Journey to the Center of the Earth iNB
advertisement

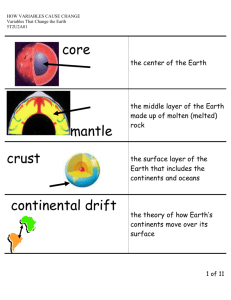
1 Table of Contents Left Side 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 Right Side 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 3 Vocab 1 – Cornell Notes Lesson 1 Outline (pp. 14-15) Sphere- shaped like a ball Geosphere – solid surface of Earth Gravity – force that pulls matter towards Earth Density – mass in a specific volume •crust –the brittle, rocky outer layer of the Earth. •mantle – the thick middle layer in the solid part of Earth. •lithosphere – the solid, outer layer of Earth that consists of the crust and the rigid upper part of the mantle •Asthenosphere – hot, plastic zone in the upper mantle directly beneath the lithosphere. •Core – the dense metallic center of Earth •Magnetosphere – the outer part of Earth’s magnetic field that interacts with charged particles from the sun 2 EARTH SYSTEMS CONCEPT MAP Directions: use your textbook p. 12 or my website (Journey to the Center of the Earth) to create a concept map of Earth’s systems. Make sure to include a picture, description and arrows showing the interactions between each system. LESSON 1 & 2 VOCABULARY Sphere Geosphere Gravity Density Crust Mantle Lithosphere Asthenosphere Core magnetosphere 3 4 EARTH’S LAYERS DIAGRAM Use your textbook p. 23 or my website to create a diagram showing Earth’s layers. Make sure to include the name of the layer, the composition (what it’s made of) and it’s density. 5 Building Background: How Did Earth Form? http://www.neok12.com/video/Earth/zX7f15586d75 044a774d7c59.htm Directions: View the video clip. Write a paragraph describing what you learned. Use the questions below to guide your writing. 1. What was the composition of Earth like at it’s earliest stage? 2. Describe how the core of the Earth formed. 3. How old is the Earth? 4. How does the core effect the surface of the Earth? 6 How did Earth form Close Read pp. 13-15 The Influence of Gravity The Solar Nebula p. 13 para 2 p. 14 para 1 How did Earth form Close Read pp. 13-15 Early Earth p. 14 para 3 The Formation of Layers Summary: p. 15 7 8 WHAT’S INSIDE EARTH? REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. How have scientists determined what's inside the earth? 2. What are the earth's interior layers? 3. The outer shell is broken into more than a dozen moving pieces. What are these pieces called? 4. What are faults?. 5. What causes earthquakes? 6. How is energy released during an earthquake? 7. Seismic waves are similar to what type of commonly seen waves? 8. Uplifted sections of the earth's crust create what?. 9. What type of mountain is formed when the Earth's crust is squeezed together? 10. What is the hot liquid that erupts from volcanoes? 11. What is magma? 12. What is a lava fountain? 9 WHAT’S INSIDE EARTH? REVIEW QUESTIONS 13. What is a lava curtain? 14. What are large underground lava deposits called? Underground lava deposits are called magma chambers. 16. What type of rock is formed when a magma chamber cools? 17. What is the name of the rock type which is formed by reheating? 18. What is the name of the place where water erupts from the ground? 19 . How does a geyser erupt? 20. How often does Old Faithful erupt? 21 . What can you find within layers of sedimentary rock? 22. What important things do we obtain from the Earth's crust? 10 Dynamic Earth Interactive Lesson Earth’s Structure http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html 1. Create this chart in your iNB and fill in the details for each layer. Use the glossary button to find information about the lithosphere and asthenosphere. Layer Thickness Composition Crust Lithosphere Asthenosphere Mantle Outer core Inner core 3. What did the continents of the Earth look like 250 million years ago? 4. What is the name of the single large landmass of this time? Dynamic Earth Interactive Lesson 11 5. Who is the scientist who proposed the ideas that led to the development of tectonic plate theory? 6. What is modern “Plate Tectonic Theory”? 7. What are some geologic events that occur due to plate movement? 8. Name the 15 major tectonic plates. 9. What are the 2 types of crust called? Compare/contrast them. 10. What is the border between 2 plates called? 11. Name the 3 types of plate boundaries and describe each using a chart like this: Convergent Divergent Transform Movement Examples 12. What is a subduction zone? 13. What is Pangea? How long ago did it begin to break apart? 12 Florida Landforms Find and label the following landforms on your map: Coastline Bay Peninsula Gulf Archipelago Beach Everglades Cape Sand Strait 12 Directions: Florida Landforms Map Identify & Label: Atlantic Ocean Gulf of Mexico Lake Okeechobee Straits of Florida Dry Tortugas Rivers: St. Johns Kissimmee Suwannee Caloosahatchee Bays: Tampa Apalachee Florida Find and label 10 of the landforms on your vocabulary list Your Map and surrounding water MUST BE IN COLOR LESSON 3 VOCABULARY What is a landform? 13 A feature on land formed by geologic processes What is a plain? What is the difference between elevation and relief? Elevation is the height above sea level Relief is differences in elevation What is topography? The general shape of an area What is a plain? Low relief & elevation (forms when wind or rain deposits sediment) What is a plateau? Low relief & high elevation What are the 4 major Landform regions in US? Coastal plains, interior plains, Appalachian Mts., Rocky Mts., & Colorado Plateau Summary: LESSON 3 VOCABULARY What is a landform? What is the difference between elevation and relief? What is topography? What is a plain? What is a plateau? What are the 5 major Landform regions in US? 13 Summary: Lesson 2 Rocks Vocabulary 15 Rock mixture of rock fragments, organic matter &/or glass Grain individual particles Magma molten rock (so hot it flows) Lava magma on Earth’s surface Texture grain size & arrangement Sediment loose rock & mineral fragments Lithification when the weight of upper layers of sediment compact lower layers into rock Foliation pressure makes minerals line up in rock summary Lesson 2 Rocks Vocabulary Rock Grain Magma Lava Texture Sediment Lithification Foliation Summary: 15 14 Rock Cycle Poster You will be working cooperatively with your table group. EVERYONE MUST PARTICIPATE! Draw a diagram of the rock cycle: Label & describe the following processes: Cooling & crystallization Uplift Weathering & erosion Deposition Compaction & cementation Heat & pressure Plate tectonics Your poster must be in color Write your name (each team member) date & period on the back in the lower right hand corner 16 Rocks Venn Diagram C Sedimentary Metamorphic Igneous Classifying Rocks Type of Rock Characteristics How it formed 17 Examples