(sydney, courtney, michelle) edited - 34
advertisement
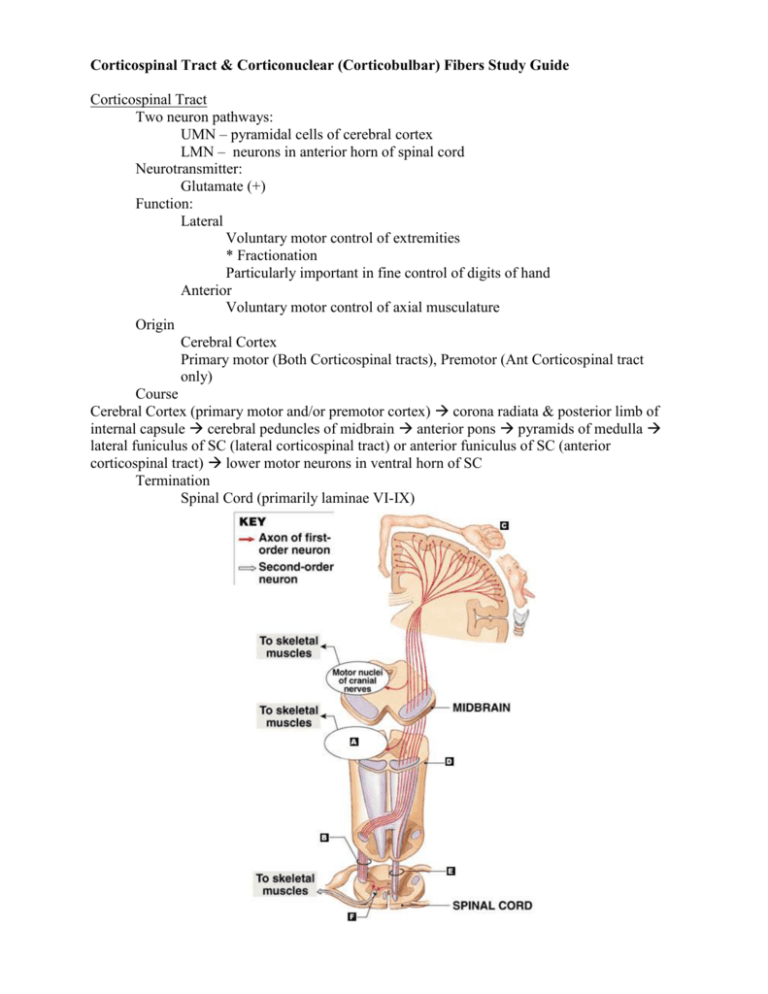
Corticospinal Tract & Corticonuclear (Corticobulbar) Fibers Study Guide Corticospinal Tract Two neuron pathways: UMN – pyramidal cells of cerebral cortex LMN – neurons in anterior horn of spinal cord Neurotransmitter: Glutamate (+) Function: Lateral Voluntary motor control of extremities * Fractionation Particularly important in fine control of digits of hand Anterior Voluntary motor control of axial musculature Origin Cerebral Cortex Primary motor (Both Corticospinal tracts), Premotor (Ant Corticospinal tract only) Course Cerebral Cortex (primary motor and/or premotor cortex) corona radiata & posterior limb of internal capsule cerebral peduncles of midbrain anterior pons pyramids of medulla lateral funiculus of SC (lateral corticospinal tract) or anterior funiculus of SC (anterior corticospinal tract) lower motor neurons in ventral horn of SC Termination Spinal Cord (primarily laminae VI-IX) Corticonuclear (Corticobulbar) Fibers Two neuron pathway: UMN – cells of cerebral cortex LMN – motor cranial nerve nuclei in brainstem Fibers influence motor nuclei of oculomotor, trochlear, trigeminal, abducens, facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory, & hypoglossal nerves Function Controls muscles of face, head & neck Initiation and control of voluntary & fine movements Neurotransmitter Glutamate (+) Innervated by the cranial motor nuclei (V, VII, XII), nucleus ambiguus (IX and X) & by accessory nucleus DOES NOT innervate nuclei for nerves III, IV, and VI Fibers do NOT project to the oculomotor, trochlear, and abducens DIRECTLY (from frontal eye fields to terminate in mesencephalon [sup colliculus] and then relay input to the motor nuclei Origin Precentral gyrus - somatomotor cortex, area 4 (primary motor cortex) Frontal eye fields - areas 6 and 8 Postcentral gyrus - areas 3, 1, 2 (some) Course Precentral gyrus descends through corona radiata genu of internal capsule (few fibers in the posterior limb of the internal capsule) crus cerebri brainstem Major Structures Precentral gyrus, corona radiate, genu of internal capsule, posterior limb of internal capsule, cerebral peduncles (midbrain), brainstem (medulla & pons), cranial nerve nuclei Termination Rostral Interstitial Nucleus of the MLF Paramedian Pontine Reticular Formation Precentral gyrus Brainstem motor nuclei: CN V (bilateral), CN VII (contralateral), CN XII (contralateral tongue) Nucleus Ambiguus (bilateral): CN IX, CN X (soft palate, pharynx, larynx) Accessory Nucleus (bilateral): CN XI Upper half of the facial motor nucleus receives BILATERAL corticonuclear projections Lower half of the facial motor nucleus receives only CONTRALATERAL projections











