logic-syllabus-new-form-2013 File - LMS
advertisement
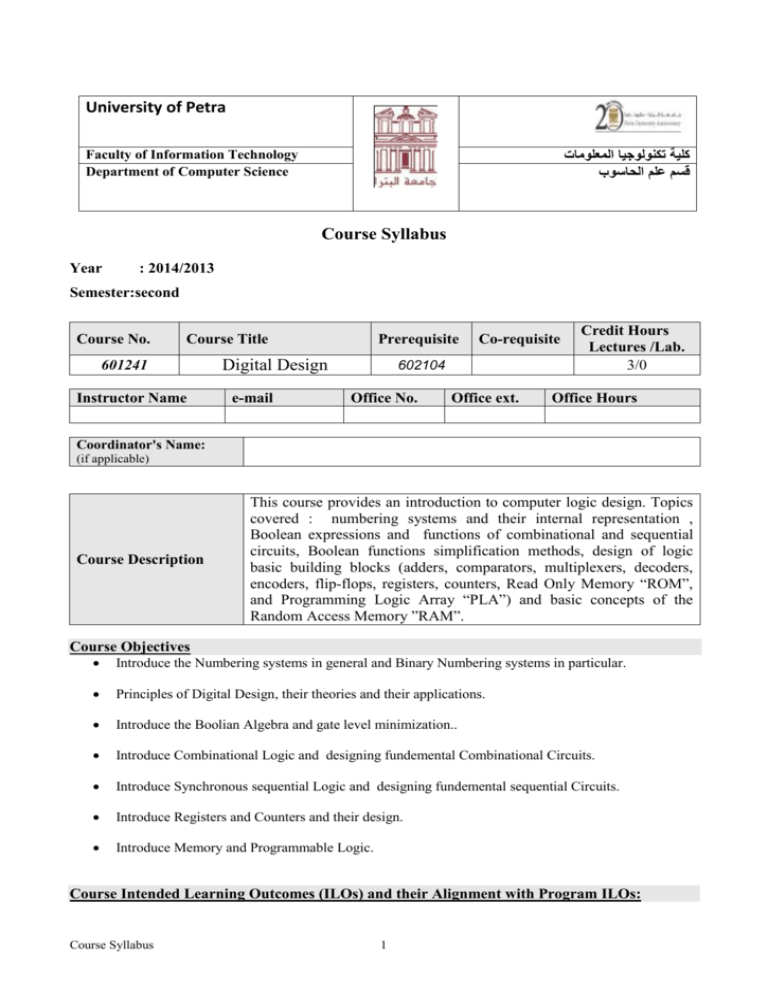
University of Petra كلية تكنولوجيا المعلومات قسم علم الحاسوب Faculty of Information Technology Department of Computer Science Course Syllabus Year : 3102/3102 Semester:second Course No. Course Title 601241 Instructor Name Prerequisite Digital Design e-mail Co-requisite 602104 Office No. Office ext. Credit Hours Lectures /Lab. 3/0 Office Hours Coordinator's Name: (if applicable) Course Description This course provides an introduction to computer logic design. Topics covered : numbering systems and their internal representation , Boolean expressions and functions of combinational and sequential circuits, Boolean functions simplification methods, design of logic basic building blocks (adders, comparators, multiplexers, decoders, encoders, flip-flops, registers, counters, Read Only Memory “ROM”, and Programming Logic Array “PLA”) and basic concepts of the Random Access Memory ”RAM”. Course Objectives Introduce the Numbering systems in general and Binary Numbering systems in particular. Principles of Digital Design, their theories and their applications. Introduce the Boolian Algebra and gate level minimization.. Introduce Combinational Logic and designing fundemental Combinational Circuits. Introduce Synchronous sequential Logic and designing fundemental sequential Circuits. Introduce Registers and Counters and their design. Introduce Memory and Programmable Logic. Course Intended Learning Outcomes (ILOs) and their Alignment with Program ILOs: Course Syllabus 1 Upon successful completion of this course, students are expected to achieve the following learning outcomes: A-Knowledge and Understanding (students should): A1. Understand the concept of Binary systems and its application in Digital Design. A2. Understand and recognize Digital Logic Gates. A3. Understand the concepts of Combinational and sequential Circuits. A4. Understand the concept of Registers, Counters, Memory, and Programmable Logic. A5. Identify the different Application areas of Digital Design. B- Intellectual Skills (Student should be able to): B1. Analyze Digital Circuits and their functionalities. B2. Compare and criticize different Digital Circuits C- Subject Specific Skills (Student should be able to): C1. Learn the essentials of the Logic Gates. C2. Building the truth tables. C3. Constructing the Boolean function. C4. Gate-Level minimization C5. Constructing the Digital Circuit C6. Write reports about application of selected Digital Circuits. D- Transferable Skills (Student should be able to): D1. Work in a group in order to build different Logic Circuits. D2. Deploy communication skills. D3. Deploy proper report writing skills. Course Schedule: Week Topics 1 Binary System 2 Binary System 3,4 Boolian Agebra and Logic Gates Gate-Level Minimization Gate-Level Minimization 5 6 Topic Details Digital systems, Binary Numbers, Number Base Conversions, Octal and Hexadecimal Numbers. Signed Binary Numbers,operatins(+,-,*,/), Binary Codes, Binary Logic. Axiomatic definition of Boolian Algebra, Basic Theorems and Properties of Boolian Algebra, Conical and Standard forms(SOM and POM), Digital Logic gates. The Map Method, two-three-four and five Variable Map, Product of Sums simplification. Don't care Conditions, NAND and NOR implementations, Exclusive OR Function. Reference (chapter) Chp.1 Chp.1 Chp.2 Chp.3 Chp.3 TEST 1 7 8 9 10 Combinational Logic Combinational Logic Combinational Logic Combinational Logic Combinational Circuits, Analysis procedure, Design Procedure, Chp.4 Binary Adder, Binary Subtractor. Chp.4 Magnitude Comparator, Decoders, Encoders Chp.4 Multiplexers,Demultiplexer,ROM. Chp.4 TEST 2 Course Syllabus 2 11 Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential Circuits, Latches, Flip-Flops. Desittgn and analysis procedures. Chp. 5 12 Registers and Counters Registers, Shift Registers. Chp.6 13 Registers and Counters Sequential circuits analysis Memory and Programmable Logic Memory and Programmable Logic Ripple Counters, Synchronous Counters, Other Counters. Chp. 6 Analysis of Clocked Sequential Circuits Chp. 6 Random-Access Memory, Read Only Memory. Chp. 7 Programable Logic Array, Programable Array Logic. Chp.7 14 15 15 16 Final Exam Assessment Methods: Assessment method Attendance, Participation, and Homework Outside-classroom activities Quizzes Grade 10 Homeworks, Discsstions. Students will work in a project in groups (2 to 3 students in a group). UnAnnounced Short quizes Covers Chapters 1, 2, 3 Five to Ten Multiple Choice Questions worth 25% of exam Grade. Three to Five Essay Questions worth 75% of exam grade. Covers Chapters 4, 5, 6 Five to Ten Multiple Choice Questions worth 25% of exam Grade. Three to Five Essay Questions worth 75% of exam grade. Covers Chapters 1–7 Ten to Fifteen Multiple Choice Questions worth 25% of exam Grade. Five to six Essay Questions worth 75% of exam grade. 5 5 First Exam 20 Second Exam 20 A Comprehensive Final examination 40 Comments 100 * Make-up exams will be offered for valid reasons. It may be different from regular exams in content and format. Alignment of Teaching and Learning Methods, Assessment and Course ILOs: Teaching method Interactive lectures Contact Hours Assessed through ILOs numbers Attendance ,discussion ,quizzes A1, A2, A3, A4, A5 Textbook Problems Report of homework assignments Outside-classroom activities Report of the project Course Syllabus 3 A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, C2, C3, C4, C5 B1, B2, C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, D1, D2, D3 Learning References: 1- Textbook (s): Digital Design 5th edition M. Morris Mano Prentice Hall, 2012 Digital Design 3rd edition M. Morris Mano Prentice Hall, 2002 2- References: Electric Circuits (9th Edition) James W. Nilsson Introduction to Digital Logic Design J. P. Hayes Addison-Wesley, 1993 Design of Computer Logic First Edition Dr Saleh Al-Oqeili Dar Al-Shuroq Publishing, 1993 (Arabic Text Book) 3- Other Resources: <<Labs, computer resources, lecture rooms needed for the course>> Companion Website: www.prenhall.com/mano www.youtube.com/watch?v=QxvyaBKl3d8 http://nptel.iitm.ac.in/Onlinecourses/Srinivasan/ http://nptel.iitm.ac.in/video.php?subjectId=117106086. Course Policies1 Attendance Policy: University regulations apply to attendance. Academic Honesty: Academic dishonesty is an unacceptable mode of conduct, and will not be tolerated in any form at University of Petra. All persons involved in academic dishonesty and plagiarism in any form will be disciplined in accordance with University rules and regulations. Approved by Head of Department Faculty Dean Course Syllabus Name Dr. Mohammed Abu-Arqoub Dr. Ghasan Issa 4 Date 15-10-2013 15-10-2013 Signature 1 Additional information may be added in this section according to the nature of the course. Controlled Copy Course Syllabus 5