Pregnancy Lecture Notes - Lindbergh School District
advertisement

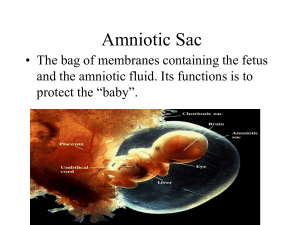
PREGNANCY -Lecture NotesWeeks 1 & 2Signs and Symptoms of Pregnancy: Missed menstrual period Nausea – with or without vomiting Fatigue Breast tenderness/changes Frequent urination Beginning of pregnancy is figured from beginning of last menstrual period. A due date is important in pregnancy because: *Helps doctors determine when to perform certain tests/procedures. *Helps estimate baby’s growth and development. Pregnancy lasts about 280 days, or 40 weeks, from beginning of last menstrual period. Trimester- pregnancy divided into 3 periods – each about 13 weeks long First Trimester*Baby’s body structure forms *Organ system develops *Most miscarriages occur Third Trimester- most maternal problems occur – hypertension – pre-eclampsia – gestational diabetes Due dates are only an estimate, not an exact date. Only one out of 20 women delivers on her due date. Menstruation- two important cycles occur at the same time*Ovarian cycle – provides egg for fertilization *Endometrial cycle-provides suitable site for implantation of fertilized egg inside uterus Over-the-counter pregnancy tests are reliable and can be positive (indicate pregnancy) as early as 10 days after conception. Good health is one of the most important factors in your pregnancy. Healthcare ProvidersObstetrician – specializes in pregnant women/ delivers babies Perinatologist- specializes in high- risk pregnancies – which is 1 out of 10 pregnancies Family Practitioner- family doctor serves as internist, gynecologist/obstetrician, and pediatrician Certified nurse-midwives- Registered nurses with additional training/certification in nurse midwifery. Delivers low-risk, uncomplicated pregnancies. Board certified- trained professional – taken exams to qualify in their specific field of medicine. Adverse affects on babyCigarette SmokingA pregnant woman who smokes 20 cigarettes (1 pack) a day inhales tobacco smoke more than 11,000 times during a normal pregnancy. 1. Increase rate of fetal death/fetal damage 2. Interferes with absorption of Vitamin B, C and Folic acid (neural tube defects) 3. Infants weigh about 7 oz. less 4. Lower IQ scores 5. Reading disorders 6. Hyperactivity 7. Increased risk of miscarriage 8. Increased chances of fetal death or death of baby soon after birth 9. Placenta abruption 10. Placenta previa AlcoholModerate drinking has been linked to an increased chance of miscarriage. FAS-Fetal Alcohol Syndrome 1. Growth retardation – before/after birth defect in limbs-heart-facial characteristics 2. Facial characteristics – nose upturned – short upper jaw line is flat – eyes slanted 3. Behavior problems – impaired speech – fine/gross motor functions are impaired FAE- Fetal Alcohol Exposure – can result from very little alcohol There is no safe level of alcohol consumption. Week 3Fertilization – joining together of one sperm and one egg The developing ball of cells is called a zygote. About a week after fertilization, the blastocyst attaches to the uterine cavity (implantation) Benefits of Pregnancy*Allergy/asthma sufferers may feel better – natural steroids produced during pregnancy helps reduce symptoms. *Helps protect against breast/ovarian cancer. *Migraine headaches often disappear during 2nd and 3rd trimester. *Endometriosis – pregnancy can stop the growth. Week 4The implanted blastocyst is embedded more deeply into the lining of the uterus, and the amniotic cavity, which will be filled with amniotic fluid, is starting to form. Placenta- plays important role in hormone production and transports oxygen and nutrients. The younger a woman is when she starts having babies, and the more pregnancies she has, the greater the benefit. Germ layers develop into specialized parts of the baby’s body such as various organs. Three germ layers*Ectoderm-becomes the nervous system – brain – skin – hair *Endoderm – develops into lining of the gastrointestinal tract – liver – pancreas – thyroid *Mesoderm – skeleton – connective tissue – blood system – most of the muscles – urogenital system Teratology- study of abnormal fetal development Exact cause/reason for birth defect is found in less than half of all cases. Week 5Central nervous system and muscle and bone formation are beginning to take shape. Brain/spinal cord – Baby’s skeleton is starting to form. Ectopic pregnancy – occurs when egg implants outside the uterus – (ovary – cervix – abdomen) 95% of the time this occurs in the Fallopian tube Occurs 1 of every 100 pregnancies. Week 6Extremely important developmental time. Embryo most susceptible to factors that can interfere with development. Most malformations originate during this time. Development1. Early brain chambers form 2. Eyes start to form 3. Limb buds appear 4. Heart tube fuse 5. Heart contractions begin Week 7Incredible growth spurt this week. 1. Arm buds have grown longer – divided into hand segments – arm and shoulder segments 2. Hand and foot have digital plates- where fingers and toes will be formed 3. Heart bulges from body and divides into right and left chambers 4. Primary air passages (bronchi) in the lungs are forming 5. Cerebral hemispheres (make up the brain) are growing 6. Eyes and nostrils are developing 7. Intestines are developing and bulges into umbilical cord 8. Appendix is present 9. Pancreas (produces insulin) is present NutritionMilk - Need 3-4 glasses of skim milk a day Strong bones and teeth for baby Keeps woman’s bones healthy Minerals-iron requirements increase to produce additional blood cells Blood volume increases by 50% Week 8Development1. Eyelids folds are forming on the face 2. Tip of nose is present 3. Ears are forming – internally/externally 4. Heart – aortic and pulmonary valves are present 5. Tubes leading from throat to functioning part of lungs are branched 6. Body’s trunk area is getting longer and straightening out 7. Elbows are present – arms and legs extend forward 8. Arms have grown longer – they bend at elbows and curve slightly over heart Miscarriage- when the embryo or products of conception have emptied out of the uterus. Bleeding should subside quickly, as should any pain or cramping. Occurs in only about 15% of all pregnancies. Threatened Miscarriage- may be presumed when there is a bloody discharge from vagina during first half of pregnancy – the cervix remains closed Bleeding many last days/weeks May/may not be cramping – mild back aches Resting in bed is about all you can do – Being active does not cause a miscarriage About 20% of all women experience bleeding during early pregnancy but not all miscarry. No procedure/medication can keep a woman from miscarrying Inevitable miscarriage-rupture of membranes – dilation of cervix – passage of blood clots and tissue Uterus usually contracts, expelling fetus or products of conception (no embryo/fetus present) Incomplete miscarriage-entire pregnancy may be passed at once – part of pregnancy is passed while part remains in uterus – bleeding is heavy and continues until uterus is empty – bleeding and cramps may persist if the miscarriage is not complete. Missed miscarriage-women can experience a miscarriage without knowing it. A missed miscarriage is when embryonic death has occurred but there is not any expulsion of the embryo. It is not known why this occurs. Signs of this would be a loss of pregnancy symptoms and the absence of fetal heart tones found on an ultrasound. Habitual/Recurrent miscarriage-defined as 3 or more consecutive first trimester miscarriages. This can affect 1% of couples trying to conceive. Dilation and curettage (D&C)-a procedure in which the doctor removes tissue from the inside of the uterus. Dilation and curettage is used to diagnose or treat various uterine conditions. – such as heavy bleeding – or to clear the uterine lining after a miscarriage. To diagnose a condition- In a diagnostic D&C, the doctor takes a sample of the tissue that lines your uterus (the endometrium) so tests can be performed on it. This is generally done when: Abnormal uterine bleeding Bleeding after menopause Severe menstrual pain Unable to get pregnant Doctor discovers abnormal cells during a routine test for cervical cancer To treat a condition- in a therapeutic D&C the doctor removes the contents of the uterus. The doctor can do this to: Remove a molar pregnancy, in which a tumor forms instead of a normal placenta Treat excessive bleeding after birth by clearing out any placenta that remains in the uterus Remove cervical or uterine polyps, which are usually benign Remove fibroid tumors, which are benign tumors formed on the uterine wall Clear out any tissue that remains in the uterus after a miscarriage – to prevent infection or heavy bleeding, and to make room for a future pregnancy. Toxoplasmosis-is an infection caused by a parasite that can threaten the health of an unborn baby. You can get the infection from handling soil or cat litter that contains cat feces infected with the parasite. You can also get it from eating undercooked meat from animals infected with parasite or from uncooked foods that have come in contact with contaminated meat. Because the majority of people with toxoplasmosis have no symptoms, it may be difficult to know if you have been infected. When symptoms do appear, they can resemble the flu and include fever, muscle aches, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes. Approximately one-half of women infected with toxoplasmosis can transmit the infection across the placenta to their unborn baby. Infection early in the pregnancy is less likely to be transmitted to the baby than infection later in the pregnancy. Early infection results in more severe symptoms in the baby than a later one. Most babies infected during pregnancy show no signs of toxoplasmosis when they are born, but they may develop learning, visual, and hearing disabilities later in life. If you have toxoplasmosis infection during pregnancy, there are several ways to check if the baby is infected*The fluid around the fetus or the fetal blood can be tested for infection. *About a third of infected babies have a problem that may be visible on an ultrasound. *The baby’s blood can be tested after birth. Toxoplasmosis can be treated during pregnancy with antibiotics. The earlier the infection is identified and treated, the greater the chance of preventing infection of the unborn child. If the child has already been infected, treatment can make the disease less severe. The baby can be treated with drugs that are taken throughout the first year of life, and in some cases even longer. Week 9Baby now moves body and limbs. Hard to distinguish between male and female How pregnancy weight is distributed7 lbs. - maternal stores – fat – protein- other nutrients 4 lbs. - increased fluid volume 2 lbs. - breast enlargement 2 lbs.-uterus 7 ½ lbs.-baby 2 lbs.-amniotic fluids 1 ½ lbs.-placenta Cost of having a baby – it costs a lot and cost varies from one part of the country to another Week 10The end of the week 10 is the end of the embryonic period. Chorionic Villus Sampling- test used to detect genetic abnormalities Performed between 9-11th week – identifies Down syndrome Done much earlier than amniocentesis – get results in about a week Instrument is placed through the cervix or abdomen to remove fetal tissue from placenta. Fetoscopy- Use a scope through abdomen to view baby inside the uterus. Corrects defect before problem worsens, which could prevent the fetus from developing normally. Week 11Fetal growth is rapid Crown –to-rump length doubles Head is almost half of baby’s entire length External genitalia are beginning to show distinguishing features Ultrasound- (Sonogram)- Sound waves bounce off tissue – different tissues of body reflect ultrasound signals differently – noninvasive – no known risks associated with it – motion can be detected – fetal heart can be seen beating as early as 5-6 weeks – Babies body and limbs can be seen moving as early as 4 weeks of embryonic growth (6th week of pregnancy) Week 12Able to hear heartbeat with Doppler (magnifies sound) Development: Skeletal system now has bone formation (ossification) Fingers and toes have separated Nails are growing External genitalia shows distinct signs of male or female Digestive system (small intestines) capable of producing contractions that push food through bowels is forming Week 13- end of 1st trimester Fetal body growth accelerates as fetal head growth slows. Eyes which started out on side of head move closer together on face. Ears come to normal position on side of head. Week 14- Fetus is the size of a fist and weighs about 1 oz. Week 15- Fine hair called lanugos hair covers the baby’s body. Alpha-fetoprotein testing- between the 16-18 weeks As baby grows inside womb, it produces alpha-fetoprotein. This protein is found in increasing amounts in the amniotic fluid. Alpha-fetoprotein crosses fetal membranes and enters circulation. Elevated levels can indicate problems with the fetus. (spina-bifida- anencephaly – central nervous system) Week 16*Fine lanugos hair covers baby’s head *Fingernails are well formed *Arms and legs are moving *May feel baby move at this point “Quickening” Amniocentesis-Usually performed around 16-18 week Ultrasound is used to find a pocket of fluid when fetus and placenta are not in the way About 1 oz. of fluid is needed to perform certain tests – fetal cells that float in the amniotic fluid can be grown in cultures. Week 17Fat begins to form on the baby during this week. Adipose tissue is important to heat production and metabolism. Week 18Fetus in now 5-51/2” long and weighs 51/4 oz. Week 19Hydrocephalus- Cerebral spinal fluid circulates around the brain and spinal cord. If openings are blocked flow is restricted and this can cause hydrocephalus – enlargement of the head. One in every 2,000 births. Week 20When the baby is born, its skin is covered by vernix, a white substance that looks like paste. Protects baby’s skin from amniotic fluid. Secreted by glands in skin around the 20th week. Week 21Swallowing a small amount of amniotic fluid is beneficial to the baby as it helps build up the digestive system. Meconium-Undigested debris from swallowing amniotic fluid in the fetal digestive system. Greenish black to light brown. Baby passes from its bowels several days/weeks before delivery, during labor or after birth. If baby swallows fluid and inhales meconium into the lungs the baby could develop pneumonia. Week 22Liver function – breaks down and handles bilirubin Bilirubin-produced by breakdown of blood cells – lifespan of fetal red blood cell is shorter than an adults- fetus produces more blood cells than adult. Fetal liver has limited capacity to convert bilirubin than remove it from the fetal blood stream. Bilirubin passes from fetal blood through the placenta to mom’s blood. Jaundice-high levels of bilirubin – yellow tint to skin and eyes Phototherapy – penetrates skin and destroys bilirubin. Week 23Baby’s pancreas is developing necessary for hormone and insulin production. Insulin is necessary for the body to break down and to use sugar. Gestational Diabetes-affects 10% of all pregnancy If this occurs with one pregnancy there is almost a 90% chance it will recur with other pregnancies. Causes*Mother’s body produces less insulin during pregnancy. *Mother’s body can’t use the insulin appropriately Both situations result in high blood sugar levels. If left untreated mother and baby are exposed to high levels of sugar, *Results in excessive amounts of amniotic fluid *Premature labor because uterus becomes over distended *Long labor because baby is large. Week 24Amniotic fluid*Provides environment in which baby can move easily *Cushions fetus against injury *Regulates temperature for the body *Provides a way of assessing health/maturity of baby There is a maximum of 2 pints (32 oz.) at 36-38 weeks gestation. Week 25Baby weighs 1 ½ lbs. 8.8” crown-to-rump If baby were delivered at this time, it would have a good chance of surviving. Week 26Baby weighs 2 lbs. – Crown-to-rump 9.2” – Baby is beginning to put weight on. Week 27This week marks the beginning of the 3rd trimester. Now is the time to sign up for pre-natal classes that prepare you for labor and childbirth. Week 28Baby’s body is becoming plumper and rounder. Weight – 2.4 lbs. – Crown-to-rump-15 3/4” Week 29Birth weight increases with increasing number of pregnancies or the number of babies a woman delivers. Boys weigh more than girls. Average baby’s birth weight at full term is 7-71/2 lbs. Baby born between 38th-42nd weeks – Term baby – Full-term infant Born before 38th week- Pre-term At 42 weeks – Post term or Past date infant Babies born prematurely usually weigh less than 5 ½ lbs. Week 30Baby weighs – 3 lbs. Total length-17” Average weight gain during pregnancy is 25-33 lbs. Week 31Intrauterine-Growth Retardation- (IUGR) - indicates newborn infant is small for gestational age. Confirmed by ultrasound. Birth weight is below 10% percentile. Healthcare provider measures you and weighs you with each visit. Causes of IUGR Tobacco – inhibits baby’s growth Poor weight gain in mother-to-be – good nutrition and healthful diet are important – don’t attempt to restrict weight gain Maternal blood flow problems – Pre-eclampsia or high blood pressure can have marked effect on fetal development. Kidney disease Altitude – women who live in high altitudes are more likely to have babies that weigh less than babies born who live in lower altitudes. Alcoholism – Drug use Multiple fetuses Infections in the fetus Maternal anemia Abnormalities of the umbilical cord or placenta (baby receiving less nutrition) History of IUGR – once deliver a small baby more likely to deliver again Preeclampsia or Toxemia: (Pregnancy Induced Hypertension) - a condition of high blood pressure during pregnancy. Blood pressure goes up, you retain water, and protein is found in the urine. Preeclampsia prevents the placenta from getting enough blood. If the placenta doesn’t get enough blood, the baby gets less oxygen and food. This can result in low birth weight. However, the exact cause of preeclampsia is unknown. Risks of developing preeclamsia: *A first-time mom *Women whose sisters or mothers had preeclampsia *Women carrying multiple babies: teenage mothers: and women older than age 40 *Women who had high blood pressure or kidney disease prior to pregnancy SymptomsMild- high blood pressure, water retention, protein in urine Severe-headaches, blurred vision, inability to tolerate bright light, fatigue, nausea/vomiting, urinating small amounts, pain in the upper right abdomen, shortness of breath, and tendency to bruise easily. At each prenatal checkup the healthcare provider will check blood pressure, urine levels and may order blood tests. Treatment depends on how close to due date. If close to the due date and the baby has developed enough, the health care provider will probably deliver the baby as soon as possible. Mild preeclampsia and the baby has not reached full development the doctor will probably recommend: *Rest, lying on the left side to take the weight of the baby off the major blood vessels. *Increase prenatal checkups. *Consume less salt. *Drink 8 glasses of water a day. With severe preeclampsia, the doctor may try to treat with blood pressure medication until the baby is far enough along to deliver safely. Week 32Multiple Births - Week 33Placental Abruption- separation of placenta from wall of uterus – 1 in every 80 births Causes*Physical injury to mother – ex. Car accident *Short umbilical cord *Sudden change in size of uterus –from delivery or rupture of membranes *Hypertension *Dietary deficiency *Uterine abnormality – placenta doesn’t attach properly *Previous surgery on uterus – removal of fibroids – D&C for miscarriage Episiotomy- incision made from vagina toward rectum during delivery to avoid undue tearing First-degree- cuts only the skin Second-degree-cuts skin and underlying tissue Third-degree-cuts skin – underlining tissue – rectal sphincter (muscle that goes around the anus) Fourth-degree-cut goes through the three layers and the rectal mucosa Week 34Biophysical profile-test used to examine fetus while still in the uterus Checks fetal breathing movements – fetal body movements – fetal tone – heart rate – amount of amniotic fluid Labor-dilation (stretching and expanding) of the cervix Braxton Hicks-many women begin to experience Braxton Hicks contractions during the last several weeks of pregnancy. Contractions can begin as early as the second trimester; however, they are most common in the third trimester. Painless, non rhythmical contractions that last for approximately 30 to 60 seconds or as long as 2 minutes. Braxton Hicks are also called “practice contractions” because they will prepare you for the real thing, and you practice the breathing exercises in the childbirth classes. True labor usually starts at top of uterus and radiates over entire uterus through lower back into pelvis. Bloody Show-cervix stretches and dilates – mucus plug Labor lasts approx. 14-15 hours for first pregnancies Nonstress test-when mom is lying down a fetal monitor is put on abdomen – records baby’s heart beat – checks how baby is tolerating inside the uterus. Stages of LaborStage One- uterine contractions – intense – cause thinning (effacement) and dilation of the cervix – 1st stage ends when the cervix is 10cm. Stage Two – 10 cm until baby is delivered Stage Three-ends with the delivery of the placenta and the membranes that surround the fetus Contractions of uterus control bleeding. Week 35Placenta Previa-condition where the placenta lies low in the uterus and partially or completely covers the cervix. The placenta may separate from the uterine wall as the cervix begins to dilate (open) during labor. Affects about 1 in 200 women in the third trimester of pregnancy. More common in women who have had one or more of the following: *More than one child *A cesarean birth *Surgery on the uterus *Twins or triplets Signs and symptoms vary, but the most common symptom is painless bleeding during the third trimester. *Premature contractions *Baby is breech, or in transverse position *Uterus measures larger than it should according to gestational age Once diagnosed, bed rest is required and frequent hospital visits. Depending on the gestational age, steroid shots may be given to help mature the baby’s lungs. If bleeding cannot be controlled, an immediate cesarean delivery is usually done. Week 36Reasons for Cesarean delivery Previous cesarean delivery – most common Baby too big to fit through the birth canal Fetal distress Umbilical cord compressed Placenta abruption/Placenta previa Week 37Dilatation – amount of opening of the cervix Cervix is fully open when the diameter of cervical opening measures 10cm. Week 38Fetal monitoring –baby’s heart rate is monitored throughout labor Postpartum Distress Syndrome- “baby blues”- associated with a short term sense of sadness after birth which usually only last for about 2 weeks. Quite common, especially after the excitement of pregnancy and the drama of giving birth. Postpartum Depression- extremely serious. It should not be underestimated at any time. Seek help as soon as possible, it can be treated and it should be treated before anything happens to anyone. It does not always show signs right after birth and it can affect anyone. Warning signs: Constantly feeling restless Irritability that doesn’t fade day after day Feelings of sadness that last more than a few hours or an entire day Frequent and unexplainable crying Persistent lack of energy Inability to sleep despite fatigue Weight loss/gain that is extreme Feelings or fears that you will harm your baby Guilt Feelings of inadequacy Excessive anger Lack of interest in your newborn Intrusive thoughts Week 39Breastfeeding: *Contains all nutrients baby needs during first month. *Protection against infection – builds antibodies *Baby less likely to get colds and infections. *Encourages tooth and jaw formation. *Decreased cost. *Mom regains figure easier. Epidural Block- regional block administered by an anesthesiologist After placenta is delivered, the mother may be given pitocin to contract the uterus. Cord-Blood Banking-blood from the umbilical cord contains valuable cells that are found in the bone marrow – stem cells that are building blocks of blood and immune systems. Can be used to treat: Cancer Genetic diseases Bone marrow transplants Frozen and cryogenically stored. Week 40Bilirubin-breakdown product from red blood cells – increases 3-4 days after delivery and then decreases – before baby is born; bilirubin is transferred across placental from fetus to maternal circulation. Jaundice-high levels of bilirubin in blood – yellowing of skin and whites of eyes Phototherapy-light penetrates skin and destroys bilirubin Pregnancy is considered overdue when it exceeds 42 weeks or 294 days. While baby is growing/developing in utero it depends on important function of the placenta. *Respiration *Nutrition Choosing where to give birth: LDRP-Labor – delivery – recovery – postpartum Remain in the same room for the entire hospital stay. Labor-Delivery Suites-Labor in suite – moved to delivery room – go to post partum floor Rooming/Boarding-have baby in room as long as you want Birthing Room- deliver baby in same room as you labor in Apgar Score-evaluation of the baby’s health after delivery. Baby is examined 1 and 5 minutes after delivery. *Heart rate *Respiratory effort *Muscle tone *Reflex *Color Most babies receive a score of 7-8-9. The goal of labor and delivery is a healthy baby.