used to operate lasers Lasers in Medicine Detects cancer – forms of cancer produce chemicals which enter the blood stream -a sample of blood can be taken and shining a laser light through the blood can detect certain kinds of cancer before they cause symptoms or grow large enough to be detected by an X-ray Photonics Photons – tiny packets of energy Photonics – technologies that make use of the way in which light travels as photons Solar cells – convert sunlight energy into electrical energy