Intro test 2
advertisement

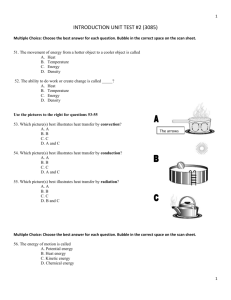
INTRODUCTION UNIT TEST #2 (3086) Multiple Choice: Choose the best answer for each question. Bubble in the correct space on the scan sheet. 51. The average amount of energy of motion in the molecules of a substance is called A. Heat B. Temperature C. Energy D. Density 52. The movement of energy from a hotter object to a cooler object is called A. Heat B. Temperature C. Energy D. Density 53. The ability to do work or create change is called _____? A. Heat B. Temperature C. Energy D. Density Use the pictures to the right for questions 54-56 54. Which picture(s) best illustrates heat transfer by convection? A. A B. B C. C D. A and C The arrows 55. Which picture(s) best illustrates heat transfer by conduction? A. A B. B C. C D. A and C 56. Which picture(s) best illustrates heat transfer by radiation? A. A B. B C. C D. B and C Multiple Choice: Choose the best answer for each question. Bubble in the correct space on the scan sheet. 57. The energy of motion is called A. Potential energy B. Heat energy C. Kinetic energy D. Chemical energy 1 58. As you raise the temperature of a substance, what happens to its molecules? A. The molecules become larger, spread out and have more kinetic energy. B. The molecules become smaller, contract and have less kinetic energy. C. The molecules become faster, spread out and have more kinetic energy. D. The molecules become slower, contract and have less kinetic energy. 59. Which statement correctly identifies how solid water is different from liquid water? A. In solid water the molecules are farther apart. B. Only in solid water are the molecules not polar. C. In solid water the molecules are closer together. D. Only in solid water do the molecules have spaces between them. 60. Which of the following is the BEST example of how the water cycle carries on energy transfer? A. A flooding river depositing silt on a floodplain B. A warm ocean current warming the air above it C. Ocean water depositing sand particles on a shore D. Water seeping through the soil and dissolving salts 2 Use the Periodic Table below to answer questions 61- 65 61. Which element has two protons, neutrons and electrons? A. Hydrogen (H) B. Oxygen (O) C. Helium (He) D. Nitrogen (N) 62. How many protons does Oxygen (O) have? A. 5 B. 8 C. 1 D. 17 63. How many neutrons does Sulfur (S) have? A. 16 B. 32 C. 34 D. 33 64. How many neutrons does Cobalt (Co) have? A. 27 B. 58 C. 31 D. 32 65. If Nickel (Ni) has 28 protons how many electrons does it have? A. 59 B. 28 C. 31 D. 30 66. What is an example of compound? A. He (a gas) B. oxygen plus nitrogen (O + N) C. Na (solid) D. NaCl (salt) 3 Use the pictures below for questions 67-70. A B C 67. Rate the jars of molecules shown in the three different phases above from the least energetic to the most energetic molecules. A. (A, B, C) B. (B, C, A) C. (C, A, B) D. (C, B, A) 68. Which of the states of matter above will not take the shape of its container? A. A B. B C. C D. A and B 69. Which jar of molecules vibrates in place? A. A B. B C. C D. A and B 70. Which of the states of matter above travels the fastest and farthest? A. A B. B C. C D. B and C Matching: 71. Temperature at which a substance changes form a solid to a liquid A. Solid 72. Temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a solid B. Freezing point 73. Definite shape and definite volume C. Liquid 74. No definite shape and no definite volume D. Melting point 75. No definite shape and definite volume E. Gas 4 Matching: 76. From a solid to a liquid A. Energy gained 77. From a liquid to a gas B. Energy lost 78. From a solid to a gas C. No energy gained or lost 79. From a gas to a liquid 80. From a liquid to solid 81. Sublimation 82. Melting 83. Evaporation 84. Freezing Matching: 85. Process by which a liquid changes to a gas A. Condensation 86. Process by which a solid changes to a gas B. Sublimation 87. Process by which a gas changes to a liquid C. Evaporation 88. Process by which a gas changes to a solid D. Deposition Matching: 89. Flammability A. Chemical property 90. Color change B. Physical property 91. Mass change 92. Ripening of fruit 93. Boiling point 94. Chemistry in a Ziploc lab 95. Change in temperature 96. Phase changes 97. Size and shape change 5 Matching: 98. Heating up your dinner in a microwave A. Exothermic 99. Chemistry in a Ziploc lab B. Neither endothermic or exothermic 100. Hand warmers C. Endothermic 6