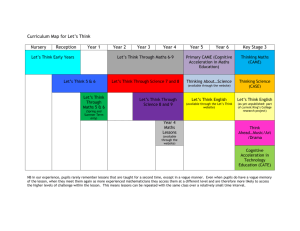
Numeracy Assessment Summary of Questionnaires 2014

Results of Maths Questionnaires- 2013-2014
Parents
Strengths
1.
Parents reported that 85% of pupils love or like maths and 80% identified child’s strengths at Maths Curriculum
2.
Parents [68%] reported that maths curriculum presented at right level for their child and
86% reported that their child never or sometimes needed help with maths homework
3.
The areas of maths which parents. [J.I. – 2 ND ] reported that their children enjoy most /have high competency skills were addition/ subtraction 93% , Fractions 73% ,Shapes and angles
73%, Algebra 66%, Measurement 74% , Time 90% ,Money 87% , Data 74% ,Problem Solving
81% ,
4.
The areas of math which parents [ 3 rd – 6 th ] reported that their children enjoy most/ have high competency were Number operations 94% , Fractions Decimals and percentages 82%,
Shapes Angles and Lines 82% , Algebra 71% , Measures 82%, Time 96% , Money 97% , Data
85%,Problem Solving 84%
Weaknesses
1.
Only 65% of parents felt that the school was giving good information on how their child was performing in maths
2.
Only 34% of parents felt their children always understood maths language with 47% sometimes finding in confusing and 15% often finding it confusing
3.
76% of parents felt it would be helpful 28% and a great help 48% to have examples of maths language used in school explained so that they can help their children
Results of Maths Questionnaire- Pupils
Strengths
1.
77% pupils reported that they liked maths.
2.
31% of pupils reported that they were very confident at maths and 67% identified themselves as average at maths
3.
Everyone [100% ]reported that they were very confident [94% ] or average [6%] at easy maths.
4.
34% of pupils felt very confident and 59% were average when working maths sums out in their head
5.
72% of pupils felt very confident and 22% were average when working maths sums out on paper.
6.
Everyone [100%] reported that the use of maths equipment made the very confident or average competence when working on maths questions
7.
59% reported maths as their favourite subject with 88% stating that they usually do well at maths
8.
70% reported that maths was interesting and 90% said it would be useful in the future.
9.
The areas of math which pupils enjoy most/ have high competency were Number operations
Addition and Subtraction 91% love / like and 9% O.K.
Division 71% love / like and 18% O.K. , 11% dislike
Multiplication 83% love / like and 11% O.K. , 5% dislike
Table 81% love / like and 16% O.K. , 2% dislike
Shapes Angles and Lines 74% love / like and 19% O.K. , 8% dislike
Measures 72% love / like and 21% O.K. , 8% dislike
Time 79% love / like and 13% O.K. , 8% dislike
Money 85% love / like and 10% O.K. , 6% dislike
Data 75% love / like and 19% O.K. , 6% dislike
Maths on Computer/ ipad 90% love / like and 6% O.K. , 3% dislike
Weaknesses
1.
Only 16% felt very confident with more difficult maths and there were 22% who felt not so confident
2.
17% of pupils reported that they were not so confident when asked a question in class and it raised to 19% for those doing problem solving.
3.
41% reported that maths was not a favourite subject and 24% stated that they were not good at maths.
4.
55% sometimes 13% often or always have difficulty understanding maths language
Most dislikes strands of maths were Algebra 49% love / like and 33% O.K. , 17% dislike,
Problem Solving 51% love / like and 29% O.K. , 19% dislike, Fractions 50% love / like and
33% O.K. , 17% dislike and Decimals and percentages 54% love / like and 32% O.K. , 17% dislike
Results of Maths Questionnaire- Teachers
Strengths
1.
81% of teachers reported that they were familiar with the curriculum for their class level
2.
Metal Maths working well 81%
3.
Active learning and guided discovery working well 67% and pupils given opportunity to explain their answer [69%] , encouraged to work out own ideas for problem solving 63% working well where process and answer equally important 75 %
4.
Agreed approach to number formation working well in Junior Classes
5.
Assessment and record keeping working well at school level 81% at class level 81% and at individual pupils level for screening and diagnosis 88%
6.
Assessment of areas that need re teaching from assessment 81%, teacher observation 94% and teacher designed test 88% , work samples 63% , standardised test 100%all working well
7.
Differentiation in maths programme for pupils with difficulties 81% working well and supplementary teaching for these pupils working well 81% and collaboration with resource and learning support working well 88%
8.
Homework is differentiated 69 %and reflect active learning approach 75% and care taken not to load pupils attention learning support 88%
9.
Teachers familiar with recommendations for use of calculator 69%
Weaknesses
1.
56% felt there was an over reliance of text books in planning
2.
56% felt more work needed to give equal attention for all strands
3.
Whole school approach to maths in copies needs attention 88%
4.
Wider range of problem solving needed Puzzles Maths trails etc 62% and need for maths trails in school environment 81%
5.
Common approach to teaching number facts needs attention 69%, multiplication agreed approach needs attention 56% 3 x 4 or 4 groups of three , Subtraction use of resources needs attention 56%, Addition and subtraction of fractions and time 63% needs attention
6.
Agreed list of maths terminology and language needs attention 93%
7.
Maths games to support maths skills needs attention 75%
8.
Maths work on display boards needed [71%]
9.
Provision for very well able pupils needs attention [69%] organisation of research work for these pupils [86%]
10.
Maths resources need attention 81% and list of software needs attention 65%
11.
Parent involvement and advice for maths activities/ strategies 63% and maths language 69%
12.
Topics that prove difficult for J.I. – 2 nd
Fractions- Often difficulties 75% ,Time -often/ most challenging 83%, Money often/ most challenging 75%, Data 66%
13.
Topics that prove difficult for 3 rd – 6 th
Fractions - Often difficult /most challenging 94% ,Time -often/ most challenging 81%,
Money often/ most challenging 69%, Decimal and percentages 94%
Important factors for teaching of maths are :
Understanding of formulas and procedures 75%
Knowledge of tables 100%
Sequential thinking 75% and understanding of concepts 75%
Understanding of how maths works in the real world – Somewhat important 63% /very important
38%
Understanding of maths solutions – Somewhat limits teaching 56% /very much limits teaching 44%
Special Needs pupils limit teaching of Maths 75%
Structured approach to maths language needed 100%Maths language needs attention 44% strongly agree ,50% agree Understanding of how maths works in the real world – Somewhat important 63%
/very important 38%